When you purchase through links on our land site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
A rare , warped supernova that appears three times in a single ikon could serve researchers finally solve a long - standing incompatibility about the universe that has menace to unravel our discernment of the cosmos , one expert claims .
The type 1a supernova , name SN H0pe , wasfirst discoveredlurking in photographs captured byNASA’sJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) in March . In these images , the exploding asterisk can be watch as an arc of orange light with three bright points that skirt part of the galaxy clump PLCK G165.7 + 67.0 ( G165 ) , which is around 4.5 billion light - year from Earth .

The distant supernova “H0pe” can be seen three times (labeled SN2a, SN2b and SN2c) in the orange arc of light surrounding a galaxy cluster on the left side of this James Webb Space Telescope image. Other gravitationally-lensed objects are also labeled in this image.
The light arc is the result of gravitative lensing — an effect caused when light from a distant object , such as a supernova , passes throughspace - timethat has been garble by thegravityof a monolithic foreground object , like a large wandflower , that is positioned directly between the distant physical object and the observer . This also blow up the distant object , make it easier for researchers to analyze .
The three brilliant spots in the bow around G165 make it seem like there are three separate loose source being visually manipulated , or lensed by the foreground Galax urceolata . But in reality , the supernova , which is locate around 16 billion light - years from us , has been duplicate twice by the lensing effect .
Related : distortion in distance - time could put Einstein ’s theory of theory of relativity to the ultimate trial
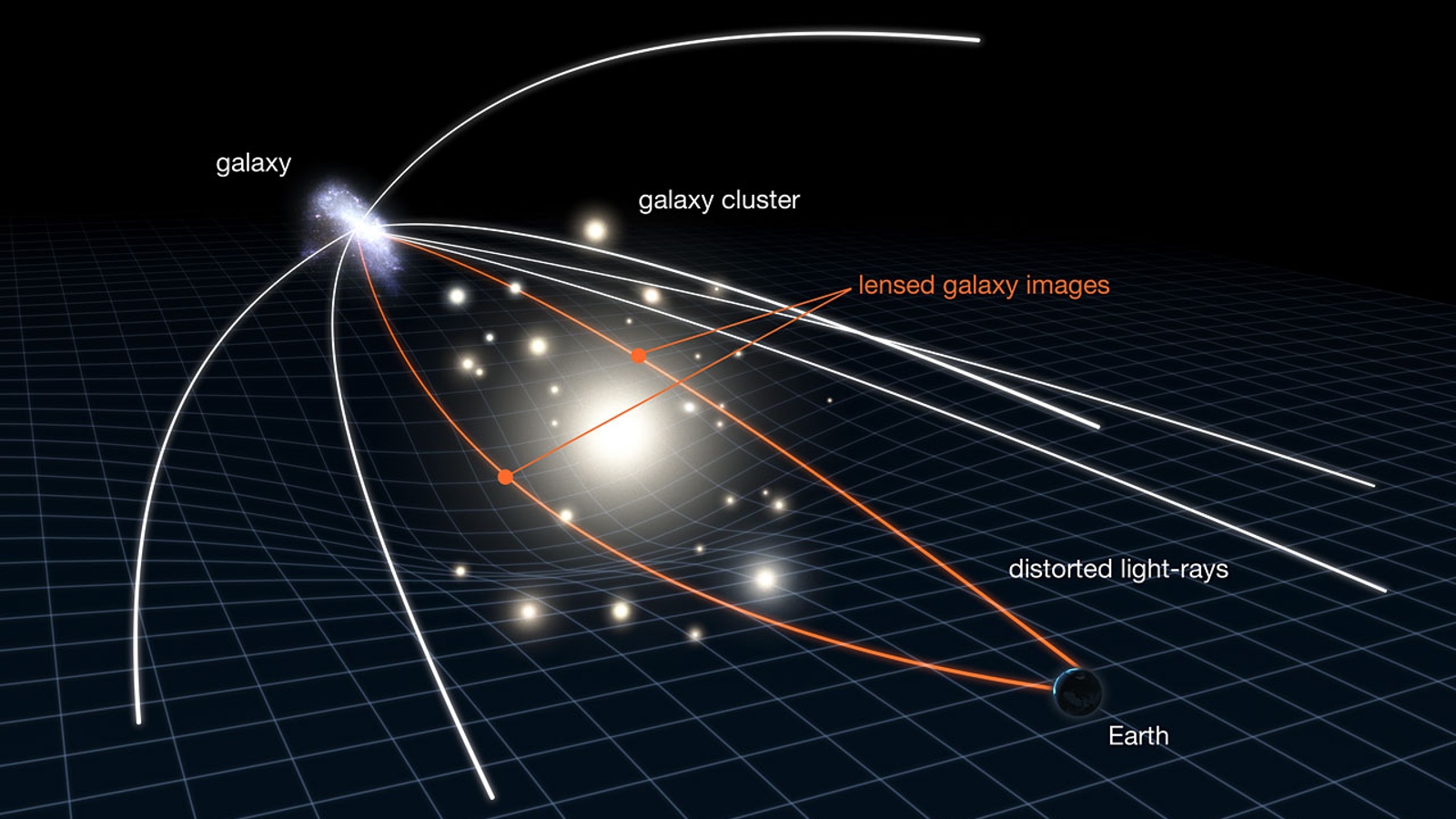
A diagram that shows how gravitational lensing works. In this example, the light of a galaxy travels through curved space-time surrounding a galaxy cluster.
In a newfangled article published onBigThink.comon Sept. 20 , astrophysicist and scientific discipline communicatorEthan Siegel , who was not involved in the bailiwick , wrote that SN H0pe could help solve a longstanding repugnance about the expansion of the existence — the " Hubble tensity . "
The Hubble tension is based on a discrepancy between the two primary ways of estimating the rate of the population ’s enlargement , know as theHubble constant . The first method acting , which take measuring expansion using thecosmic microwave background(CMB ) — leftover radiation from theBig Bangthat was first detected in 1964 — derive out with one time value for the Hubble invariable . But the 2nd method , which affect measure out how far specific objects , such as galaxies and supernova , are locomote off from us , systematically comes out with a slightly mellow value .
