When you buy through connection on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Scientists have finally discovered what ’s get a Switzerland - sizing gob to repeatedly open up in Antarctica ’s ocean ice .
investigator first spotted the cakehole , call in the Maud Rise polynya , in 1974 and 1976 in Antarctica ’s Weddell Sea , and since then it has reappeared fleetingly and sporadically — opening up in different size but in the same place , then sometimes not at all for years . This left scientists puzzled as to the exact conditions needed for the hole to constitute .

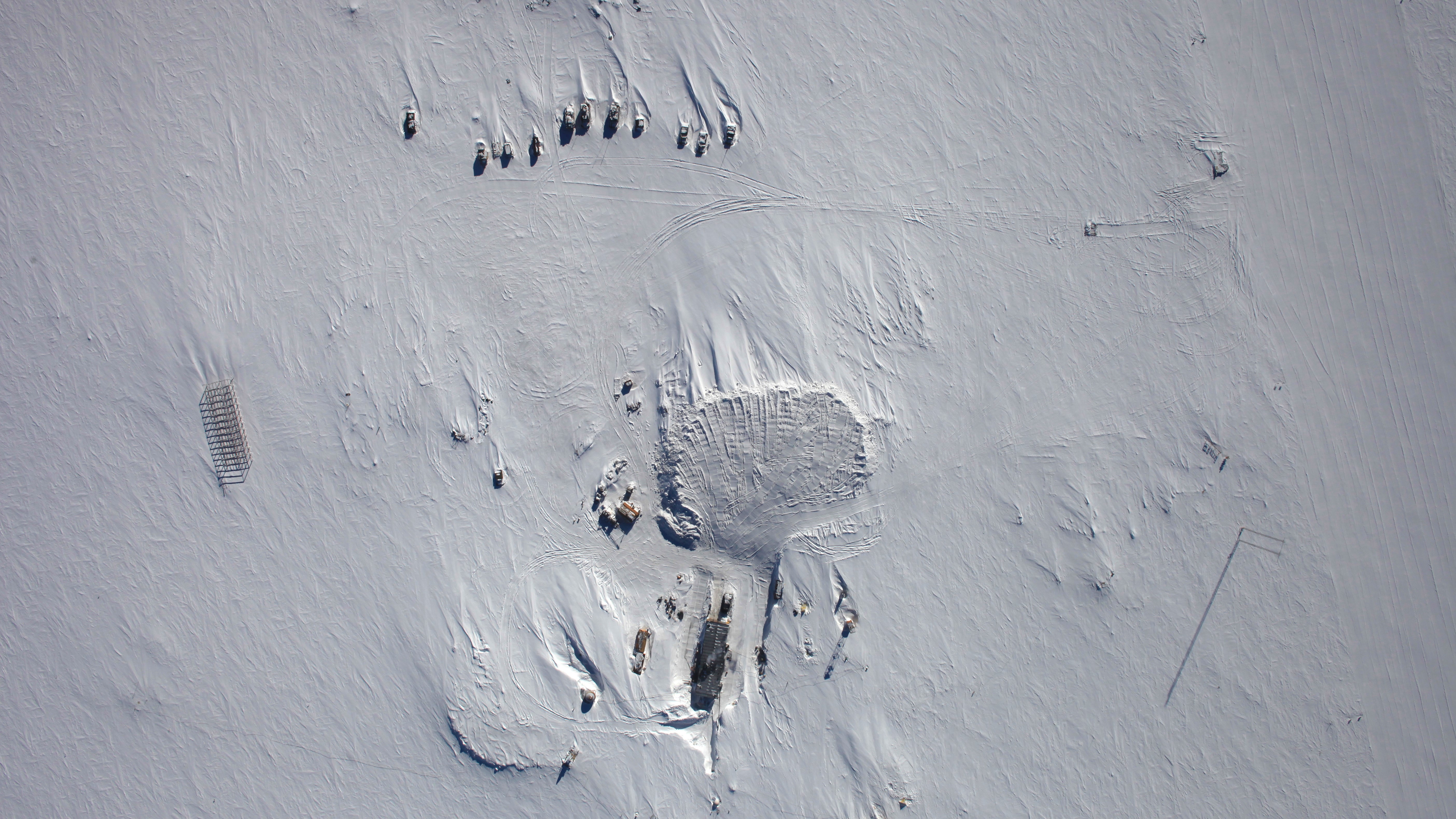
An aerial view of the Maud Rise polynya.
In 2016 and 2017 , a immense 309,000 straight air mile ( 80,000 hearty km ) open up for several hebdomad during both wintertime , enable scientists to get a close spirit at the phenomenon and finally solve the 50 - year closed book . They reported their findings Wednesday ( May 1 ) in the journalScience Advances .
" 2017 was the first time that we ’ve had such a large and long - live polynya in the Weddell Sea since the 1970s , " lead authorAditya Narayanan , a postdoctoral research worker at the University of Southampton in England , said in a command .
When summertime turn to winter in Antarctica , ocean ice expands from its lower limit of around1 million solid miles ( 3 million square km ) to 7 million square Roman mile ( 18 million square km ) , covering 4 % of Earth ’s aerofoil in irregular , porcelain - white tiles .

