When you buy through link on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it work .
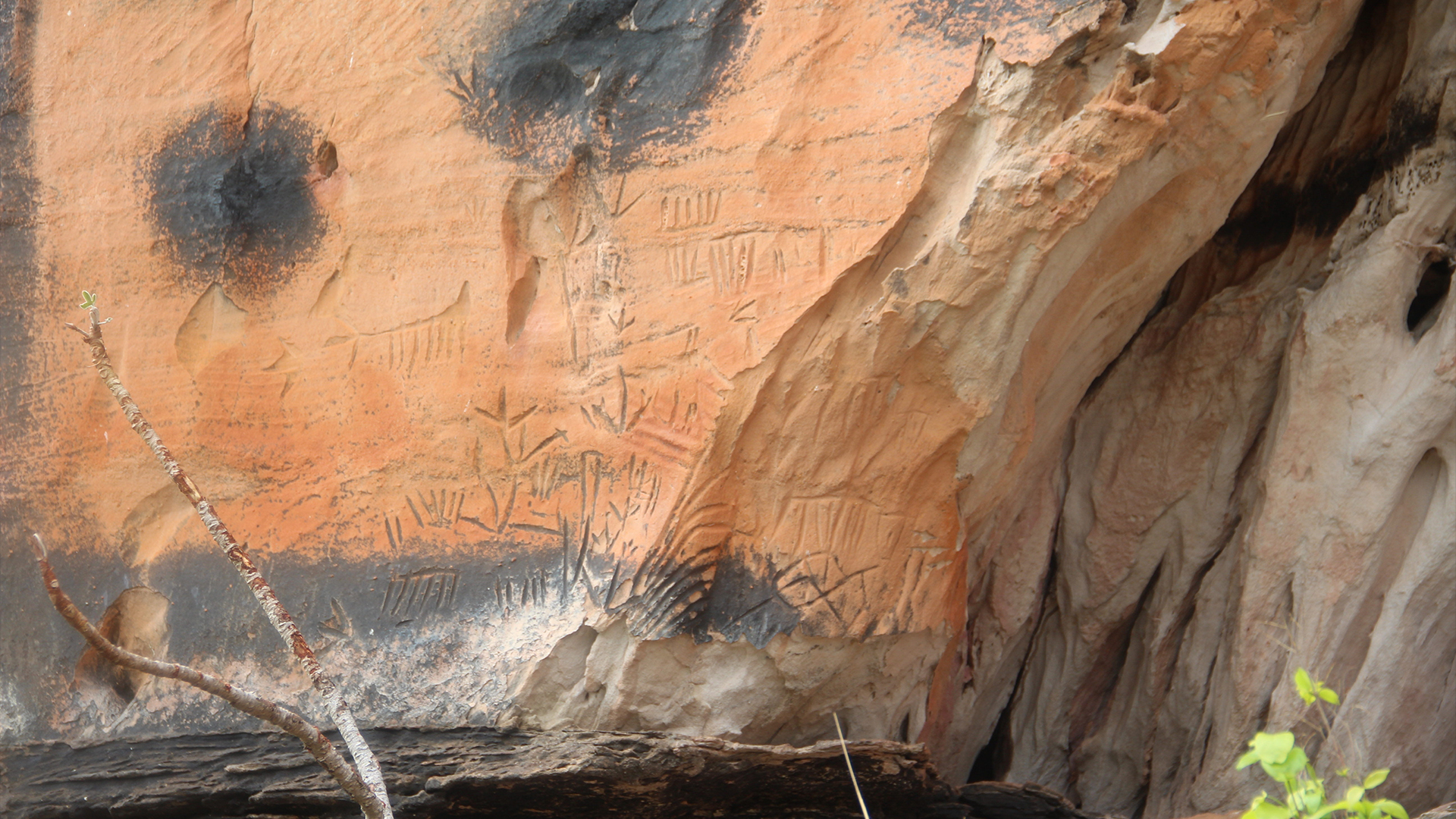
Brazilian archaeologists have strike a vast numeral of 2,000 - twelvemonth - old rock carvings that depict human footprints , heavenly - body - same figures , and theatrical performance of animals , such as deer and risky pig .
