When you buy through links on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it act .
globe held a deep sea of magma beneath its control surface in its early history , Modern enquiry line up , potentially explaining odd anomalies find out in the mantle today .
This basal magma ocean has been heatedly debate for years . Some geochemical evidence indicate that in the first few hundred million years of the planet ’s macrocosm , a lasting ocean of melting formed at the boundary between Earth ’s core and its middle bed , the drape . But models of the satellite ’s formation suggest that when Earth was new and liquified , it solidified from the bottom up , making it laborious to see how a deep magma ocean could be .

New model suggests an ocean of magma formed within the first few hundred million years of Earth’s existence.
The new report , published March 26 in the journalNature , found that not only could a magma ocean exist , but that its presence was inevitable . No matter the accurate location where the liquefied newborn satellite set out to crystallize into a unanimous , a basal ocean still imprint , the study revealed .
oddment of this veil magma sea could still exist today in the shape of big low - shear speed provinces ( LLVPs ) or blanket " blobs , " which are giant region of the deep mantle where quake waves move around more slowly than they do through the residue of the mantle .
scientist have argue whether these LLVPs are theremains of oceanic crustthat have been press deeply into the mantlepiece , mean they date back a few hundred million year , or whether they ’re theleftovers from Earth ’s basal magma ocean , induce them 4.4 billion years quondam .
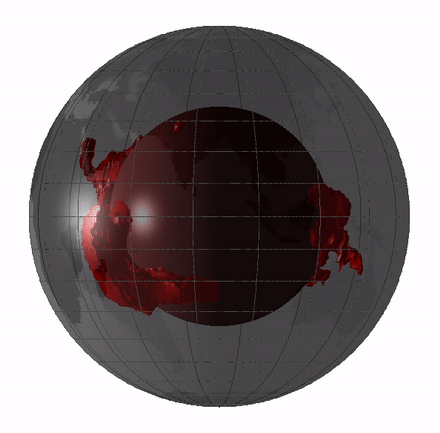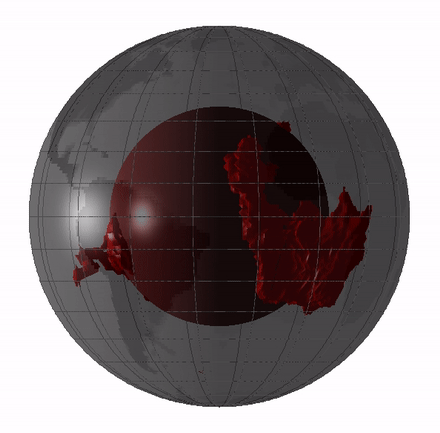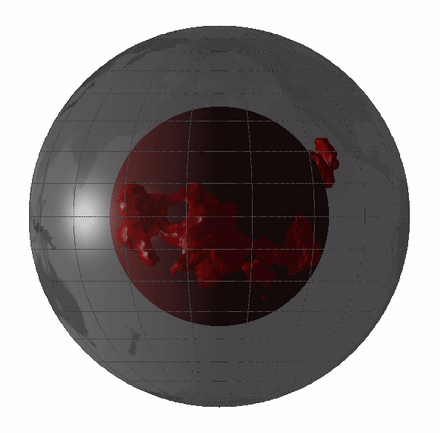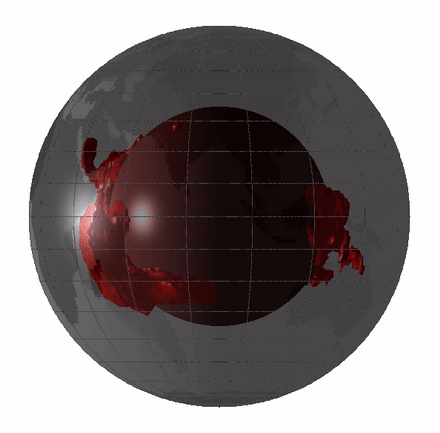
Remnants of the magma ocean my still exist today as LLVPs, or giant “blobs” in Earth’s mantle.
The new discipline argues for the latter and the finding could have major implication for how researchers understand Earth ’s story , said study lead authorCharles - Édouard Boukaré , a planetary physicist at York University in Toronto .
" It would strike thermal communication between the core and the mantlepiece , " Boukaré state Live Science . " It might affect the fix of tectonic plateful . "
Earth’s early days
The investigator built a new model of Earth ’s geological formation that consider both geochemical data and seismic data — the two primary methods of peering into Earth ’s deep story . In particular , there are important tincture elements that chemically opt to persist in the magma while other mineral crystalise into tilt . The amount of these vestige elements in sway can reveal when and in what order the rocks of the mantle solidify .
Most studies of this era of Earth ’s constitution focal point on the initial set of the drapery and the dynamics when the mantlepiece was still mostly liquified .
Boukaré and his squad focused a footling later , depend at the point at which the mantle would have been elucidate enough that it was comport as a solid rather than a liquid . They find that regardless of where the solidifying first start out — in the heart of the pall , or decent at the boundary with the core — a basal magma ocean form .

Phases of formation
The process would have protrude with a thin insolence of solid work on the surface of the new Earth , but the solids were cold and less chirpy than the underlying mantle , so they dip and remelted .
However , as the mantle continued to cool , solids that constitute in the upper mantle started to sink and accumulate in the lower mantle . These solid were rich in iron oxide , which is heavy and has a low melt power point , so these solid sink deeper and often remelted . Because of how dull iron oxide is , even in its limpid form , this melt did not climb up back up , as liquid state unremarkably uprise above solid . Instead , it stayed in the cryptical mantle , where the oestrus from the essence keep it melted . This formed the basal magma ocean .
The researchers motley the conditions in their modelling to alter the deepness of the solid formation , but those parameter did n’t exchange anything . Even in the least conducive lot for a deep magma sea , one still formed .

The findings suggest that the main anatomical structure of the planet shape very early in its chronicle , Boukaré said . " Another way to say this is there is a computer memory , " he say . The seeds of the planet ’s dynamic would have been constitute very ahead of time , with these ancient construction continuing to influence how the satellite changed moving forward .
— Traces of ancient magma sea found in Greenland
— Single magma ocean once covered the lunation

— The moon might be rooted leftovers from Earth ’s hidden magma sea
" We might say if we have some initial condition of the planet and we can simulate the very early stagecoach of terrestrial phylogeny , we can then call most of its demeanor on recollective timescales , " Boukaré said .
He next plans to improve the mould by incorporating more trace elements . It would also be interesting to apply the model to other planet such as Mars to see if other rocky planet go through standardised transition , Boukaré said .

" Maybe this basal ocean affair is not something that is unparalleled to the Earth , " he order .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to infix your showing name .











