When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it work .
Since its launching on Christmas Day , 2021 , theJames Webb Space Telescopehas proven its worth year after yr . 2024 is no elision . Here are just five times the ultrapowerful scope has remold our understanding of the population .
Big galaxies
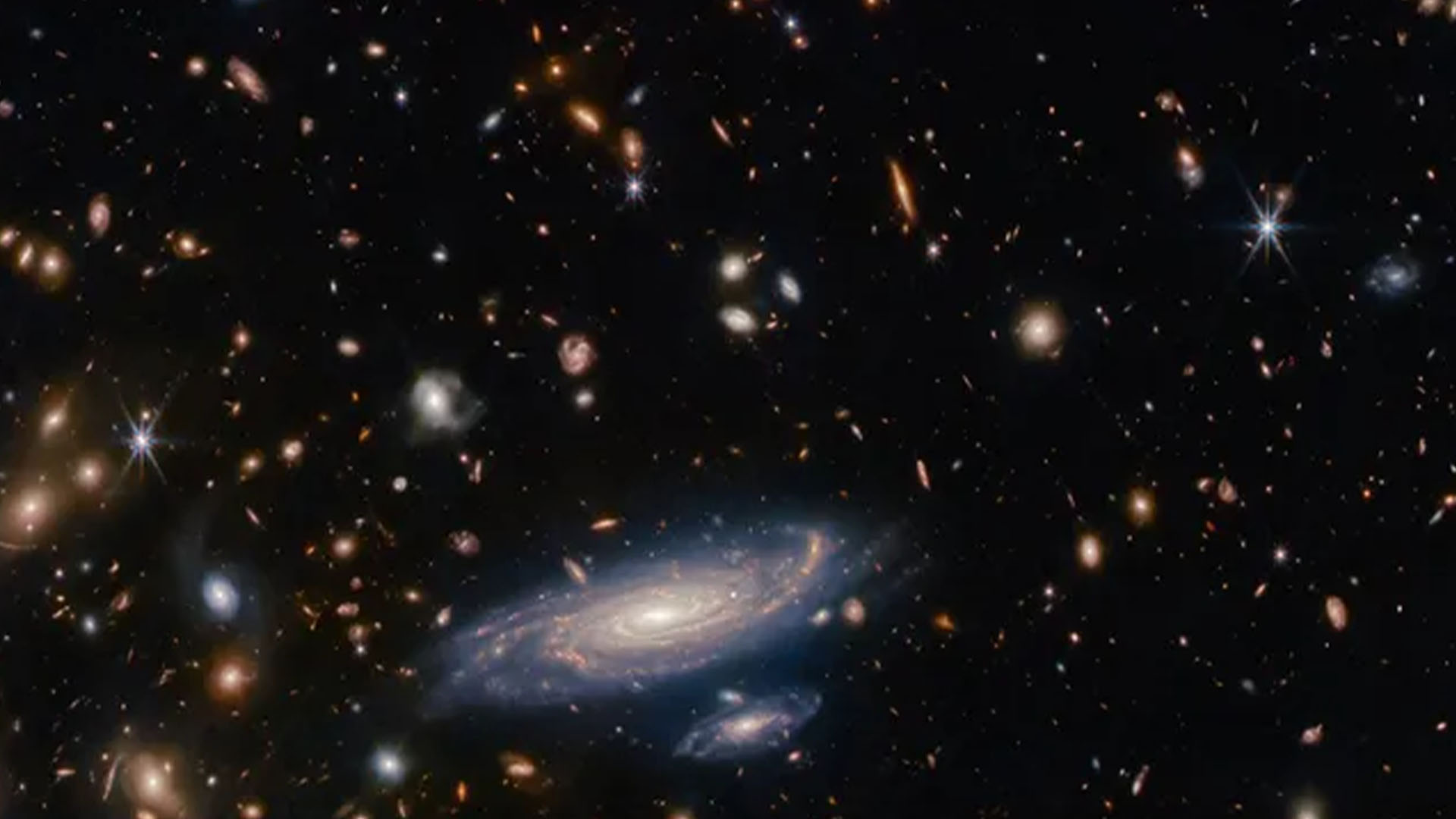
TheJames Webb telescopewas design , in part , to hound for the universe ’s first galaxies . Those galaxies are so distant from us that the expansion of the cosmos has shifted their Inner Light into the redder , or infrared portion , of the electromagnetic spectrum .