Most of this sea ice grows during the weeks - long polar night on the floating ice ledge that envelop around the continent . hole in this methamphetamine hydrochloride , address polynyas , form when strong malarkey from inland advertise the tiles apart .
Related:‘Unprecedented , ' ' Gobsmacked ' , ' improbable ' : Changes in Antarctica ’s ocean ice could have spectacular impacts , says climate scientist Edward Doddridge
This cold wind also freezes more seawater inside the polynyas , adding extra chunks to the sheet of pack ice .

But in the heart-to-heart sea and off from these coastal winds , where the Maud rise up polynya conformation , holes in the sea chalk are much less probable to develop . This , along with astartling decrease in the overall ice extentacross the Southern Ocean , lead scientist to wonder what specific stipulation could be causing the Maud Rise polynya to form .
Antarctica ’s sea ice has been declining since 2016 . What does that signify for Earth ’s climate ?
Read more :

— ' 2023 just blew everything off the charts ' : Antarctic ocean methamphetamine strike worrisome first gear for third consecutive year
— Collapse of the West Antarctic ice sheet is ' unavoidable , ' study finds
— Antarctic sea deoxyephedrine reached ' record - smashing dispirited ' last month

To inquire the mystery , the scientists pored over data from satellites , self-reliant float and give chase marine mammal , as well as previous observations made by other researchers . They come up that in 2016 and 2017 , the Weddell Sea ’s rotary ocean current , call the Weddell Gyre , was unattackable than in other years , making it easy for underwater currents to bring salt and rut nearer to the open .
The Maud rising polynya is located near the Maud Rise , an underwater mountain . In 2016 and 2017 , due to the stronger current , Strategic Arms Limitation Talks hovered around this seamount while steer blew over the control surface , which created a corkscrew consequence that dragged the saltier pee around the submerged good deal to the surface . This salinity then lowered the freezing point of the control surface water , enabling the Maud ascent polynya to form and persist .
The raw finding is important for understanding Antarctica and its broad encroachment on the global ocean , harmonise to the research worker . clime modification is already have winds from the southernmost continentmore potent , likely creating more polynyas in the future . Meanwhile,40 % of the global ocean ’s watersfinds their origins in the south-polar coastline , stimulate it critical in shape regional climate across the planet .

" The impression of polynya can remain in the water for multiple age after they ’ve formed . They can change how water moves around and how currents carry heat towards the continent , " study co - authorSarah Gille , a prof of climatology at the University of California San Diego , say in the statement . " The thick water that contour here can spread out across the world ocean . "