When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Something is wrong in our expanding cosmos .
But over the past decennary , an alarming hole has been grow in this picture : Depending on where astronomers await , the rate of the universe of discourse ’s expansion ( a value address theHubble constant)varies significantly .

An artist’s illustration of the James Webb Space Telescope.
Related:‘It could be profound ' : How astronomer Wendy Freedman is endeavor to prepare the universe
Now , on the second anniversary of its launch , theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) has cement the discrepancy with stunningly precise young observations that threaten to upend the standard model of cosmogony .
The new physics need to qualify or even substitute the 40 - year - old theory is now a topic of argument .
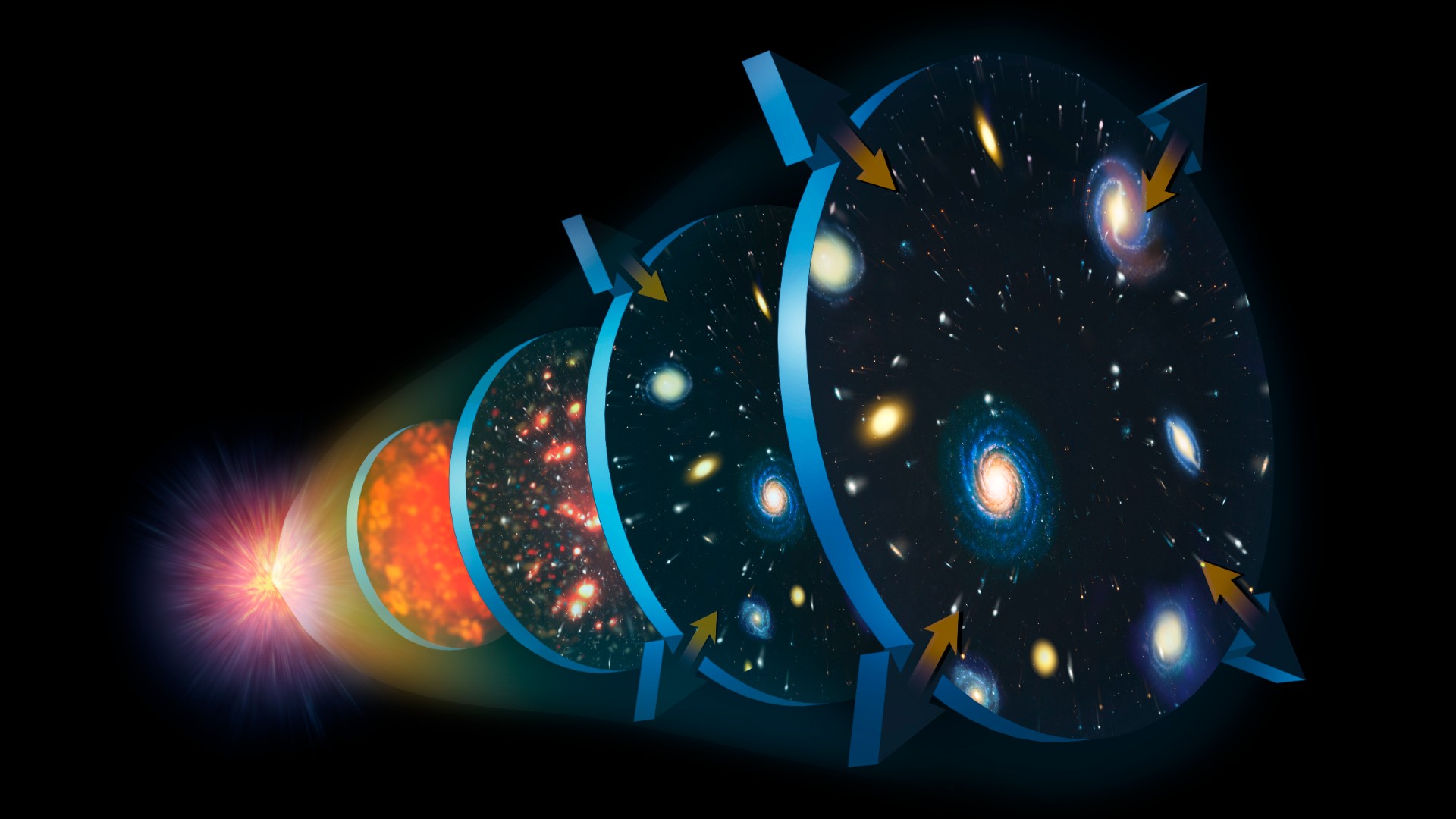
An illustration of the expansion of the Universe. The Big Bang is immediately followed by a rapid expansionary period called inflation. Then, as protons and electrons combine to form atoms, light can travel