When you purchase through links on our site , we may garner an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it sour .
member of the Blackfoot Confederacy have an ancient stock that goes back 18,000 age , intend that autochthonic the great unwashed living in the Great Plains of Montana and southerly Alberta today can trace their origins to ice age predecessors , a fresh DNA study let on .
In the fresh study , published April 3 in the journalScience Advances , a team of researcher led by three members of the Blackfoot Confederacy investigated the hereditary history of their tribes .
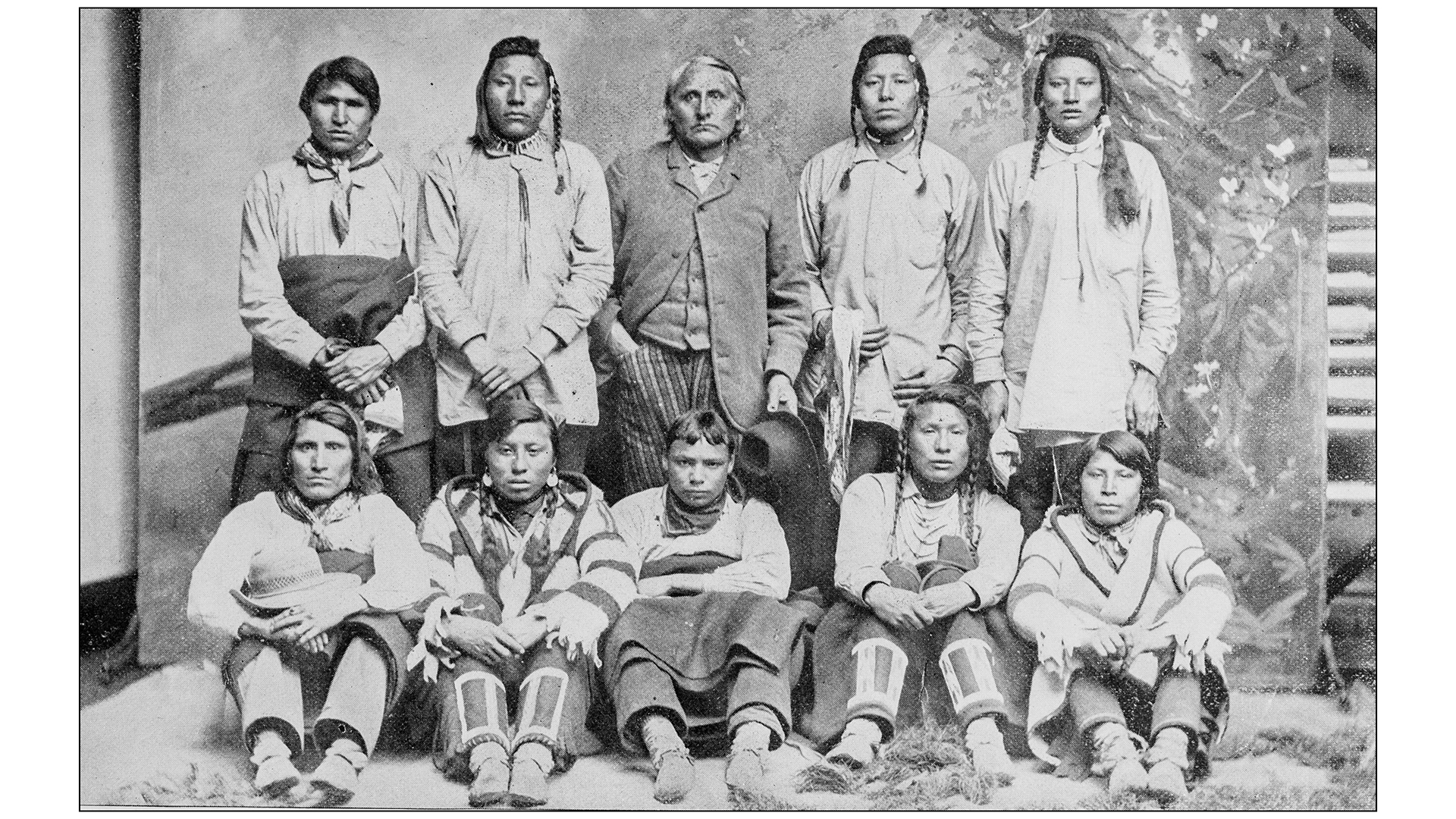

The Blackfoot Confederacy, shown here in a historical photo, has an ancient genetic lineage that goes back 18,000 years.