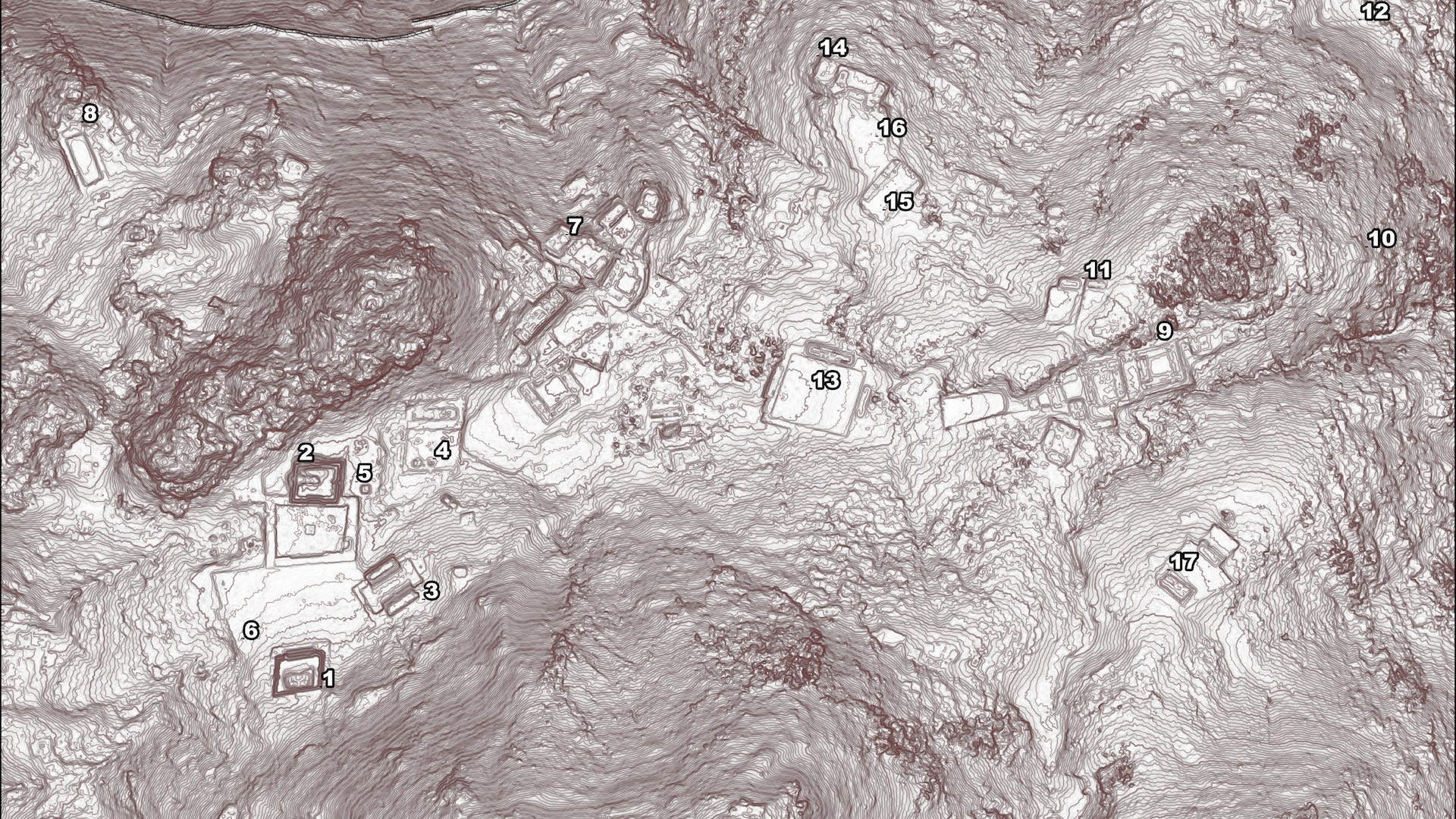
The breakthrough was made during three despatch between 2022 and 2023 in Jalapão State Park , located in the state of Tocantins . Researchers with Brazil ’s National Institute of Historic and Artistic Heritage ( IPHAN ) identified 16 precolonial archeologic site , all locate on stony cliff close to each other .