freely; leaving the cosmic microwave background imprinted upon the sky. The universe’s expansion slowed around 10 billion years ago, and it began to fill with galaxies, stars and giant black holes. Around 5 billion years ago, dark energy caused this cosmic expansion to rapidly accelerate. To this day, it shows no signs of stopping.
" It ’s a disagreement that has to make us wonder if we really do understand the authorship of the universe and the physics of the universe,“Adam Riess , a prof of astronomy at Johns Hopkins University who lead the squad that made the new JWST measurements , state Live Science . Reiss , Saul Perlmutter and Brian P. Schmidtwon the 2011 Nobel Prize in physicsfor their 1998 discovery ofdark vigour , the cryptic force behind the universe ’s speed elaboration .
Starting with a bang
On this much cosmologists can concord : It started with a bang .
Then in an blink of an eye , the young cosmos was formed : an expanding , roil plasma stock of subject and antimatter molecule that popped into macrocosm , only to annihilate each other upon contact .
leave to their own devices , the matter and antimatter inside this blood plasma mire should have consumed each other solely . But scientist believe that someunknown imbalanceenabled more matter than antimatter to be produced , saving the existence from immediate ego - destruction .
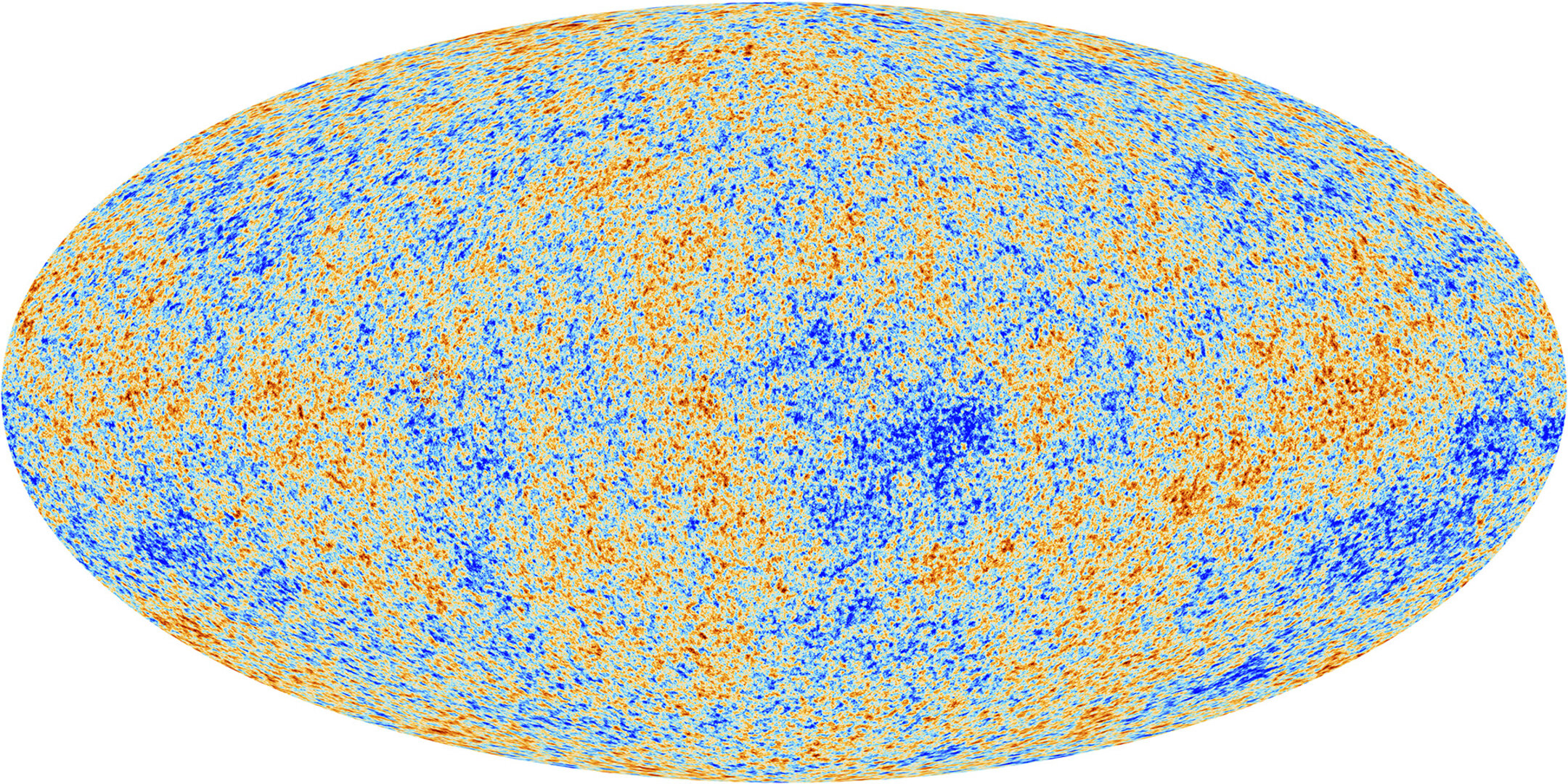
The cosmic microwave background: The universe’s ‘baby picture’ taken by the European Space Agency’s Planck satellite.
Gravity compress the plasma pockets , squeezing and heat the matter so that levelheaded waves travel just over half the speed of light , call heavy particle acoustical oscillations , rippled across their surface .
Meanwhile , the high vigour density of the early universe ’s crowded content dilute space - time , pulling a little fraction of this subject safely from the fray .
As the universe inflated like a balloon , the received report go , ordinary matter ( which interact with lighting ) set around clod of invisible dark matter to create the first beetleweed , connected together by a vast cosmic web .
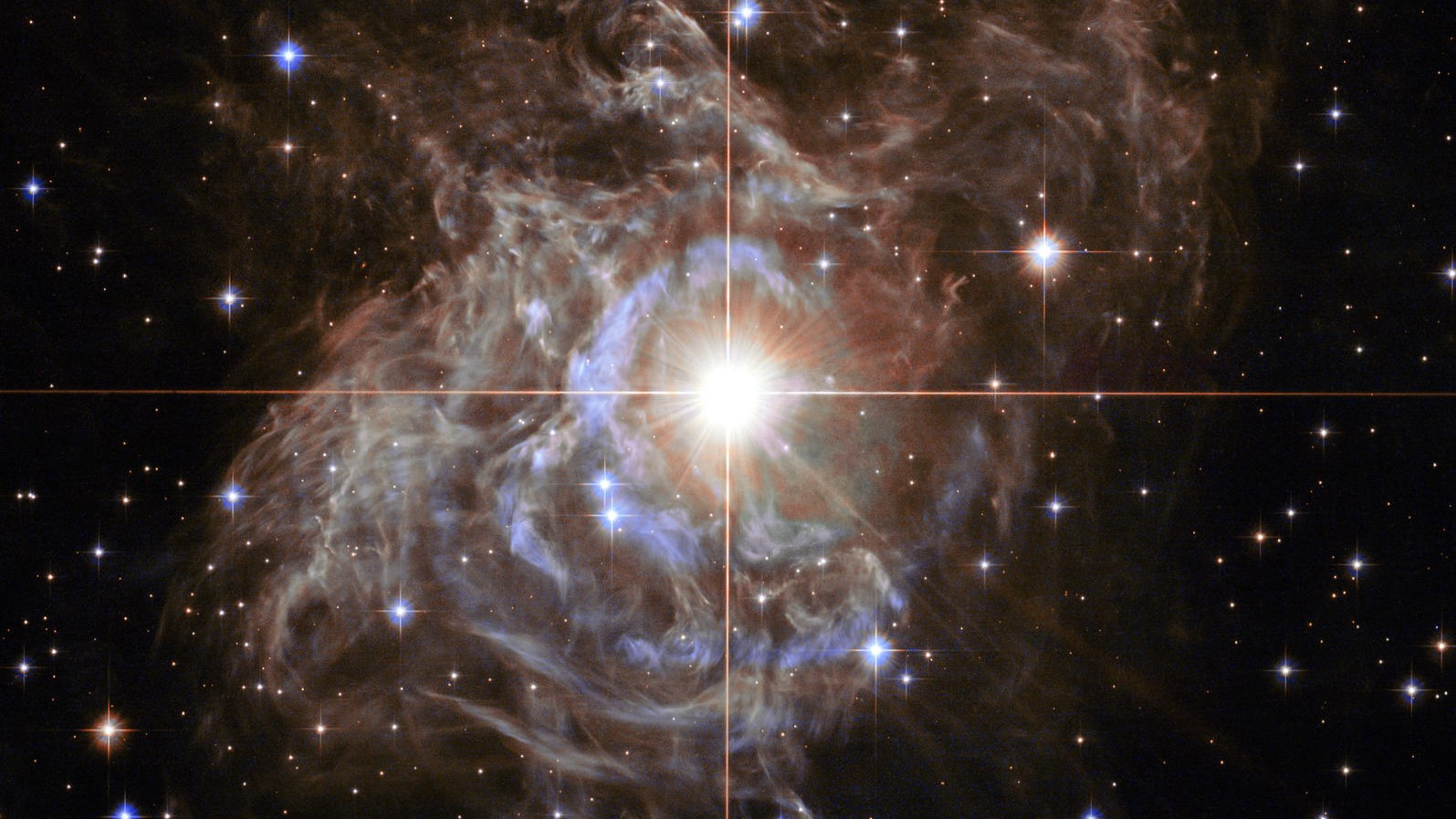

