When you purchase through links on our land site , we may clear an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it solve .
scientist have identified neurons in an evolutionarily ancient part of the mental capacity that ascendancy when you stop eating a repast — at least in rodent .
The researchers discovered that cholecystokinin ( CCK ) nerve cell — which are discover in thebrain stem , one of the Old parts of the mentality — integrate various signal produce as we deplete , causing us to finger full and not want to take another morsel . The scientists key their finding in a Modern field bring out Wednesday ( Feb. 5 ) in the journalCell .

New research in rodents suggests that specialized neurons in the brain stem control how much we eat in the course of a meal.
The eating betoken these neuron respond to relay information like how much solid food is detected by sensory receptor in the mouth ; how full the belly is ; and how high the degree of dissimilar " thirstiness - signalling hormone " in the blood are . These hormones rise and fall in response to solid food pulmonary tuberculosis and metabolism .
The new research is still in its other stages , having only been lead in mice so far . However , the human brain stem is reasonably like to that of mice , so it ’s probable that the same control mechanism pass in our brains too , the subject authors say .
Related : Does it really take 20 minutes to realize you ’re full ?
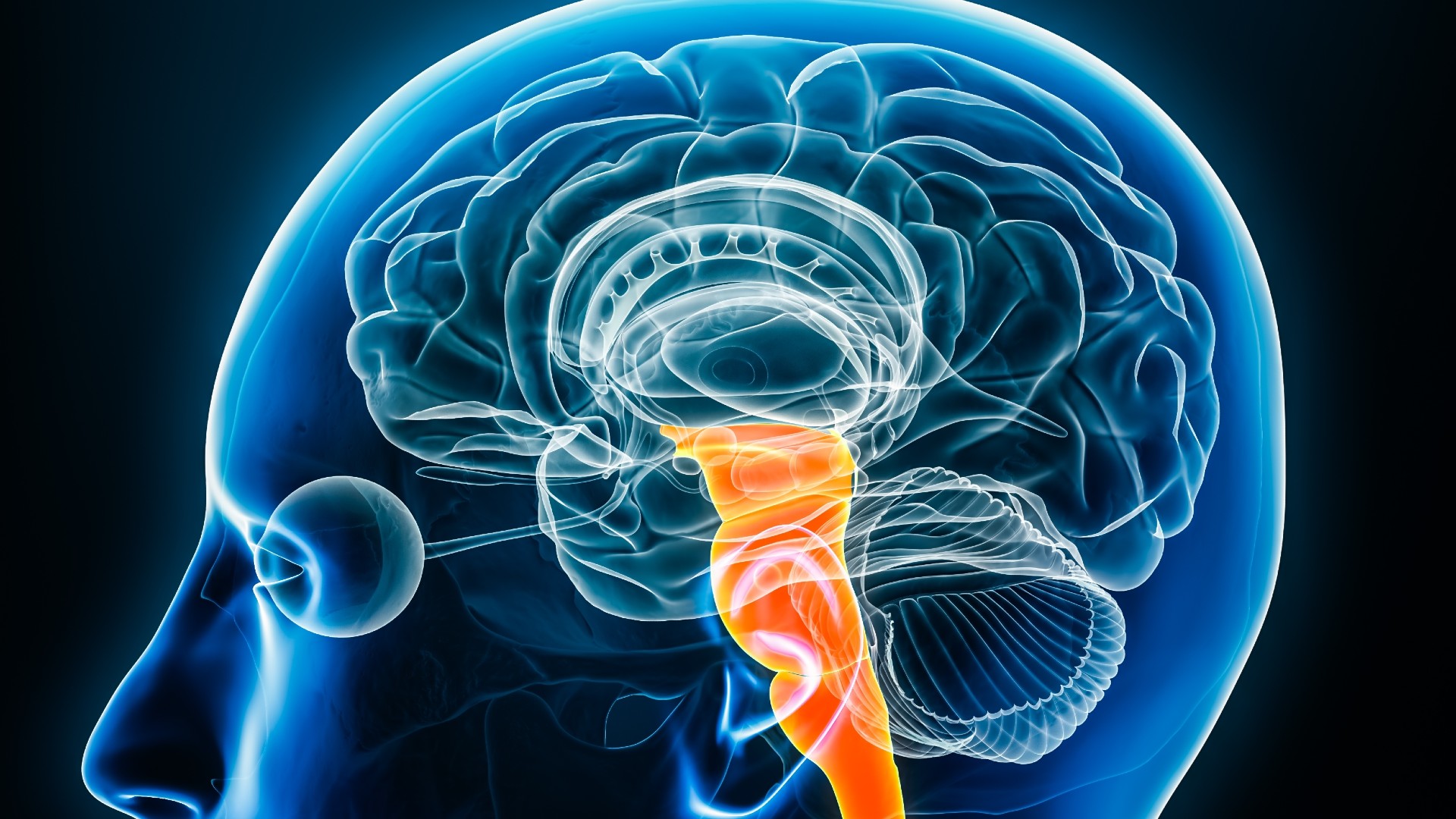
The brain stem, illustrated in orange above, connects the main part of the brain to the spinal cord.
Different cell case in the encephalon regularize various aspects of feeding behavior , such as hunger and satiation , written report tether authorSrikanta Chowdhury , an associate inquiry scientist at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons , say Live Science in an email . repletion refers to the spirit of mellowness and expiation after a filling meal .
For instance , some neurons in part of the brain called thehypothalamusdetect when metabolism levels are low andstimulate feelings of hunger to promote intellectual nourishment intake , while other neuronsregulate jaw motion while we eat , he said . But until now , slight was known about how the mastermind senses the amount of food we ’re exhaust in real time to modulate how much more we deplete , he notice .
The squad focused on the brain stems of mice to build on research in rodentsdating back to the 1970s , whichhintedthat the brain stem could play a role in regulating feelings of richness . However , which picky cell within this realm did this and and how was undecipherable .

To see how CCK neurons may influence eating , the scientists genetically modify mice so that their CCK nerve cell could be switch over on and off using light in lab experiment . They found that when these neurons were activated , the mice eat on minor meals compared to unmodified mouse , and the extent of activation determined how quickly the modified mouse block up eating .
The determination suggest that CCK neurons regulate how much computer mouse eat during a give repast , the squad concluded .
If tantamount nerve cell are find in the human brain stem , the findings could theoretically lead to the development of new treatments for precondition like corpulency .

— Ozempic - style drug tied to more than 60 health benefits and risks in large subject field - of - its - form
— Most elaborate human brain map ever contains 3,300 cadre type
— maestro regulator of excitement find oneself — and it ’s in the brain stem
This melodic theme was supported by separate experimentation conducted in the same discipline , in which the squad discovered that mouse CCK neurons can be activated by a drug call exendin-4 , which caused the mice to stop eating . Exendin-4 is in the same grade of drugs asOzempicandWegovy , which are becoming more and more popular for the handling oftype 2 diabetesandobesity , respectively .
" Whether used alone or alongside other medical interventions , these finding could provide a pathway for clinically influence eating doings and possibly for developing weight - reducing drugs , " Chowdhury said . But again , these findings in rodents must first be extended to people .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompt to enter your show name .













