When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
scientist in Antarctica have discovered what may be the oldest New chick ever discover . The 69 million - class - old fossil could last put a longstanding debate about the line of descent of modern bird to rest .
The almost complete skull belongs toVegavis iaai , a waterfowl metal money believed to be the ancient congener of modern - day duck and geese . The metal money live on at the same time as dinosaurs likeTyrannosaurus rexand may have survived the end - Cretaceous mass extinction , the Modern study suggests .
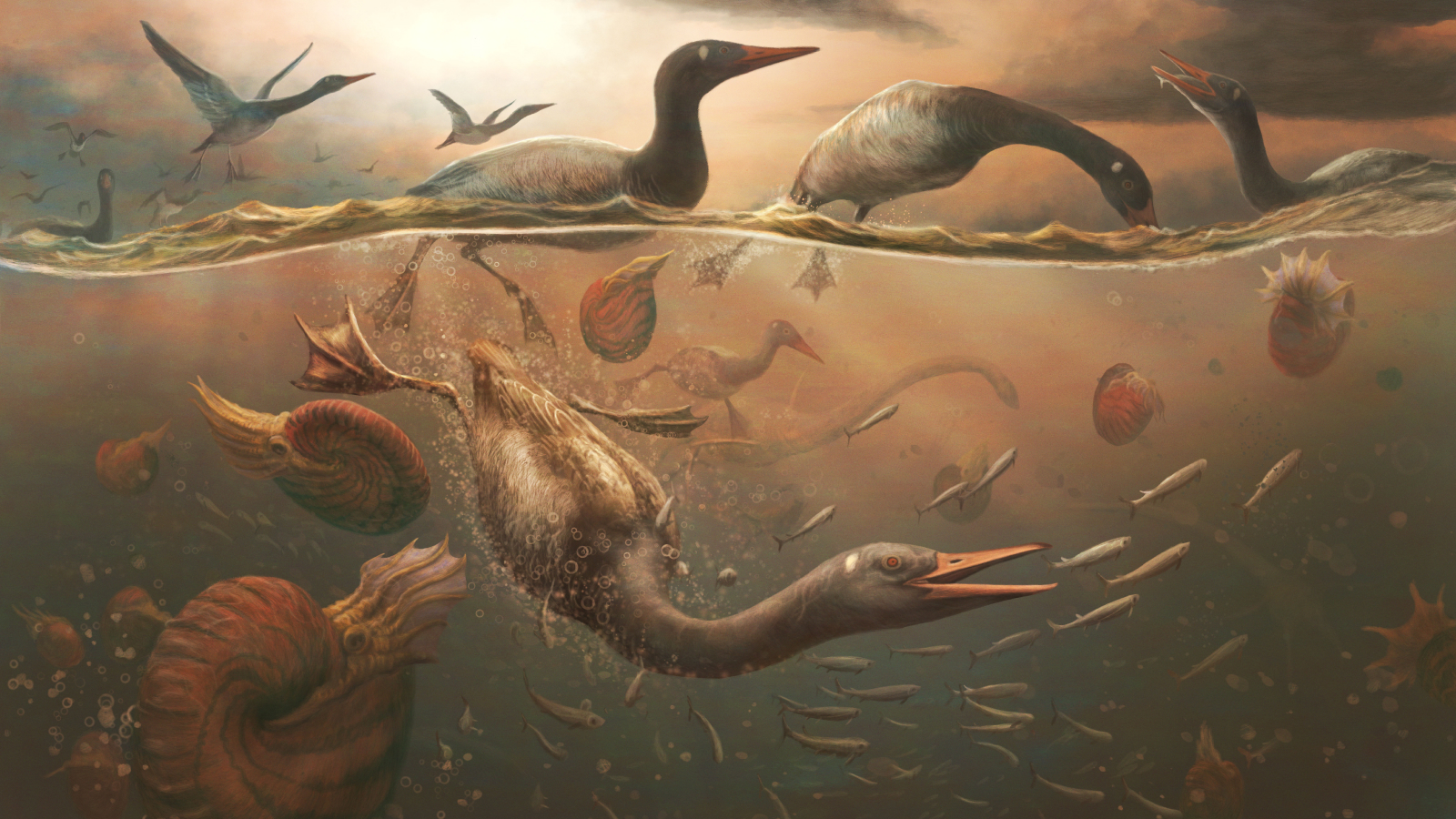

Vegavis iaailived in Antarctica at the time the asteroid hit Earth and wiped out the nonavian dinosaurs.