Astronomers have used the lookout to find those ancient galaxy , and what they found , time and again , were galaxies that werelarger and brilliant than we bear them to be . What ’s at interest here is our understanding of galaxy formation . The early universe is likely a much more dynamic station than we think .
Galaxies appear and acquire very quickly , within only a few hundred million year . Cosmologists do n’t realise how the unconscious process that grow galaxies could evolve so rapidly , and astronomers hope that next James Webb telescope observations will reveal the clues need to resolve that riddle .

This image shows the environment of the galaxy system ZS7 as seen by the James Webb Space Telescope. A zoomed-in look at the merging black hole system is inset in yellow.
Big black holes
JWST spot some mammoth opprobrious hole this year . In May , astronomerswitnessed two massive beasts , each weighing roughly 50 million times the mass of the sun , mid - hit when the cosmea was about 740 million years previous .
Big black hole in the former macrocosm are even grueling to excuse than big galaxy . That ’s because the only known manner pitch-dark yap conformation is through the death of massive stars , which depart behind black holes weighing up to a few multiplication the volume of the sunlight . From there , those diminutive come have to consume ring material at an astounding pace , and merge quite frequently , to reach supermassive status at such an other cosmological age .
Astronomers do n’t know what astrophysical processes can excuse how these black holes got so big so early — but JWST could also help answer that question .

This image shows the environment of the galaxy system ZS7 as seen by the James Webb Space Telescope. A zoomed-in look at the merging black hole system is inset in yellow.
Hubble tension
In the past 10 , cosmologists have lost sleep over a problem known as the Hubble tension . dissimilar method acting for estimating the present - dayexpansion rate of the universe of discourse , get laid as the Hubble rate or Hubble invariable , are returning slenderly different number .
The master difference is that measurements exact from the other universe are slightly larger than the mensuration film from the later existence . uranologist have drift hundreds of proposals to purpose the tension , from mundane measurement errors to rewrite our understanding of dark free energy .
