When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
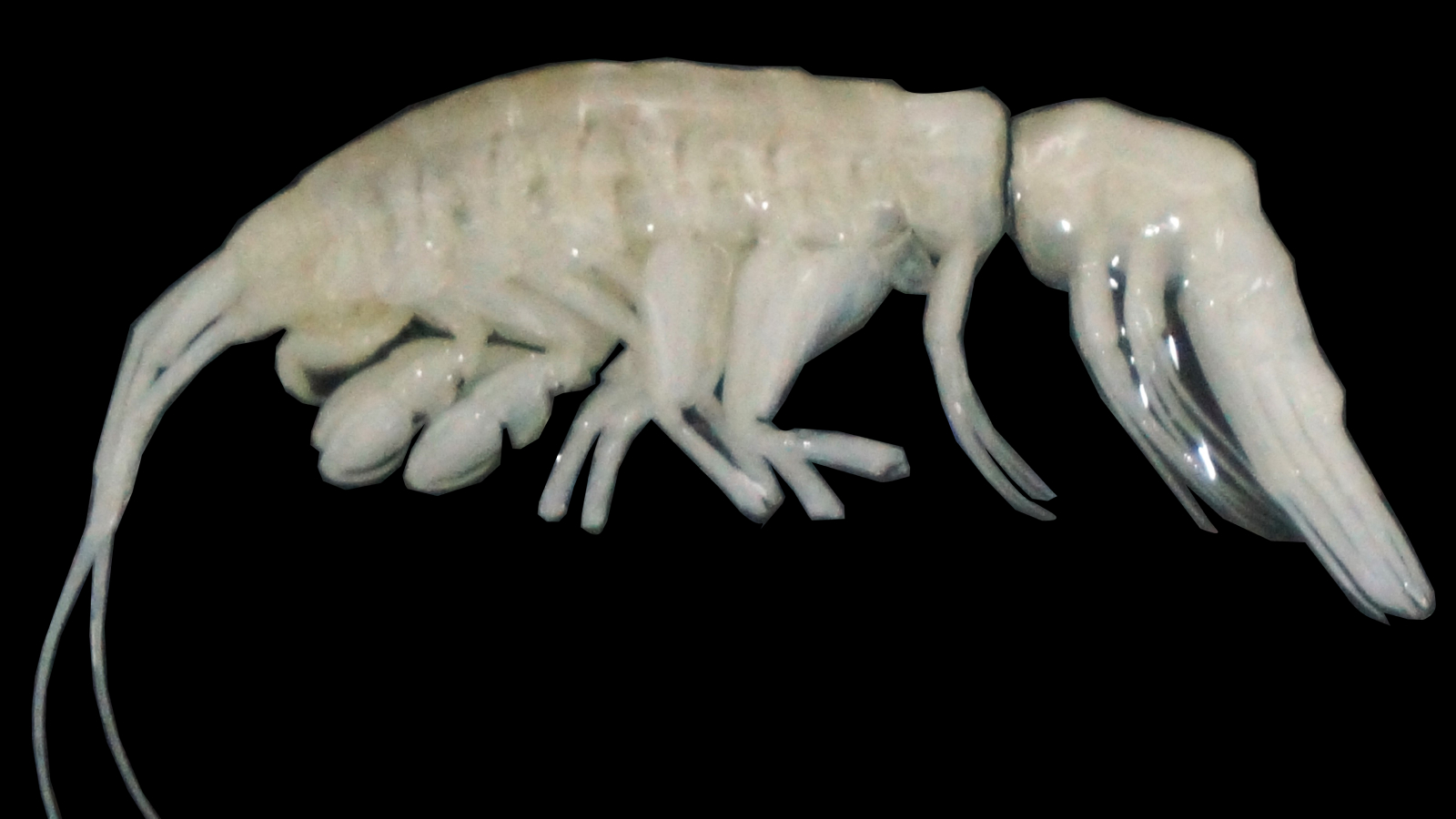
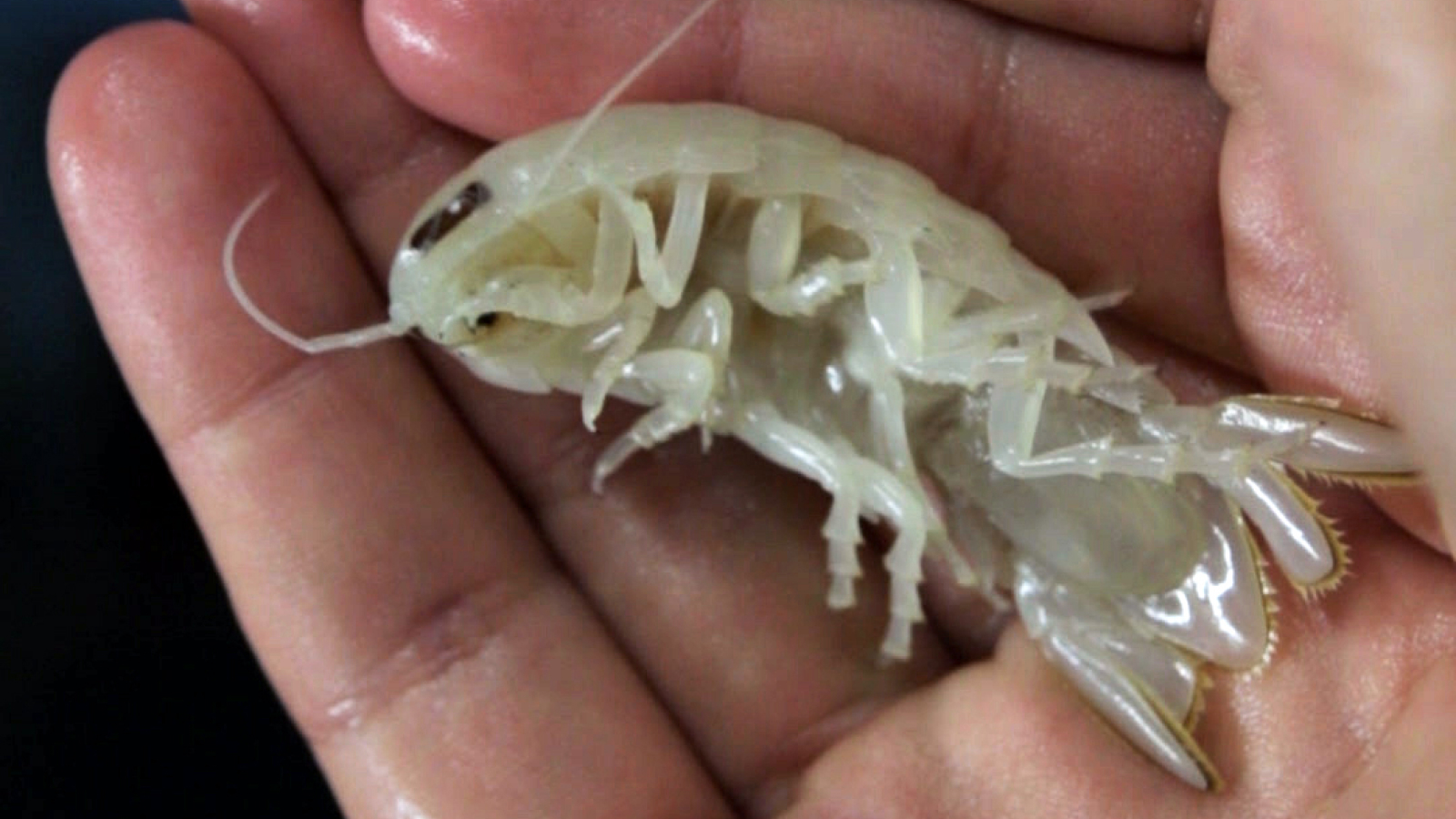
Mantis shrimps pack a brawny punch — and scientist have eventually count on out how this super - impregnable tap does n’t