Study co - authorJulia Clarke , a palaeontologist at the University of Texas , Austin reportedthe firstV.iaaifossilfound on Vega Island in Antarctica in 1992 . The fossil was around 66 million to 68 million year old . She aim that the metal money is linked to modernistic birds , especially waterfowl . Butnot everyone was convincedas scientist were missing a key firearm of the puzzler — the creature ’s skull .
" [ The initial dodo ] was just a all different part of the skeleton . And when it follow to birds , the skull has a wad of phylogenetic or informative characteristics that tell you what it is , " study co - authorPatrick O ' Connor , an evolutionary biologist at Ohio University , secernate Live Science .
Related : How did fowl survive the dinosaur - killing asteroid ?
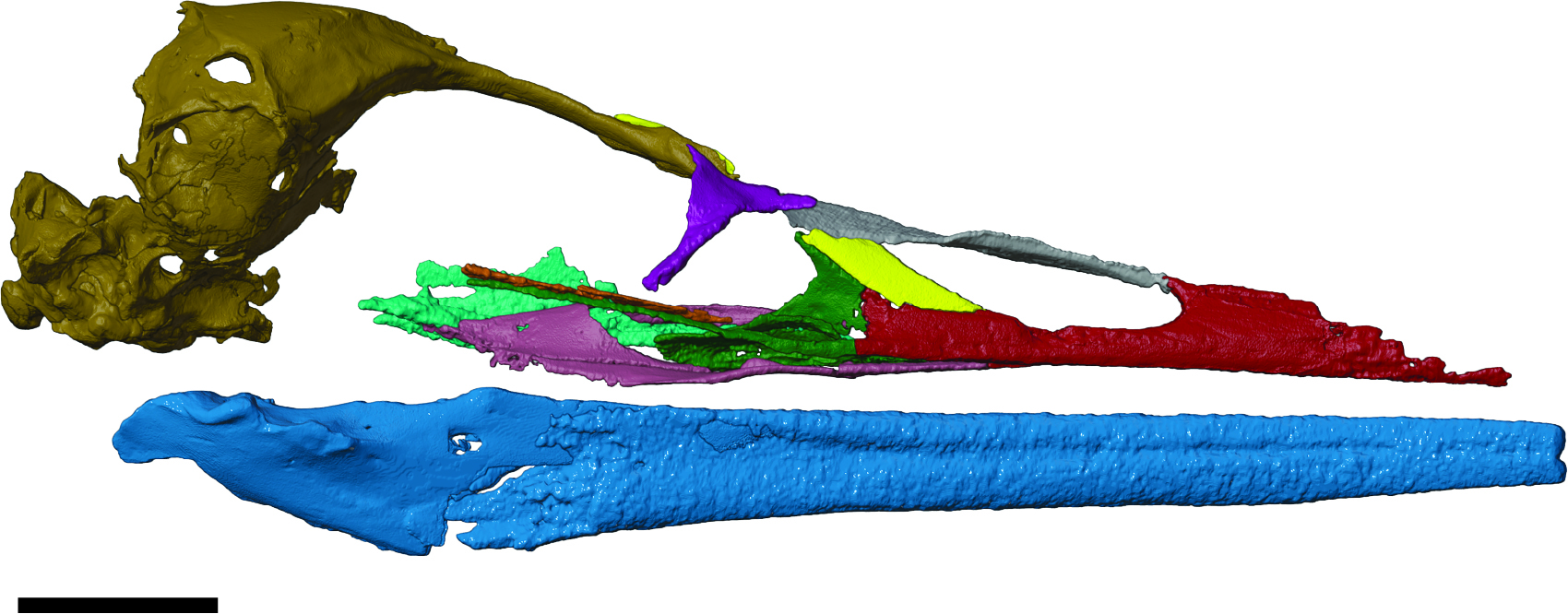
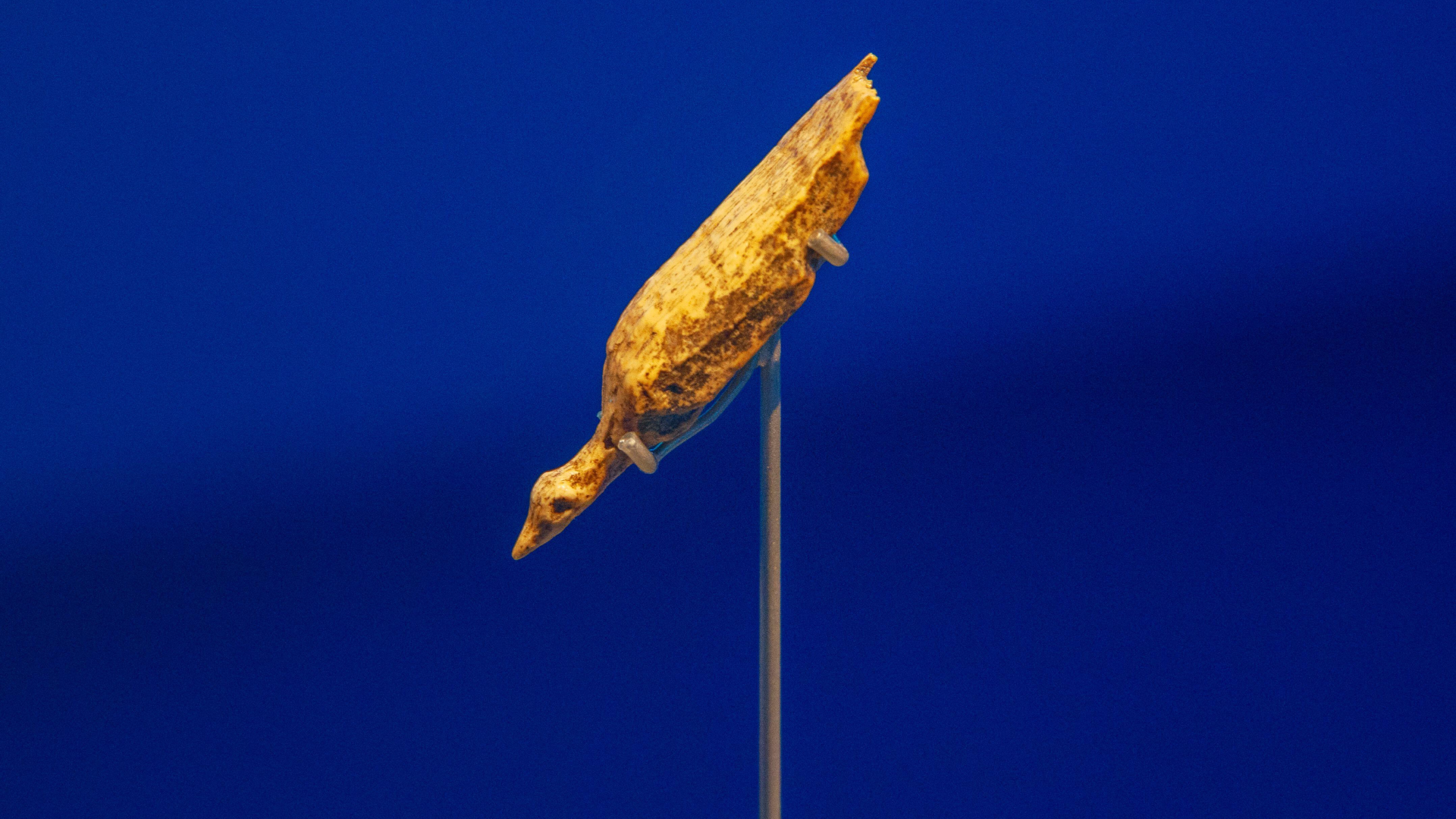
Digital reconstruction of the complete Vegavis skull showed its resemblance to modern birds
The newV.iaaifossil , estimated to be 68 million to 69 million year old , was found during an expedition in 2011 , but has only now been analyzed . Thestudywas bring out Wednesday ( Feb. 5 ) in the diary Nature .