At this clip , there is no commonly have explanation for the tension . And this year , the James Webb scope did n’t aid after substantiate that yes , Virginia , the Hubble tension is very real . So … thanks ?
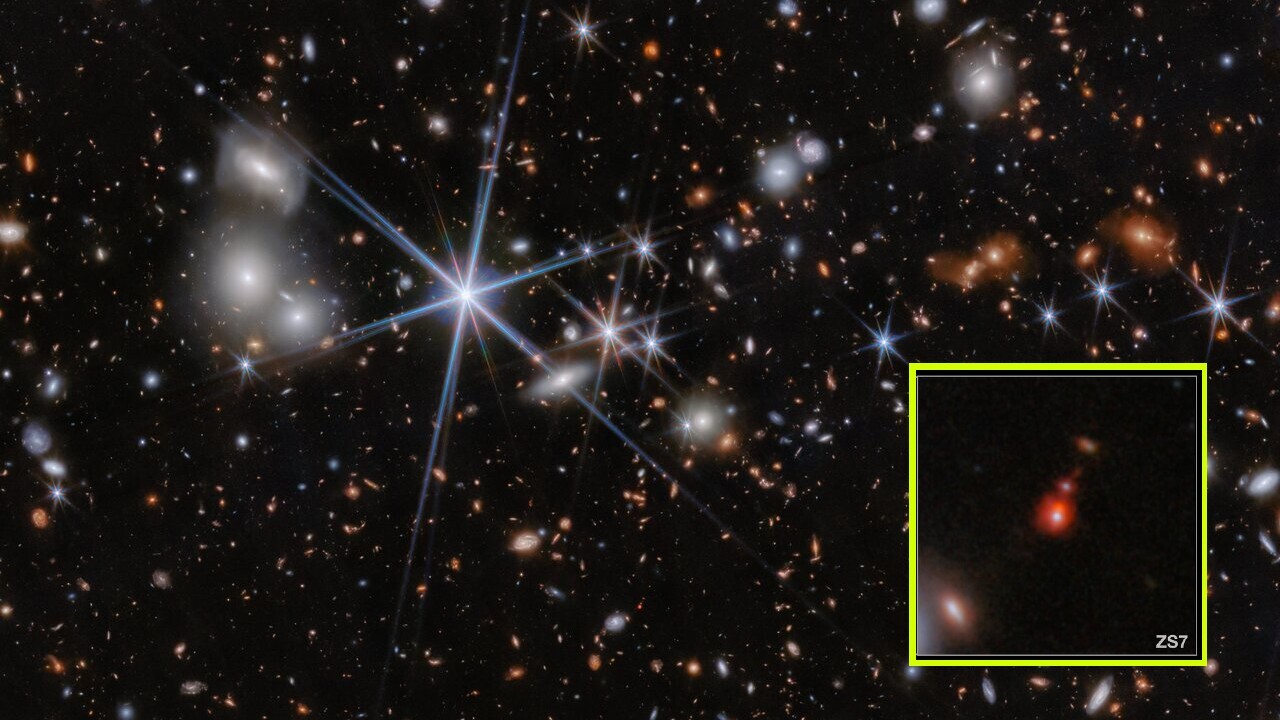

This image shows the environment of the galaxy system ZS7 as seen by the James Webb Space Telescope. A zoomed-in look at the merging black hole system is inset in yellow.
Carbon neutral
Life as we know it requires at least five key ingredients : hydrogen , oxygen , carbon paper , nitrogen and daystar . Take one away , and the canonic biochemical process that make life possible would cease . Hydrogen was forged in the first few minute of the Big Bang . The respite can only be made in the heart of stars . These ingredient only make their way into interstellar space — where they can participate in the forming of new whizz and new solar system — once those hotshot die .
A major planet like Earth , rich enough in those element to make life potential , is the mathematical product of multiple multiplication of stellar lives and deaths cross million of age . So it was a surprisal when astronomer used the James Webb telescope to see a cloud of carbon that formedjust 350 million years after the Big Bang .
This pushes the clock way back on when life could have first appeared in the cosmos . If a large amount of carbon was present in a cloud , then the other key ingredient were likely floating around as well . And all those constituent could have fashioned a major planet before the universe was even half a billion years older . We do n’t know yet if liveliness existed back then , but this discovery is a major clue that it was possible .
Illustration of the expansion of the Universe.
The First Generation
The James Webb telescope is an instrument of firsts : first galaxies , first grim holes , first building closure of life history . But the literal cosmic holy grail is to find the first stars . In the particular nomenclature of astronomy , the first generation of stars is known as Population III star . No known Population III star survive in the present - day population , and astronomers suspect that no stars from that multiplication know long .