The archaeological sites are located on rocky cliffs close to each other in Brazil’s Jalapão State Park.
" This propinquity advise a possible connexion between the sites and clarifies resolution design of the ancient communities that populate the region,“Rômulo Macêdo , the archeologist who led the employment , assure Live Science via Whatsapp .
Many of the newfound sculpture are scratch symbol create by fag out rocks . The squad also discovered a fistful of cerise painting at some of the sites . " It is likely that the paintings are older than the engraving , and that they were made by another cultural group , " Macêdo said .
The rock art finding is " rare and important " because until now , archaeologists had find only rock artefact from the precolonial Indigenous peoples of Jalapão , Marcos Zimmermann , an archaeology professor at the Federal University of Tocantins in Brazil who was not regard in the recent findings , evidence Live Science via Whatsapp .

Similar rock art findings at different sites in Jalapão suggest they are linked.
The earlier ceramic artifacts and stone putz found at archeological land site in Jalapão may have been important detail for producing graphics . " The engraving were belike made using pointed stones and pieces of Sir Henry Joseph Wood , while the house painting pigments were produced from the pulverization of iron mineral very abundant in the region ; the pulverisation was then mixed with animate being or vegetal fat and applied to the rock using fingers or control stick , " Macêdo said .
relate : knockout drouth reveals more than 100 rock sculpture in Amazonian tributary that may be up to 2,000 yr old
The finding in Jalapão have yet to be amply studied . However , they have technical and thematic similarities with other archeological sites in different country of Brazil , which suggest the rock art go steady to around 2,000 years ago , harmonise to Macêdo .

Scientists estimate that the rock carvings are about 2,000 years old.
" Further analysis of rock graphics and archeologic excavations at the land site will offer new data about the means of life and spirituality of these endemic groups , " he said . The determination may also shed light on the " symbolic repertoire of precolonial populations , " Macêdo added .
Jalapão State Park cut across an country of about 13,000 square miles ( 34,000 satisfying kilometers ) and is an arid field with dunes , rivers and giant rock formations , making it suffer out among the surrounding Cerrado biome , a alone tropical savanna known for its biodiversity . It lies about 430 to 500 mile ( 700 to 800 kilometers ) in the south of the Amazon rainforest .
However , archaeological work in Jalapão has been scarce and has focused primarily on salvage archeology studies actuate by farming or infrastructural development , Zimmermann say . Some part of the res publica have yielded artifacts go steady to between 425 and 12,000 twelvemonth ago , including ceramic and arrowheads , mention Zimmermann , who also answer as the general coordinator of research at the Tocantins Archaeology Center ( NUTA ) .

— Did nontextual matter be before modern humans ? unexampled discoveries raise adult questions .
— 10,000 - year - previous burial from unnamed hunting watch - accumulator grouping discovered in Brazil
— old deoxyribonucleic acid grounds of syphilis relative name in 2,000 - year - quondam skeleton in Brazil

Despite the implication of these discovery , the parkland front threats such as erosion , vandalism anddeforestation . IPHAN hasannouncedplans to collaborate with research institutions to develop projects to maintain and circulate the part ’s archaeological heritage . " Sandstone , along with environmental gene like wind and sun , demean rock painting , " Zimmermann said .