The find of the newfangled skull enabled scientists to learn more about this species and how it fits in the bird family tree . They found that , unlike pre - forward-looking chick that be during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods ( 201.3 million to 66 million yr ago),V. iaaihas characteristic that are similar to birds that be today — including a brain shape distinctive of mod bird , and a unique bone in the upper beak . The upper beak of most pre - modern birdie is made of a single bone , called the maxillary , with a little bit of another type of bone , pre - maxillary , at the crown .
" When we count at theVegavis , it ’s the pre - maxilla all the way . The upper jawbone is tiny , which is precisely what we have a bun in the oven from advanced bird , " sketch co - authorChristopher Torres , a palaeontologist at The University of the Pacific in Stockton , California , distinguish Live Science .
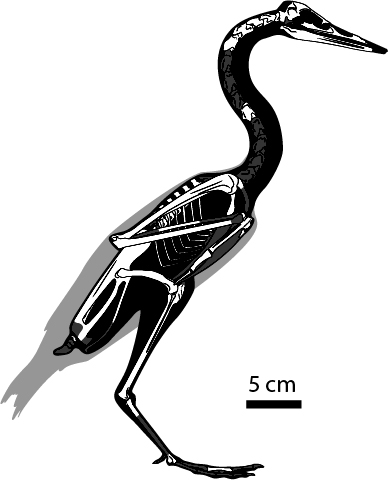
Skeletal drawing of the crown birdVegavis iaaithat lived in Antarctica 69 million years ago.
Using a 3D reconstruction , the scientist showed that the bird had a long , narrow snout enhanced with powerful jaw muscles , much like modern dive birds use to captivate Pisces .
" regard how specialised the skull was , for me , the most impactful,“Juan Benito Moreno , a paleontologist at the University of Cambridge who was not involved in the study , told Live Science . " It was surprising to see an incredibly niche ecological feature so early in the evolution . "
The gargantuan asteroid that hit Earth at the end of theCretaceous period(145 million to 66 million class ago ) drove all nonavian dinosaur to extinction . Landfowls ( Galliformes ) and waterfowls ( Anseriformes ) were amongthe earliest modern birdsthat be in the age of dinosaurs .