RS Puppis, a Cepheid star located 6,000 light-years away in the constellation Puppis and imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Related : James Webb telescope detects the other string in the ' cosmic vane ' ever seen
Initially as the universe ’s contents circularize out , its energy concentration and therefore its expansion rate decrease . But then , roughly 5 billion years ago , galaxies begin to recede once more at an ever - faster rate .
The crusade , according to this exposure , was another invisible and mysterious entity known as dark energy .
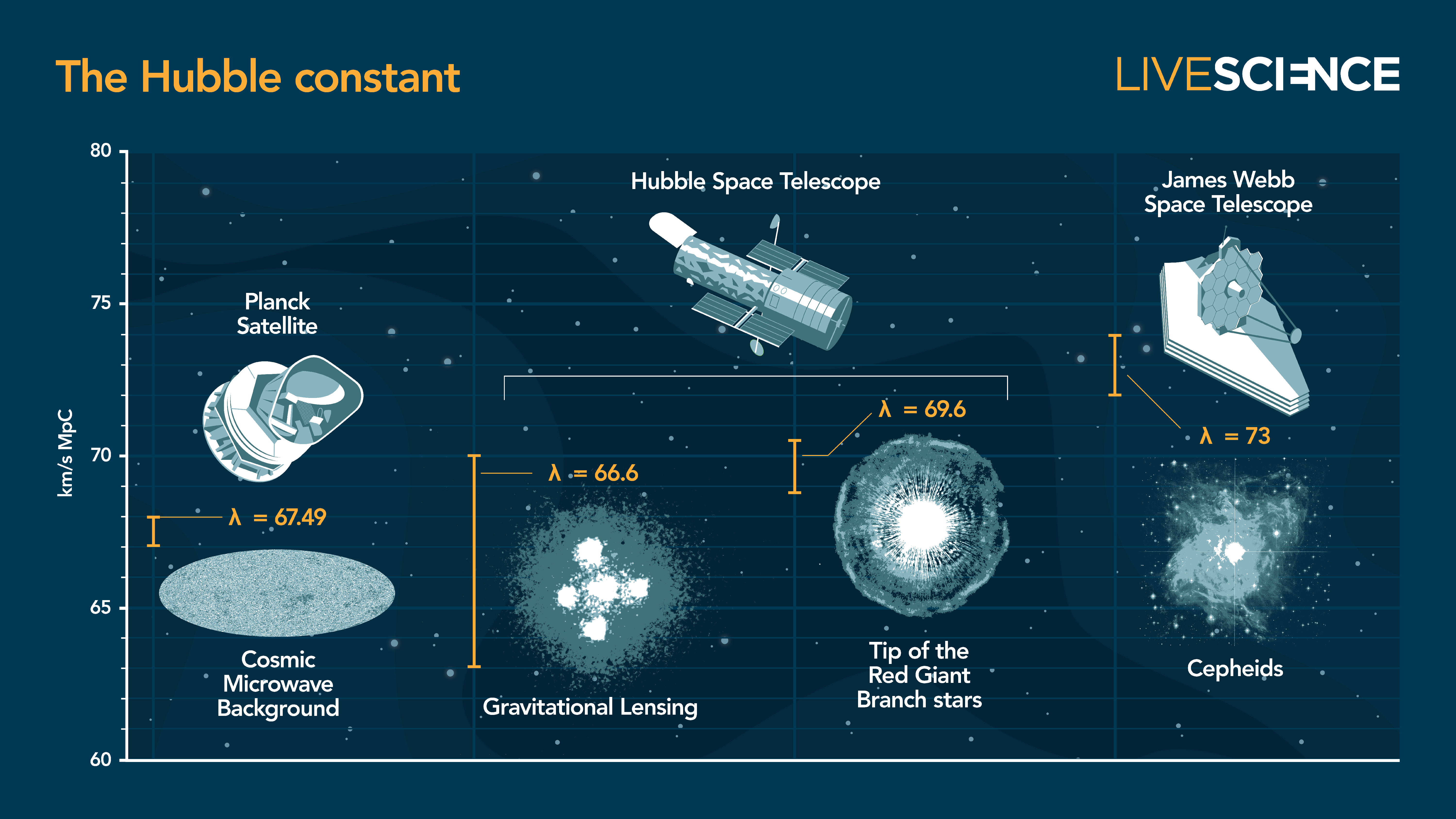
A collection of some of the most recent measurements of the Hubble constant. From left to right, the sources used to measure its value are: The cosmic microwave background captured by the European Space Agency’s Planck satellite; gravitational lensing and Tip of the Red Giant Branch stars measured by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope; and Cepheid stars seen by the James Webb Space Telescope.
The bare and most democratic explanation for dark vigor is that it is acosmological constant — an inflationary energy that is the same everywhere and at every moment ; woven into the adulterate fabric of space - time . Einstein named it lambda in his theory of ecumenical theory of relativity .
As our cosmea grew , its overall matter concentration drop while the sinister energy density stay on the same , step by step making the latter the biggest contributor to its overall elaboration .