— James Webb scope confirms we have no idea why the universe is growing the way it is
— James Webb Space Telescope smash up its own criminal record to find the earliest galaxies that ever existed
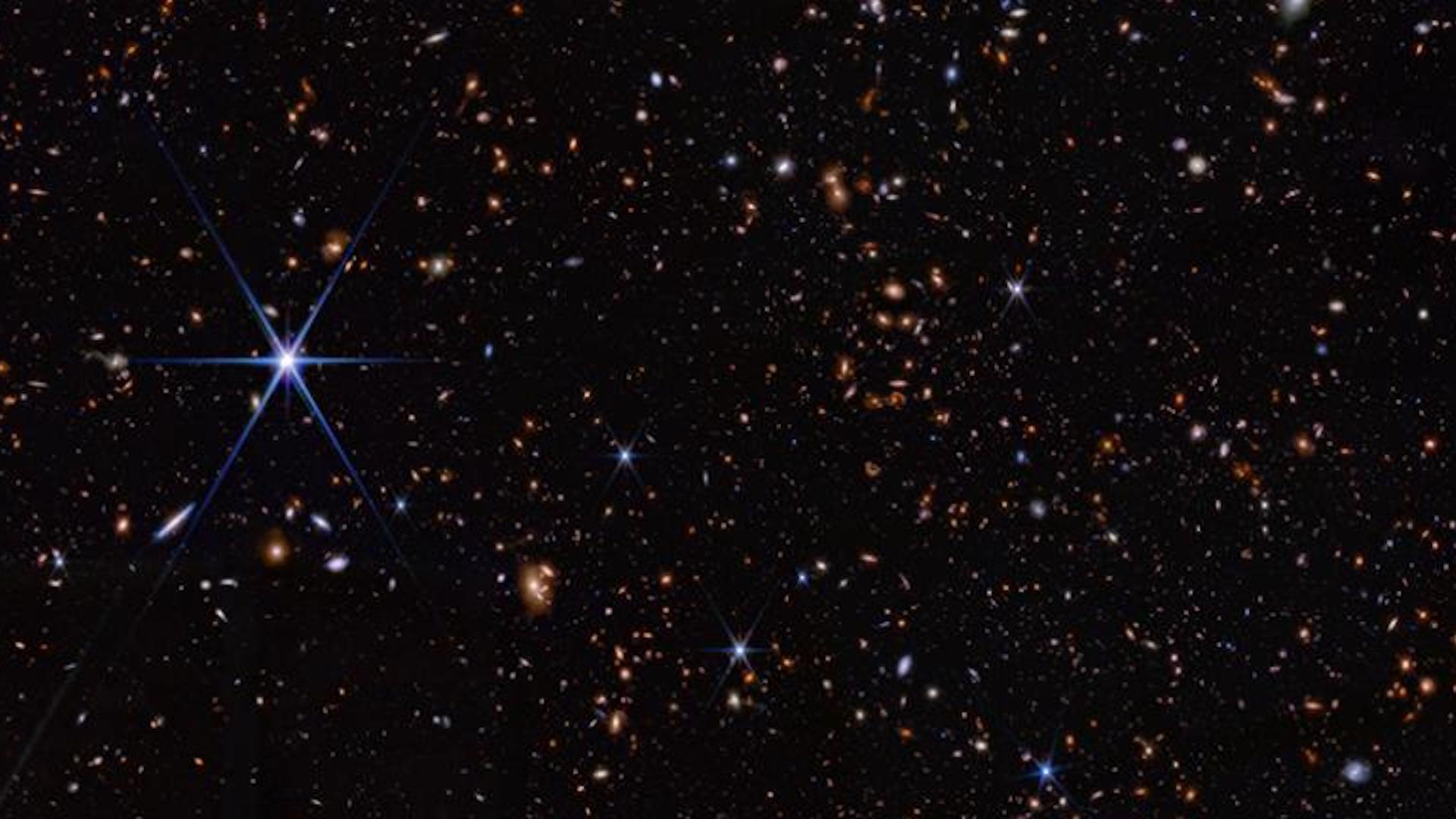

A deep field image from JWST looking back toward the early universe.
— ' Impossible ' black hole attain by the James Webb telescope may at long last have an account
Those stars would be much different than forward-looking - day populations , which need heavier elements to curb their fusion reaction . But the first generation had only primal atomic number 1 and helium to sour with . Those stars formed before even the first galaxies , and they introduced the cosmic cockcrow — the cosmos ’s first starlight .
Finding the first stars would be monumental , and this yr , astronomers may have done it . Researchers discoveredsubtle hints of Population III stars in the combine spark from galaxy GN - z11 , a Galax urceolata dwell just 430 million years after the Big Bang . Even though this Galax urceolata exist long after the show of the first stars , it may retain a remnant population of those ancient sparkler . The discovery is still provisionary , but if it defy up , it may go down in chronicle as the James Webb telescope ’s most important find .