Comprising four related to tribes — the Blackfeet , Kainai , Piikani and Siksika — members of the Blackfoot Confederacy historically included nomadic bison hunter and trout fishers . Their territorial dominion was divided in the mid-19th century by the U.S.-Canadian border , and in the belated 19th 100 both countries ' governments force the Indigenous confederacy phallus to root on reservations .
Since then , kin group in the Blackfoot Confederacy have had to defend their land claims and water right hand , in spite of botharchaeological evidenceandoral traditionstestifying to their bass history in the area . To supply an additional line of evidence that could assist plug their treaty rights as well as to gain scientific noesis of Indigenous genomic blood line , members of the Kainai Nation in Canada and the Blackfeet clan in Montana partnered with scientists from multiple U.S. universities to investigate their genetic history .
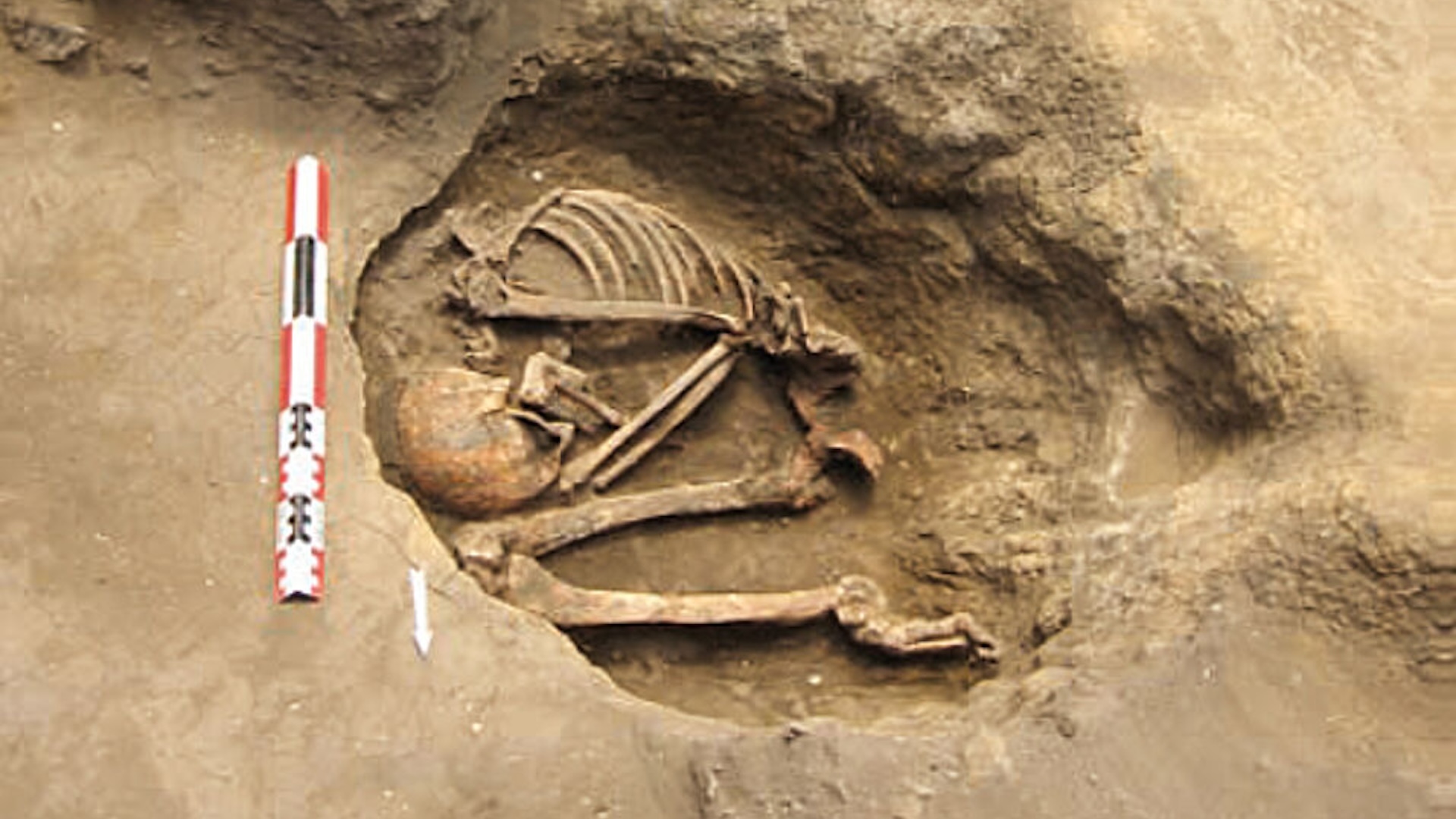