tot together the vigour densities of average subject , dark thing , dark energy and energy from lightness set the upper stop number limit of the universe ’s expansion . They are also key ingredients in the Lambda cold-blooded dark matter ( Lambda - CDM ) theoretical account of cosmogony , which maps the growth of the cosmos and predicts its remnant — with matter eventually broadcast so thin it experiences a heat death called the Big Freeze .
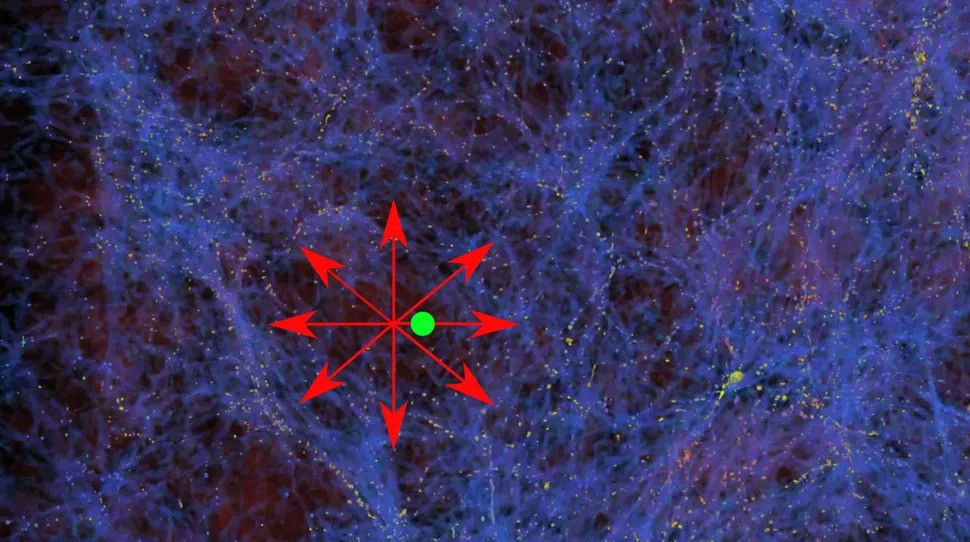
The Keenan-Barger-Cowie supervoid. Proponents of the theory of Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) argue that our Milky Way’s presence near the center of the 2-billion-light-year wide underdensity of galaxies is skewing our measurements of the Hubble constant.
Many of the framework ’s predictions have been proven to be highly accurate , but here ’s where the problems begin : despite much searching , stargazer have no hint what dark matter or dark Department of Energy are .
" Most people agree that the creation ’s present composing is 5 % average , nuclear subject ; 25 % cold , glowering issue ; and 70 % non-white energy,“Ofer Lahav , a professor of uranology at University College London who is postulate in beetleweed resume of dark energy , differentiate Live Science . " The embarrassing fact is , we do n’t see the last two of them . "
But an even greater terror to Lambda - CDM has materialized : bet on what method acting astrophysicist habituate , the universe seems to be growing at dissimilar rates — a disparity known as the Hubble tension . And methods that peer into the former universe show it expanding significantly faster than Lambda - CDM predicts . Those methods have been vetted and verified by multitudinous observations .