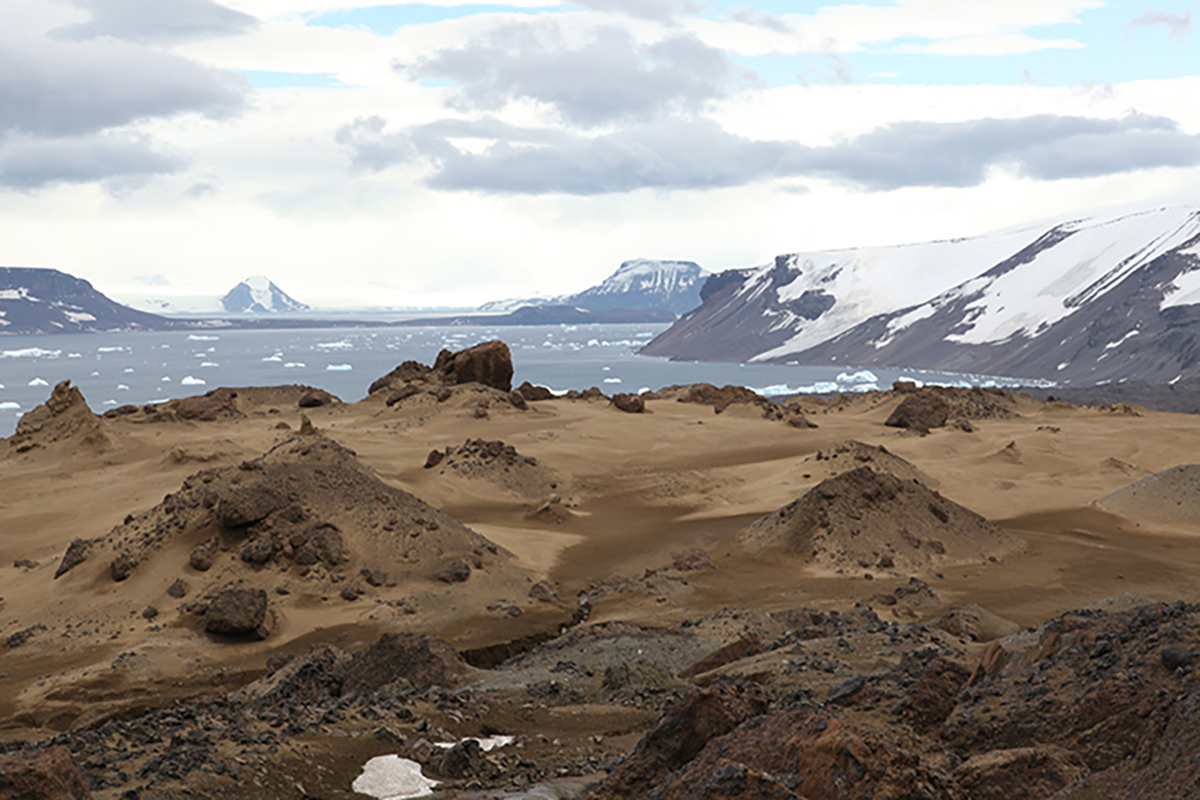

The oldest evidence of a modern bird was found on Vega Island in the Antarctic Peninsula.
While rapid evolution get hold of place after the mass extinguishing , " report that attend at genomic comparisons of modern bird predict that the earliest divergence happened prior to that mass quenching , " Torres said . " But their dodo record is extraordinarily scarce . "
While the evidence pointing toV. iaaibeing associated with modern hoot is potent , it ’s still not clear whether it really is a relative of modern ducks and cuckoo , he said .
— Clever , razzing - similar dinosaurs that lived 74 million years ago get cozy in communal nests , study suggests

— A giant crocodilian kill the declamatory ' brat bird ' ever found , 12 million years ago
— Ancient birdie with T. rex - like skull break in China
Daniel Ksepka , a paleontologist at the Bruce Museum in Connecticut who was not ask in the subject area , agree . " Vegavisseems to have been a bit of an odd duck’s egg , " he tell Live Science in an email . " Provided the organic evolution is right , a duck’s egg - like bill must have either evolved during the Cretaceous Period but been mislay byVegavis , or evolved multiple times severally . It will be interesting to see if succeeding fossils reassert one of these scenarios . "

V. iaaiexisted when global temperature were far high-pitched than they are today , and when Antarctica had a temperate climate and was covered in vegetation . Its length from the asteroid impact may have provided the species with some protection from the devastation that follow .
For type O ' Connor , this study is the beginning of more discoveries to be institute in the Cretaceous rock’n’roll of Antarctica . " The snort story is great , but we have other group[s ] of animals , and , importantly , flora , that we can track through that mass extinction result that really let us get a better grip on ecosystem response to a global environmental disturbance , " he said .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your exhibit name .