This problem has confused scientists for decade because there is no clean reason why one method acting should produce a different event from the other , Siegel drop a line . The conundrum has even caused some investigator to declare it a crisis in cosmology .
A zoomed out view of the gravitationally-lensed supernova and surrounding galaxy cluster.
SN H0pe could help work out the Hubble tenseness because it is a type 1a supernova , which astronomers refer to as a " standard candle " — an incredibly dependable reference point from which we can measure the universe ’s enlargement , Siegel wrote .
concern : The cosmos could turn back expanding ' remarkably soon ' , study suggests
Type 1a supernovas involve a white dwarf hotshot stealing matter from a binary partner asterisk , before reaching critical mass and exploding . These bright explosion all have near - equal initial luminance and dim over clock time at the same rate . By comparing these standard standard candle at various distances from Earth , scientists can work out exactly how tight they are moving aside from us and can then deduct the expansion pace of the universe .

SN H0pe is a particularly authoritative standard candle because it is the second most distant type 1a supernova ever detected , Siegel wrote . The strong gravitative lensing and duplication in the new images also give investigator more information to work with than normal , he added .
— Brightest supernova of past 420 years revealed in sensational raw James Webb telescope images
— Rare ' Einstein cross ' warps light from one of the universe ’s brightest object in this sensational image

— ghostlike garbage of oldest record supernova revealed in stunning scope image
The idea of using duplicated supernova to tackle the job of Hubble tension is not new . In May , scientists used data from a reappearing , quadruple - lensed supernova named Refsdal tocalculate a new economic value for the Hubble constant . Although this still differed from the value calculate using the CMB , the divergence between the two was reduced , suggest that they could one day touch up .
It is currently unclear whether SN H0pe can be used to calculate an even more reliable value for the Hubble constant quantity . But researchers are confident that ifJWST ’s keen eye can continue to pick out more distant standard candle , the problem of Hubble tensity may in conclusion be resolve .