" So the only reason that I can understand , at this point , for them to disagree is that the model that we have between them is perhaps lack something , " Riess said .
Climbing the cosmic ladder
Measuring the universe ’s enlargement rent a little moment more than aradar gun .
The first method acting to measure this growth looks at the so - called cosmic microwave oven background ( CMB ) , a relic of the universe ’s first igniter produce just 380,000 years after the Big Bang . The embossment can be seen across the entire sky , and it wasmapped to find a Hubble constant with less than 1 % uncertaintyby theEuropean Space Agency ’s ( ESA ) Planck satellite between 2009 and 2013 .
In this cosmic " baby picture , " the population is almost altogether unvarying , but hotter and colder patches where matter is more or less slow reveal where heavy particle acoustical oscillation made it clump . As the universe exploded outward , this scoop - bubble social system ballooned into the cosmic web — a internet of crisscrossing strands along whose intersections galaxies would be stick out .

Related:$100,000 Breakthrough physics prize grant to 3 scientists who study the enceinte scale social organisation of the universe
By studying these ripples with the Planck satellite , cosmologist infer the amounts of regular topic anddark matterand a value for the cosmologic constant , or dark energy . Plugging these into the Lambda - CDM framework spit out out a Hubble constant quantity of roughly 46,200 miles per hour per million light - years , or some 67 klick per second per megaparsec . ( A megaparsec is 3.26 million light - year . )
Let ’s pause on this numeral for a here and now : if a beetleweed is at a aloofness of one megaparsec aside from us , that means it will retreat from us ( and us from it ) at 67 klick per second . At twenty megaparsecs this corner grows to 1,340 kilometers per indorsement , and continues to grow exponentially there onward . If a beetleweed is any further than 4,475 megaparsecs away , it will recede from usfaster than the speed of twinkle .

