When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Scientists have make a mega - database revealing how half a million different desoxyribonucleic acid mutations render errors in protein in humankind . The researchers desire that the database will be used to develop fresh , personalized drug that directly revoke the mutation ' effect .
The human genome transport instructions forat least 20,000 proteins , which are essentialfor nearly all physiological processes . Each building cube of a protein — send for an amino group acid — is key to its function , and thus , swapping around the aminic back breaker can essentially break a protein . " Missense " mutations — alteration in aDNAsequence that swap one amino group acid for another — innearly 5,000 human proteinsare known to cause genetic diseases , such asHuntington ’s diseaseandcystic fibrosis .
For the first time, scientists have created a database that details how hundreds of thousands of genetic mutations disrupt the function of proteins, leading to disease.
However , in many cases , it ’s not totally absolved how these mutant affect the social system and function of protein and thus make disease . Without this sympathy , it is tricky to formulate direct treatments for genetic disorders without altering the genome itself , according to the authors of a new study published Jan. 8 in the journalNature .
" Depending on what is occur to the protein , if you were to design a drug to seek to fix the disease , then the attack would be completely different reckon on the individual variation that you are considering,“Antoni Beltran , track study author and a postdoctoral researcher at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Spain , told Live Science .
Related:2024 Nobel Prize in chemistry award to scientists who reveal a ' completely raw world of protein structures '
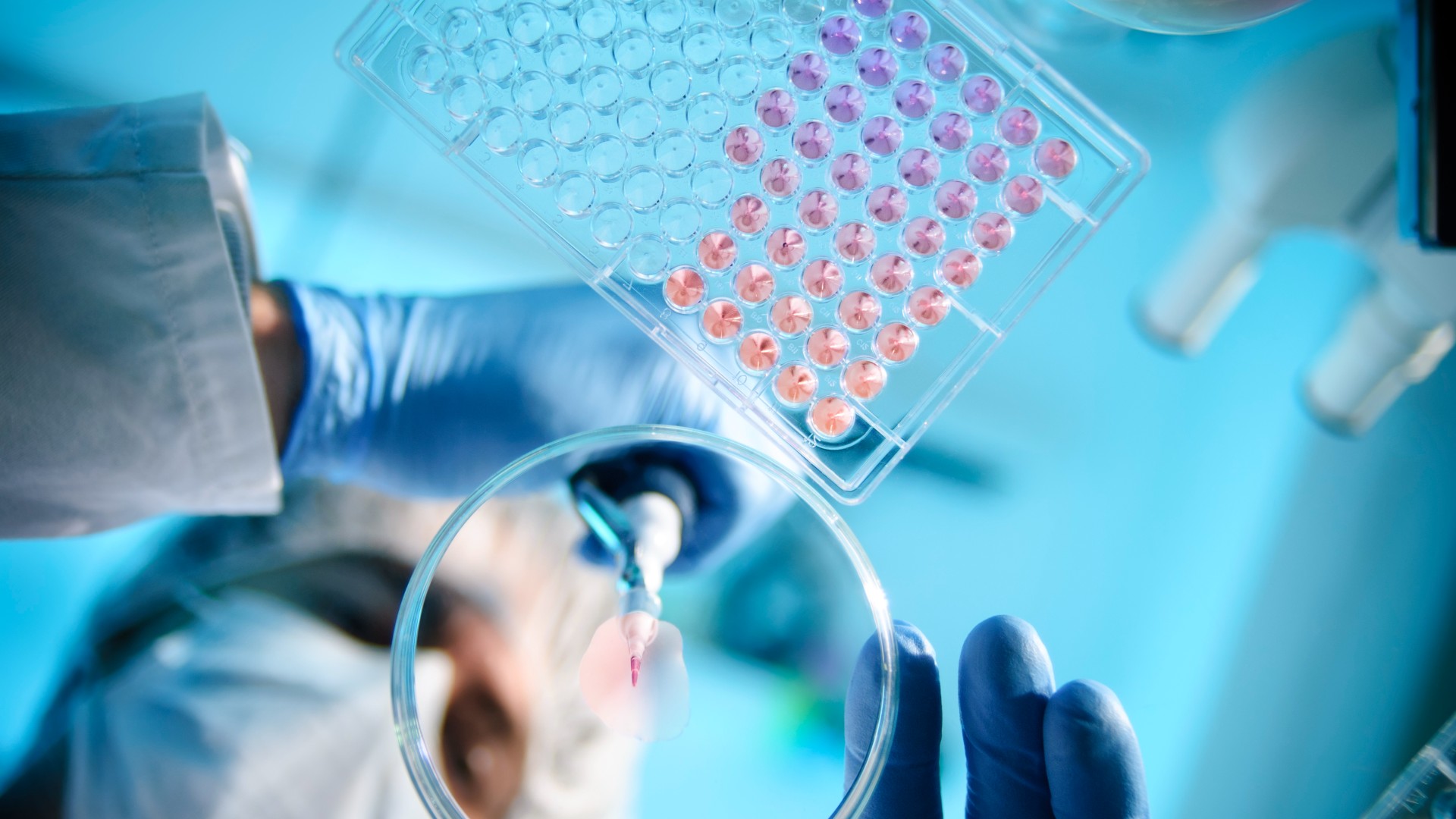

The team who created the database hope that it will one day be used to develop personalized treatments for genetic diseases
To harness this yield , Beltran and co-worker create an enormous database that catalogs the force of more than 500,000 missense mutations on the constancy of 522 protein " domains , " meaning the regions of proteins that are cardinal to their function . They call the database a human " domainome , " and they built it by consistently activate sport in protein in the science laboratory . They then channelize the mutants into yeast cellphone and monitored the effects .
In the newfangled study , the squad especially home in on 621 missense mutations from the database that were already sleep with to cause diseases in humans . They find that 60 % of these mutation made affected protein less stable . precarious proteins aremore probable to misfold or denature ; like origami , proteins must be fold a peculiar means to reach their intend conformation . Misfolded protein can pile up within cells , potentially causing damage , or simplybe degradedby the trunk , lead the cells unable to function .
For instance , the inherited form of cataract — an middle disease that clouds the lens system of theeye — is activate by mutations in genes forbeta - crystallinproteins , which normally maintain the genus Lens ’s transparency . In the Modern study , Beltran and colleagues get wind that 72 % of these mutations destabilize the crystallin proteins , increasing the odds that they cluster together and spring turbid areas in the lens .

Rather than causing instability , some missense mutations result to different changes in proteins . For example , some of the mutations behindRett syndrome , a rarified neurodevelopmental disorder , preventa specific proteinfrom bind to DNA . This process would normally activate the protein to deform genes on and off in thebrain , but in the syndrome , this goes lopsided .
— DeepMind say it can call the shape of every protein in the human soundbox
— AI system solves 50 - year - old protein folding trouble in hr
— 13 protein tied to brain aging seem to spike at ages 57 , 70 and 78
Although the first and full-grown database of its form , so far , it covers only 2.5 % of known human proteins , so more work is needed to expand it , Beltran acknowledged . More enquiry will also be necessitate to determine if the effects figure in isolated domain also show up in full - size protein .
The team ’s ultimate end is to build a database that ’s utilitarian for forebode the effect of any mutation on protein constancy , Beltran order . Such a tool could theoretically enable scientists to originate good drug for hereditary diseases that target the mistake in proteins that tug the conditions .