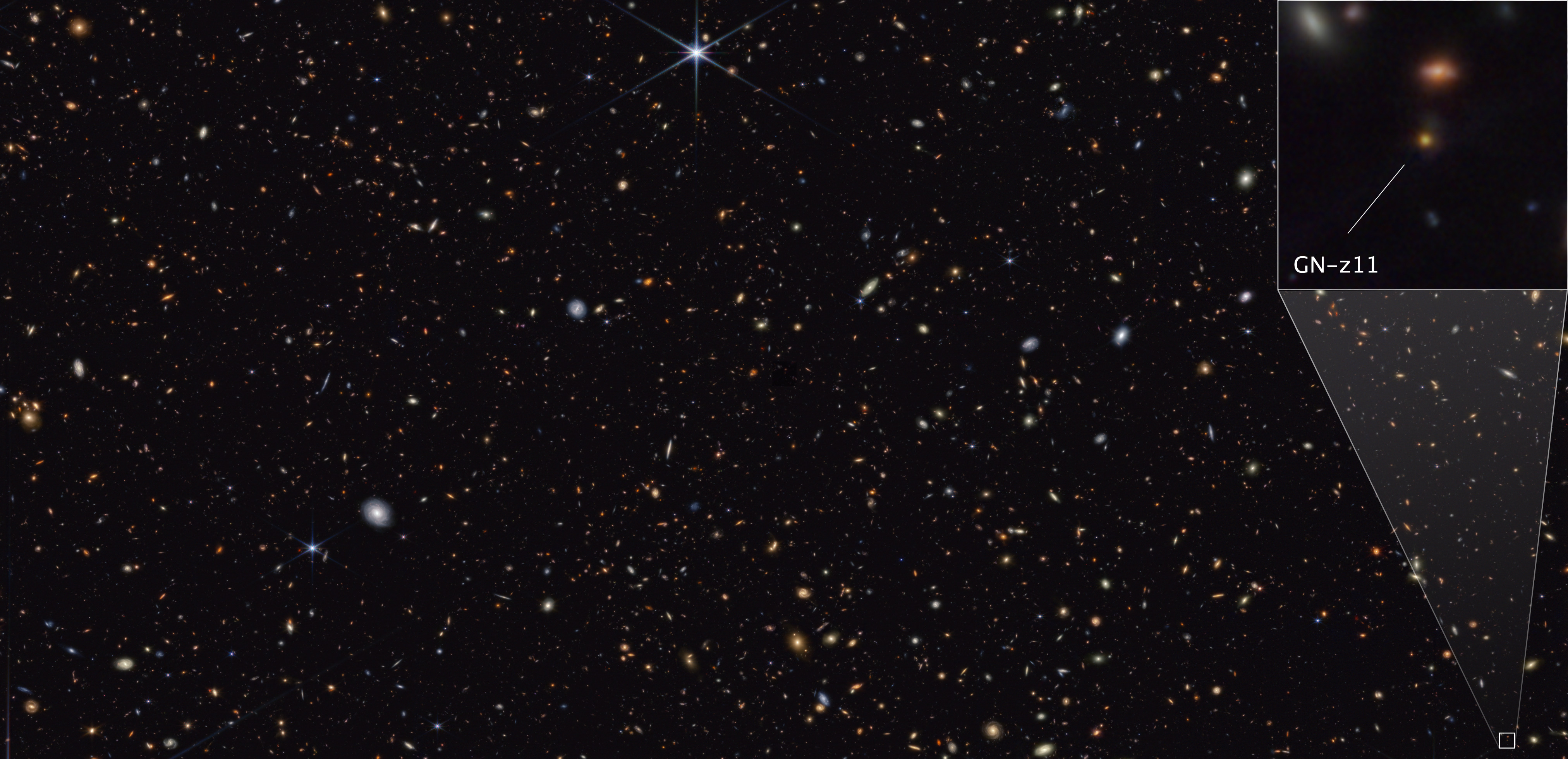

This image from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) instrument shows a portion of the GOODS-North field of galaxies. At lower right, a pullout highlights the galaxy GN-z11, which is seen at a time just 430 million years after the big bang. The image reveals an extended component, tracing the GN-z11 host galaxy, and a central source whose colors are consistent with those of an accretion disk surrounding a black hole.