The research team take samples for whole - genome sequence from seven skeleton that werecarbon - datedto between 1805 and 1917 , a period in which interactions between Blackfoot hoi polloi and Euroamericans were increasing because of the fur craft . WhileDNApreservation was not idealistic , as the samples came from skeletons that had been exposed on a interment program , all the stiff create mitochondrial DNA information , or genetic data passed down from the paternal side . Additionally , six present - day tribal members were whole - genome sequenced .
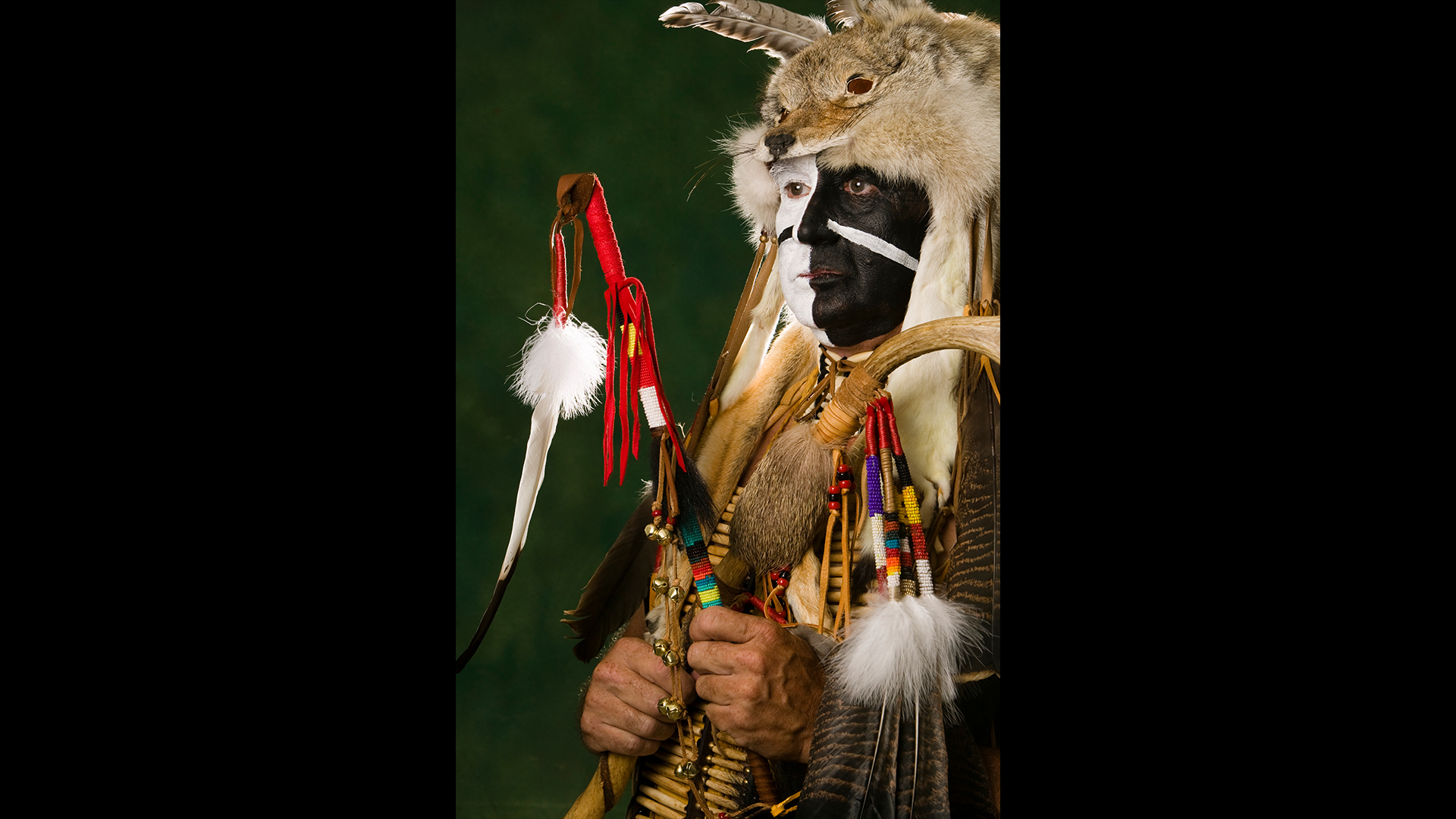

A Blackfoot dancer in ceremonial dress. In the new study, researchers looked at the DNA of seven historical members and six modern-day members.
relate : The 1st Americans were not who we think they were
The genetic info bring out that the historic Blackfoot Ancestors and the present - day Blackfeet / Kainai shared a large fraction of their genome , suggesting a biologic kinship . This continuity of genes was expected , but the squad also found that this lineage was dissimilar from antecedently reported North and South American Indigenous mathematical group . Based on statistical modeling , the squad believes that the Blackfoot masses split up from other groups in the Late Pleistocene , around 18,000 years ago , as multiple population wafture from a undivided source fanned out into the vast geographic Edwin Herbert Land of the Americas .
In gain to identifying this genomic diversity that was previously strange to science , the subject area is important because of its frame , according toGraciela Cabana , an anthropological geneticist at the University of Tennessee , Knoxville who was not regard in the research . " It ’s somewhat obvious that this was written from more of an autochthonic part , " Cabana differentiate Live Science in an electronic mail . " It ’s actually rare to see a collaborative written report that is actually led by Indigenous residential district members on Ancestors . "
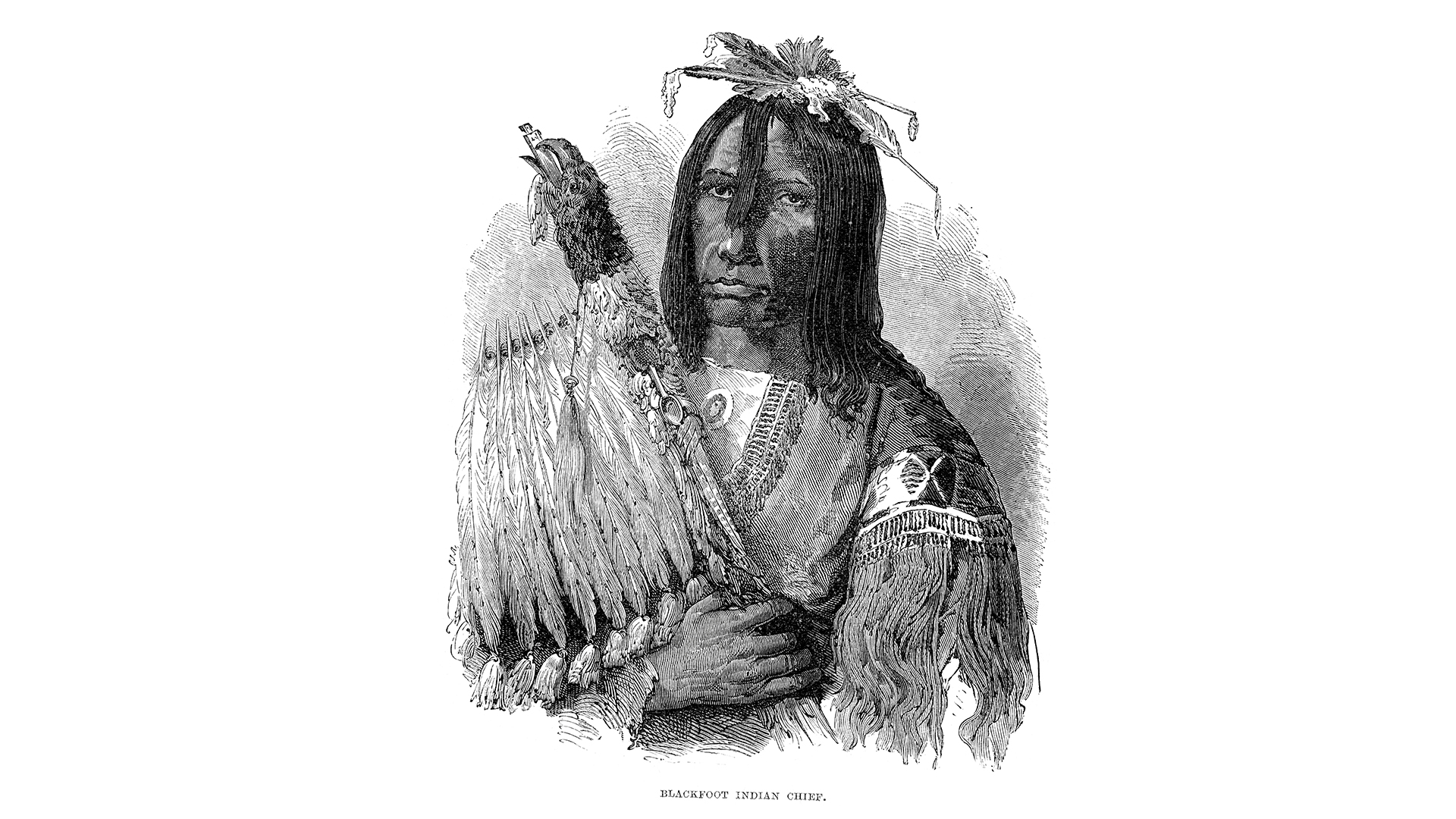

An illustration of a Blackfoot chief from 1873. The DNA investigation showed that modern-day Blackfoot members are related to historical individuals from the 19th and 20th centuries.
Co - authorRipan Malhi , a genetic anthropologist at the University of Illinois , enjoin Live Science in an electronic mail that genomics should be lead by residential district member who can use this pecker from an Indigenous point of view , " or through a community - collaborative plan of attack where residential area cooperator have equal dominance in how the inquiry is conducted and report . "
— 13 of the old archaeologic sites in the Americas
— What ’s the earliest grounds of homo in the Americas ?

— Did human being spoil the Bering Strait after the land bridge deck disappeared ?
This study comes out of the Blackfoot Early Origins Program , which documents Blackfoot pertinacity in their aboriginal territory , co - authorMaria Zedeño , a research anthropologist at the University of Arizona , who conscientious objector - directs the program , separate Live Science in an email . " Genomics study is only one project in this curriculum , " Zedeño sound out , and " the tribal leaders reviewed its blueprint and development at every step of the summons . "