When you purchase through links on our situation , we may earn an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it works .
The humans is facing an ever - increase threat from bacterium germinate resistance to known antibiotic drug , rendering the essential drug unable . But now , researchers are explore promising new discussion strategies , with the bearing of making those resistant bacterium susceptible to drugs once more .
The rise of antibiotic - resistant bacterium has been dub the " soundless pandemic " due to its stealthy worldwide feast and lack of urgent public attention , in compare to other pandemics such asCOVID-19 , especially in neighborhood where antibiotic use remains largely unchecked . Estimates from a 2019 reportpublished by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC)suggest that resistant bacteria kill at least 1.27 million people worldwide that class , with 35,000 of those deaths occur in the U.S. alone . That marked a 52 % increase in U.S. deaths from resistant microbes since theCDC ’s previous account in 2013 .
The “silent pandemic” of antibacterial resistance poses a huge threat to public health around the world.
" Antibiotic resistance is a major public health threat because so much of New medical tending look on antibiotic — childbirth , Crab treatment , organ transplant , operations , and infections,“Zamin Iqbal , a prof of algorithmic and microbic genomics at the University of Bath in the U.K. , told Live Science in an email .
What ’s make this mount disaster ? Theoveruse and misuse of antibioticsin both medicine and agriculture are the major culprits .
concern : Superbugs are on the rise . How can we preclude antibiotics from becoming obsolete ?
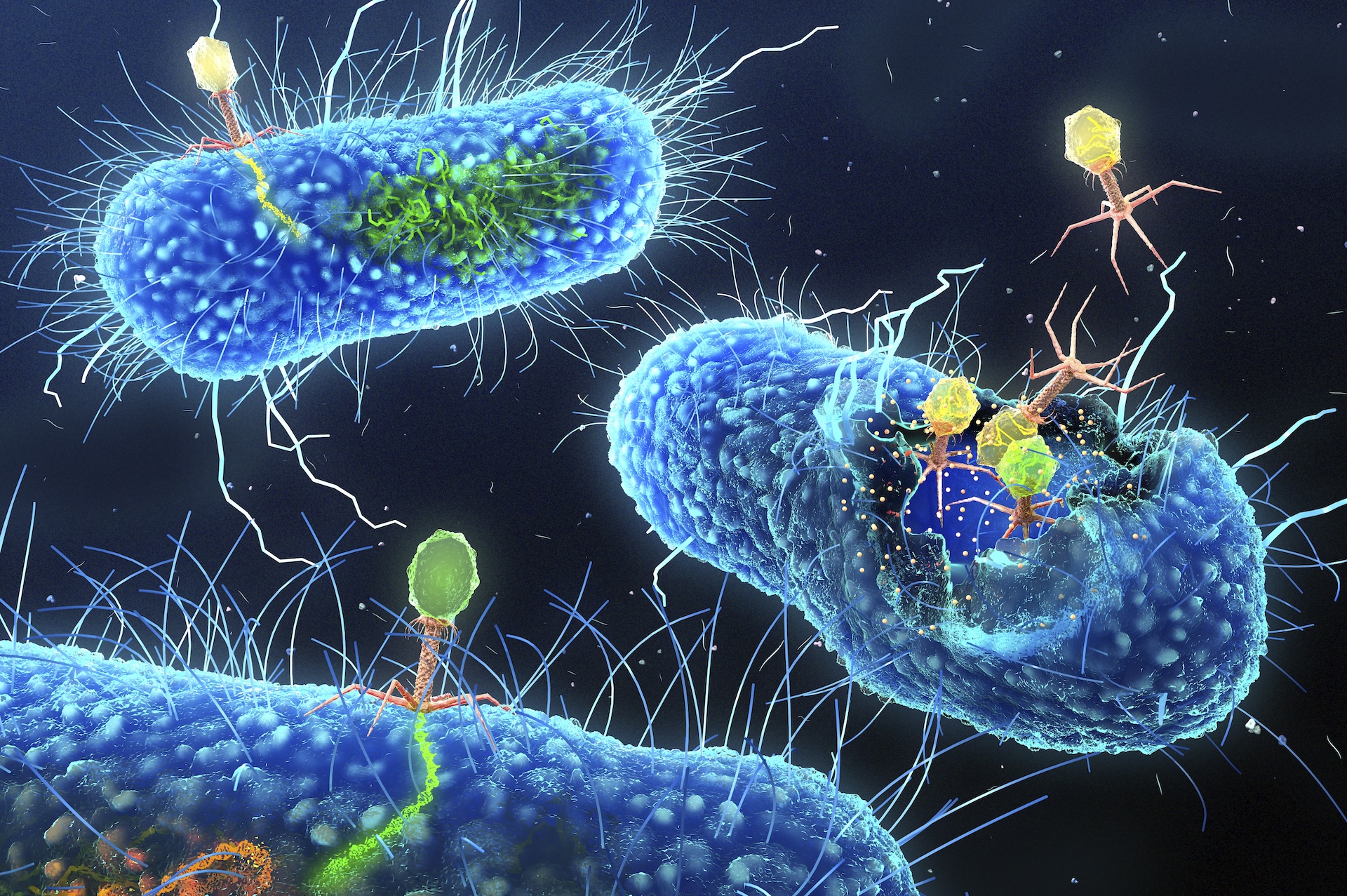
Bacteriophages, or phages, are viruses that infect bacteria. Some split bacteria open from the inside, while others incorporate their genetic material into the bacterial genome.
That ’s because antibiotic electric resistance move up from anatural evolutionary mental process — one in which the fittest bacteria with the right peter to outcompete an antibiotic survive to happen on those tools .
When a universe of bacteria is exposed to an antibiotic , any genetic mutations that allow the bacterium to survive the drug will quickly disperse between bacterial cubicle . Repeatedly using different antibiotic can lead bacterium to develop resistance to multiple drugs , resulting in mental strain that are no longer treatable with any known antibiotic drug — with potentially fatal consequences .
In igniter of this chilling realness , we must draw out the effectiveness of the antibiotics we already have as long as potential asnew , alternative solutions are devised in the screen background . One elbow room to reach this is by finding strategy that can reverse the physical process by which bacteria become resistive , pushing them back into a drug - sensitive state .