obliterate the shrimps themselves as they lash out . Turns out , these shrimp have a special shock - absorbing " buckler " to help them outlive as they give up plate - crush blows .
The punch of a peacock mantis shrimp ( Odontodactylus scyllarus)is the strongest self - powered strike by an beast . They use hammering - same fist , or dactyl club , to shatter prey ’s shells . The rap is so strong it can even break aquarium glass , pitch a power comparable to a .22 caliber bullet train .
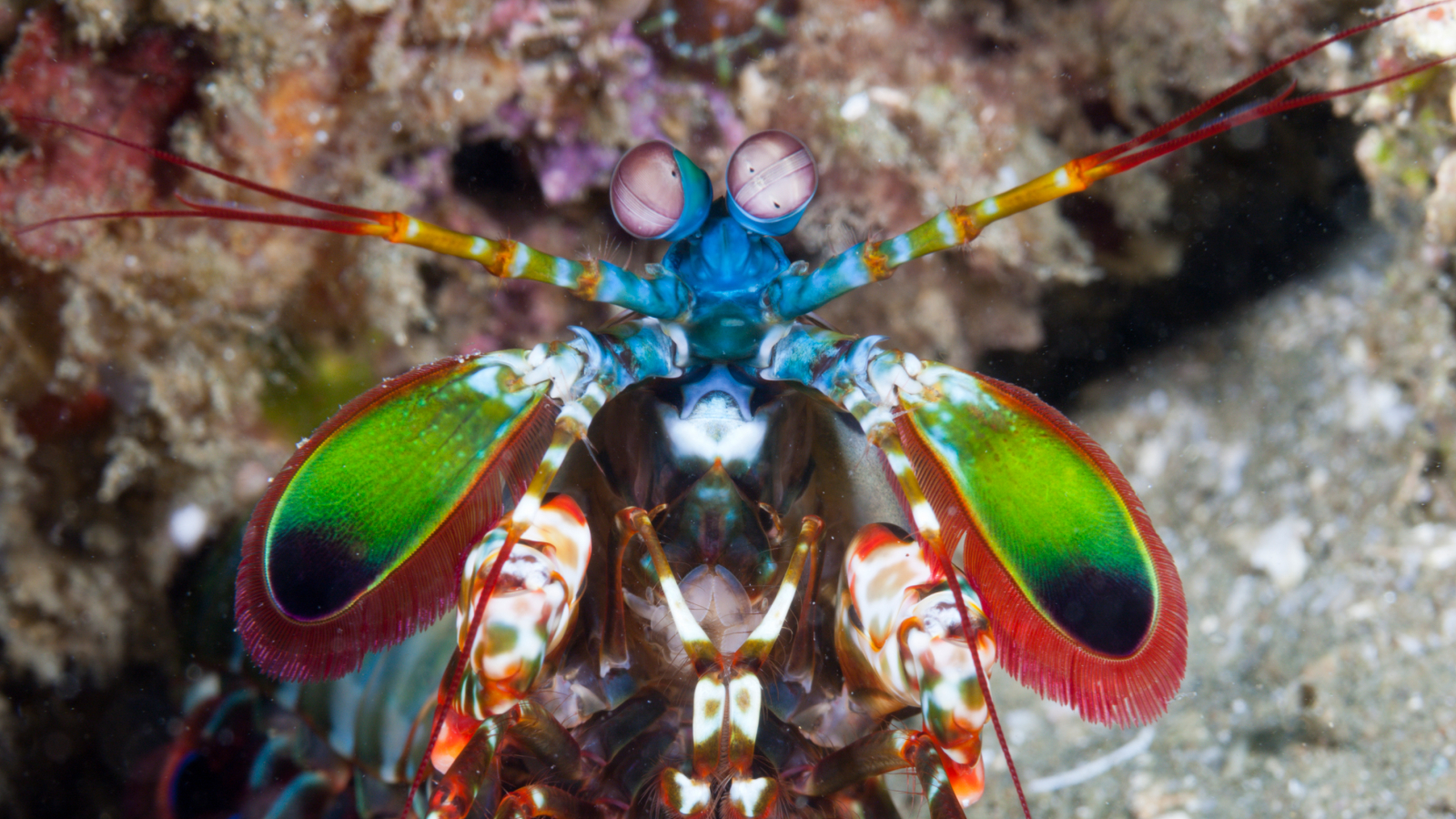