A second method acting to find this expanding upon pace apply quiver stars called Cepheid variable — dying stars with helium - petrol outer layers that grow and shrink as they absorb and release the wizard ’s radiation , make them periodically quiver like upstage sign lamps .
In 1912 , uranologist Henrietta Swan Leavitt discover that the vivid a Cepheid was , the slower it would flicker , enabling astronomers to measure a lead ’s absolute luminosity , and therefore gauge its space .
It was a landmark discovery that transformed Cepheids into abundant " standard candela " to measure the macrocosm ’s immense scale . By stringing observation of beat Cepheids together , astronomers can construct cosmic aloofness ladder , with each spoke occupy them a footprint back into the past .

" It ’s one of the most accurate mean value that astronomers have today for assess distances,“Wendy Freedman , an astrophysicist at the University of Chicago , told Live Science .
To build a distance ladder , uranologist construct the first rung by choosing nearby Cepheids and cross - check their distance based on beat light to that find by geometry . The next rungs are tot up using Cepheid readings alone .
Then , astronomers look at the space of the stars and supernovas on each rung and equate how much their lightness has been redshifted ( stretch out to longer , redder wavelength ) as the population expands .

This collapse a accurate measurement of the Hubble constant quantity . In 2019,the method acting was used by Riessand his confederate , who trained theHubble Space Telescopeon one of theMilky Way ’s faithful neighbour , the Large Magellanic Cloud .
Their result was explosive : an impossibly high expansion rate of 74 km / s / Mpc when compared to the Planck measurement .
Yet Hubble lacked the necessary preciseness for the crowded regions of outer space the team was study , have some removed Cepheids to blur into neighboring stars . Dissenting cosmologists had some elbow room leave behind to argue that the result , however shocking , could have come from a measure error .

connect : Hubble Telescope captures a galaxy ’s ' interdict ' light in sensational new icon
So when JWST launched in December 2021 , it was poised to either conclude the discrepancy or cement it . At 21.3 understructure ( 6.5 m ) wide , JWST ’s mirror is almost three time the size of Hubble ’s , which is just 7.9 feet ( 2.4 m ) wide . Not only can JWST detect objects 100 times fainter than Hubble can , but it is also far more sensitive in the infrared spectrum , enabling it to see in a broader reach of wavelengths .
By comparing Cepheids measure out by JWST in the galaxy NGC 4258 with bright Type Ia supernovas ( another received cd because they all collapse at the same absolute luminosity ) in remote galaxies , Riess and his colleagues go far at a nearly superposable result : 73 km / s / Mpc .