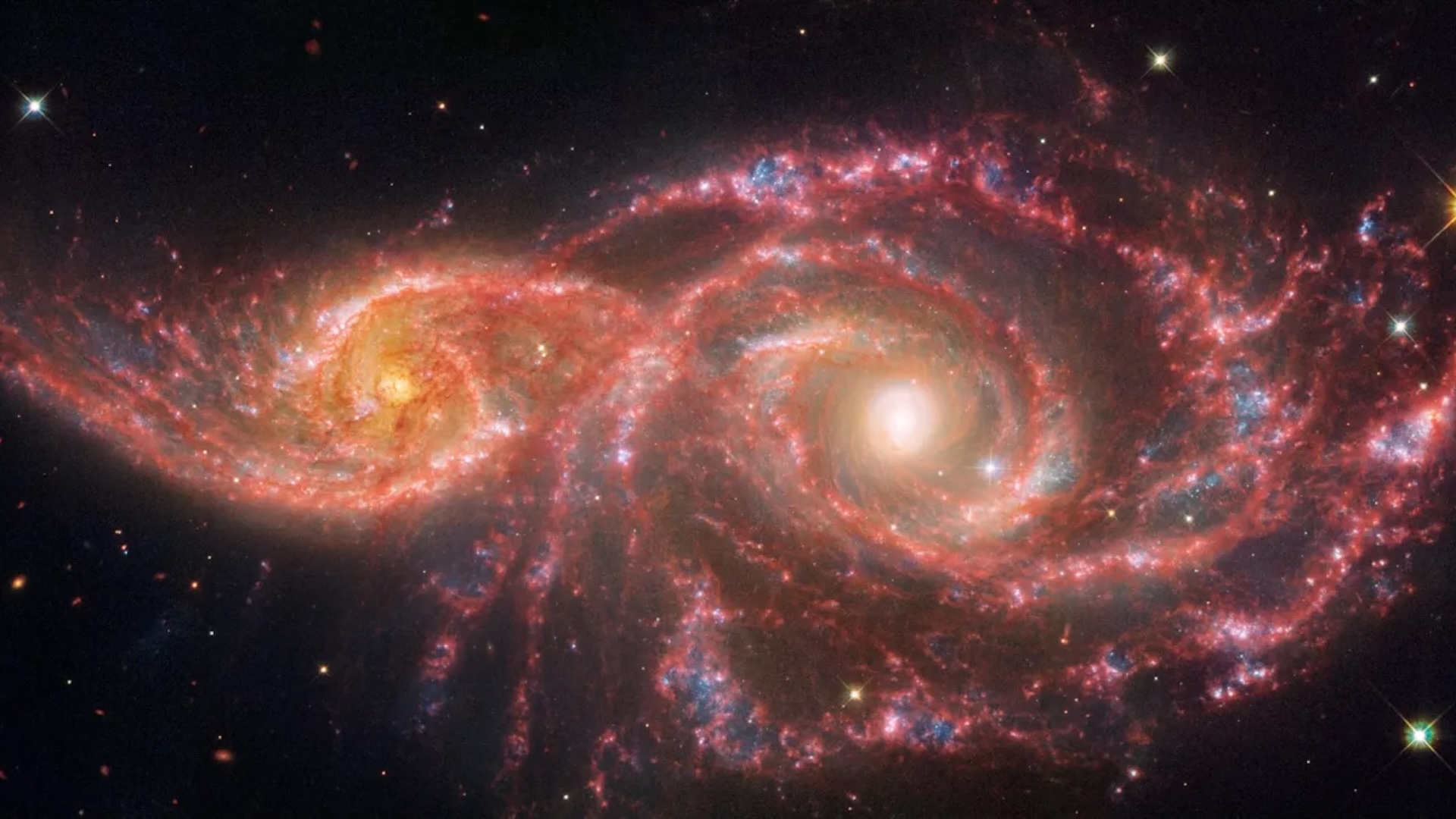
Space pic of the week : Bizarre 1 - armed spiral galaxy stuns Hubble scientist
Soviet spacecraft Kosmos 482 go down back to Earth , disappear into Indian Ocean after 53 years in range
The constant surveillance of mod life could worsen our brain function in way we do n’t fully understand , disturb studies indicate