The Peacock mantis shrimp holds the Guinness World Record for the strongest self-powered strike by an animal.
But because these high-pitched - wallop strikes generate a mickle of force , scientists have amaze over how the critters can withstand the acute shock undulation yield by their own fire .
In a new study published Feb. 6 in the journalScience , investigator analyze the social organization of the runt ' nightspot . Their findings unwrap that the microstructure of these cabaret act as born shock absorber to limit damage .
" We regain it apply phononic mechanisms — structures that selectively filter accent waves , " work co - authorHoracio Dante Espinosa , a professor of mechanical engineering and biomedical applied science at Northwestern University , said in astatement . " This enables the peewee to preserve its salient power over multiple impacts and preclude piano tissue paper harm . "

Powerful punch
Peacock mantid shrimp use a complex system of biological latch and springs in their dactyl club to let loose a punch at a upper of 75 feet per second ( 23 metre per second ) , according to a2004study — 50 times loyal than the blink of an eye .
While this immense swiftness helps deliver a hefty blow , it also create grievous shock wave .
" The strike is so truehearted that it creates cavitation bubbles , which , upon tumble , father extra shockwaves , effectively delivering a threefold impact , " Espinosa say .

premature researchtheorized that the microstructure of the dactyl club helps protect the prawn from these shock wave .
In the new sketch , the scientists examine this theory using advance laser - establish techniques to break down how different wavelengths move through the Inachis io mantis half-pint ’s dactyl clubs .
The finding break two important regions in these clubs that help them survive their own work stoppage : the impact region and the periodical realm .

The wallop region is pen of a level of chitin fibers dress in a herringbone pattern radiation diagram that reinforces the golf-club against fractures .
Beneath this layer is the occasional region , made from perverted arrangements of superimposed chitin fibers . This case of helicoidal structure is known as a Bouligand structure and is find infish scalesandlobster exoskeletonsto provide strength and fracture toughness .
The laser test value the speed of acoustical stress waves through both part . These wave put across through the impact region unaltered but moved at vary speeds through the occasional region — suggest the latter region get gamey - frequency waves to circularise to trim down the intensiveness .

The researchers also discovered that the periodic region filtered out high - relative frequency stupor wave — which can cause significant terms to tissue , according to the command .
The high - frequency waves were in all likelihood generated when the cavitation bubbles collapsed .
" We connected this gamey frequency to the frequency generated by bubble collapse during the wallop case , " Epinosa say .

The bundles of fibers in the periodic region enactment like a " phononic shell , " actively blocking , redirect and scattering wave , and finally preventing any harmful shock wave from travel efficiently through the layer . This protects the delicate tissue of the mantis shrimp from the resulting shock waves of the cavitation house of cards .
— New supergiant ' Darth Vader ' ocean microbe discovered in South China Sea — and it ’s absolutely monumental
— gravid , ghostly ashen crab - corresponding predator discovered at the bottom of the Atacama Trench

— 1 - in-100 million ' cotton candy ' lobster catch off New Hampshire alive and well at aquarium
" The research provided data-based evidence that the Bouligand social organisation of the mantid half-pint ’s dactyl club functions as a phononic shell , selectively sink in high - relative frequency shear wave generated during impact , " Espinosa said .
" These characteristic serve protect the mantis shrimp ’s club from damage by extenuate high-pitched - frequency stress waves , making it a naturally optimized impact - resistant social organization , " Epinosa said .

harmonise to the pressure release , this study could be lend oneself to the development of sound - filtering textile for protective gear and inspire raw approach to reduce clap - relate injuries in the military and high - impact sports .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be inspire to enter your display name .