Other measurements — include one made by Freedman with the Hubble Space telescope on the rapid brightening of the most luminous " tip of the leg " reddened giant stars , and another with light bent by the gravity of monumental galaxies — came back with respective solution of 69.6 and 66.6 km / s / Mpc . A separate result using the bending of light also give a value of 73 kilometre / s / Mpc . Cosmologists were leave reeling .
" The CMB temperature is measured at the level of 1 % preciseness , and the Cepheid length ladder measurement is fuck off tight to 1%,“Ryan Keeley , a cosmologist at the University of California , Merced who has been cultivate to explain the Hubble tension , told Live Science . " So a difference of 7 kilometers per secondly , even though it ’s not very much , is very , very improbable to be a random opportunity . There is something definite to explain . "
Cosmology in crisis
" We would n’t call it a tension or problem , but rather a crisis,“David Gross , former director of the KITP and a Nobel laureate , said at the league .
How things can be fixed is unclear . Riess is pursuing a pinch to the Lambda - CDM simulation that assumes dark energy ( the lambda ) is n’t constant but instead evolves across the life of the cosmos according to unknown physical science .
However Keeley ’s research , published Sept. 15 in the journalPhysical Review Letters , contradicts this . He and his colleagues found that the expansion rates pair the prediction of Lambda - CDM all the direction back to the CMB . So , if the manakin needs fixing anywhere , it ’s most likely in the very early universe , Keeley say .

It could be possible to add some extra dark energy before the emergence of the cosmic microwave background , Keeley said , giving some additional oomph to the cosmos ’s expansion that need n’t make it break dance from the standard exemplar .
Another group of astronomers is convinced that the tension , alongside the watching that the Milky Wayresides inside an underdense supervoid , means that Lambda - CDM and sour issue must be thrown out altogether .
What should replace it , consort toPavel Kroupa , a professor of astrophysics at the University of Bonn , is a hypothesis address Modified Newtonian Dynamics ( MOND ) .

The theory proposes that for gravitative pulls ten trillion times smaller than those felt on Earth ’s surface ( such as the tugs felt between upstage galaxies ) Newton ’s Torah break down and must be replace by other equality .
Other astronomers say that their own calculations nil the MOND claims , yet Kroupa insists that cosmologists looking to pick off the standard cosmogonical model are " basically add extra complications to an already very mussy and complicated possibility . "
" What I am go through and witnessing is an essential breakdown of skill , " Kroupa said .

Lahav is agnostic . It ’s possible Lambda - CDM just require a tweak , he read , or peradventure dark matter and dark push are the innovative - Clarence Shepard Day Jr. equivalent of epicycle , the small circles ancient Greek astronomers used to model planet orb Earth . " The orbits of planet were described very accurately by epicycle , " Lahav said . " It was a good model ! It fitted the datum . "
But once astronomers place the sun in the nitty-gritty of thesolar systemin new model , epicycles eventually became irrelevant , he added .
" If we desire to go philosophical , maybe that ’s what ’s go on , " Lahav said . " But maybe also there is dark matter and dark energy and it ’s just not been discovered yet . "

— What is the cosmological invariable ?
— James Webb scope discovers oldest black hole in the universe
— James Webb Telescope fleck galaxies from the dawn of clock time that are so massive they ' should n’t exist '

cosmologist are look for answers in a identification number of places . coming CMB experimentation , such as theCMB - S4 projectat the South Pole and theSimons Observatoryin Chile , are searching for hint in ultraprecise measurements of the early cosmos ’s radiation . Others will look to the dark matter maps produce by ESA’sEuclid place telescopeor to the future dark energy resume conducted by theDark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument .
Although it now may seem less likely , it ’s also still possible the Hubble stress could be conclude by see out some unobserved taxonomic flaw enshroud inside current measurements .
For Freedman , such a solution , or possibly further riddles , will come from the JWST . Her squad is using the telescope ’s powerful centre to make ultradetailed measure of Cepheid variables ; tip - of - the - violent - giant - branch star topology ; and a case of C star called JAGB stars all at once distance .

" We ’ll see how well they agree and that will give us a horse sense of an overall taxonomical reply , " Freedman sound out .
Freedman has bet only at superstar in one galaxy so far but is already take in a conflict from the Hubble infinite scope measurements .
" I ’m really frantic because I think we ’re going to have something really interesting to say , " Freedman said . " I ’m just completely open . I do n’t know where this is going to fall . "