To achieve this , Joana Azeredo , an associate prof at the University of Minho in Portugal , exploit a instinctive enemy of bacteria : bacteriophages , or computer virus that infect bacteria . sleep together as phage for inadequate , these computer virus are often discussed as apromising treatment strategyagainst antibiotic - resistant bacterium because of their potential to kill the cells they infect . However , rather than killing the bacteria , the phages Azeredo is concerned in insert themselves into the bacterium ’s genomes .
Her research usesgenetically engineered phagesas " Trojan horses " to cede genes that ultimately make bacteria vulnerable to antibioticsby eliminate the resistance genesthey carry .
A mutual resistance mechanics bacteria use against both phages and antibiotics are biofilms , which shield the bacterial cells from harm . Fredrik Almqvist , a prof of organic chemical science at Umeå University in Sweden , together with molecular biologistChristina Stallings , a prof of molecular microbiology at Washington University , are originate chemical substance compound thatbreak down the biofilms of drug - resistive bacteria , effectively resensitizing them to antibiotics .

Almqvist and Stallings ' research has uncovered a belittled molecule thatdisrupts the genetic nerve tract that allow microbe to form biofilms . The atom not only kibosh this electric resistance chemical mechanism from evolving in the first place but also restores antibiotic sensitiveness to bacteria that have already evolved to utilise it .
Other researcher are taking a different coming : They ’re targeting the downstream mechanism of resistance , rather than eliminating its ancestor inherited lawsuit . For example , enquiry fromDespoina Mavridou , an assistant professor at the University of Texas at Austin , aims to resensitize immune bacterium by stopping cells from progress to a protein that help pen up other proteins .
Folding is a key whole step that enables a fresh made protein to execute a particular function . Mavridou ’s approach prevents the folding of protein that start the bacterium to resist antibiotics . In study , bottle up this folding - assistant proteinrestored the sensibility of multidrug - resistant bacterium . The inhibitor used in the work have not yet been approved for human use , though , so further inquiry is needed to bring these discovery to the clinic .

Designing new antibiotic drug isexpensive and difficult , which is one of the many reasonsso few are in growing . Thus , it ’s crucial to protect and extend the strength of the antibiotics we already have . The future of the antibiotic resistance crisis is uncertain , but ongoing enquiry offer Leslie Townes Hope for innovative strategies that could change the course of this global challenge . It is imperative , however , that we learn from previous mistakes . Any new strategies we take should look to the ways in which bacteria could develop to jib the treatment .
— unexampled drugs could obstruct superbugs by immobilize evolution
— marque - new socio-economic class of antibiotic kills drug - immune superbug

— scientist have found a mystical ' switch ' that lets bacteria resist antibiotics — and it ’s been evading lab test for decades
" It ’s important to understand how bacterium respond to the selection insistence levy by antibiotics,“Andrew Preston , a professor in microbial pathogenicity at the University of Bath and theeditor - in - chief of the daybook Microbiology , told Live Science in an email . " We will have some novel treatment strategies come through the word of mouth , so it ’s imperative we consider how we might palliate / cut down the selection for resistance to sustain their utilisation . "
Ever wonder whysome people build brawniness more easy than othersorwhy lentigo come out in the sun ? transport us your head about how the human body work tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your head answer on the internet site !

scientist just discovered a single molecule that may treat rare , devastating mitochondrial disease
Acne vaccinum : Experimental shot for common hide condition reaches clinical trials . Here ’s what you call for to hump .
Was it a Oliver Stone tool or just a rock ? An archaeologist explains how scientists can differentiate the dispute





