When you buy through link on our site , we may make an affiliate delegacy . Here ’s how it works .
The first ever image of the supermassive opprobrious hole at the center of theMilky Waymay not be as precise as it ab initio seemed , a new study claims .
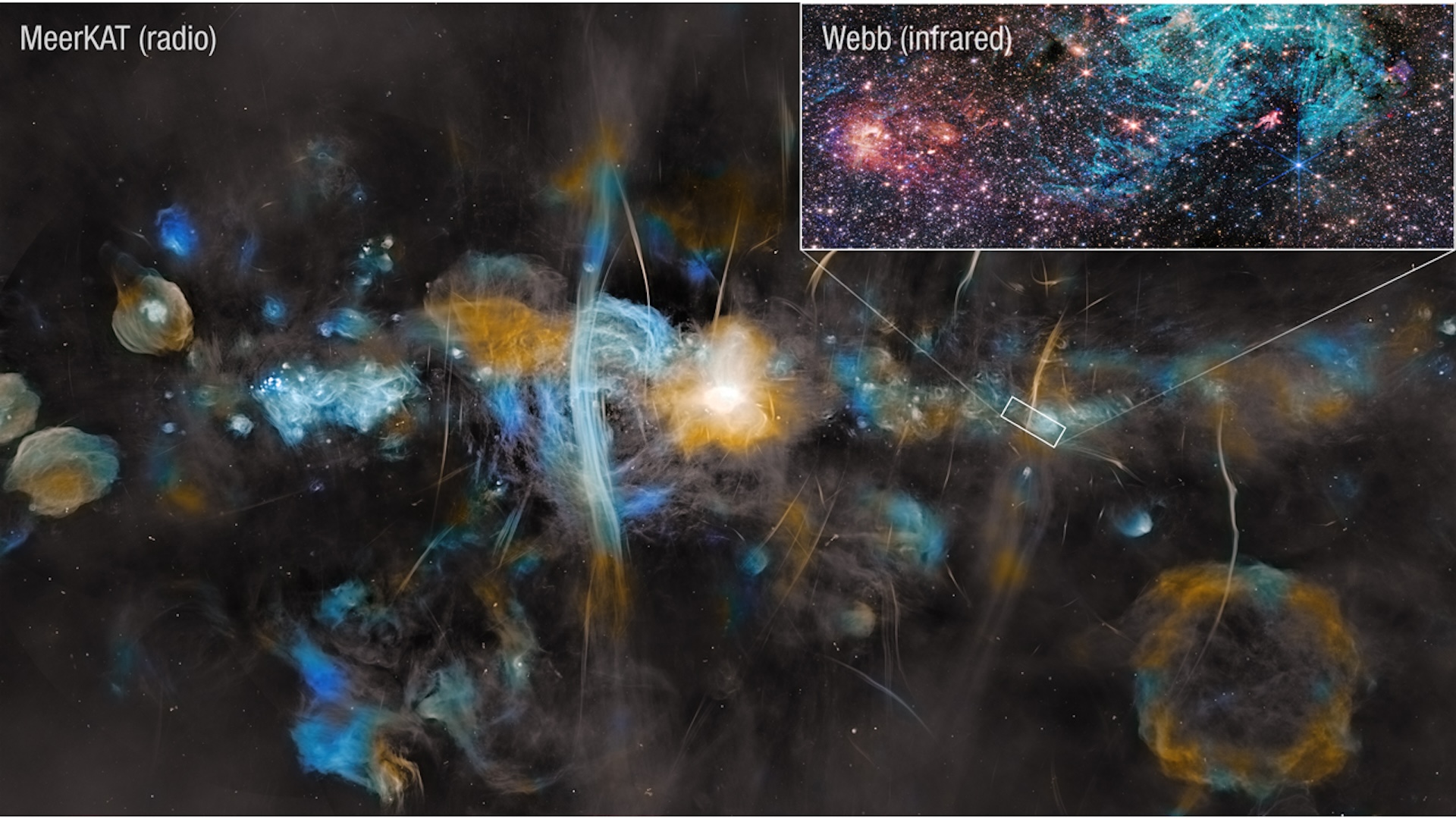
situate 26,000 light - class from Earth , Sagittarius A * is a giant snag in outer space - sentence that is 4.3 million time the mass of our sun . The groundbreaking image of the mordant hole , which was free in 2022 , was captured by the Event Horizon Telescope ( EHT ) , a internet of eight synchronized radio telescopes locate in various spots around the world .
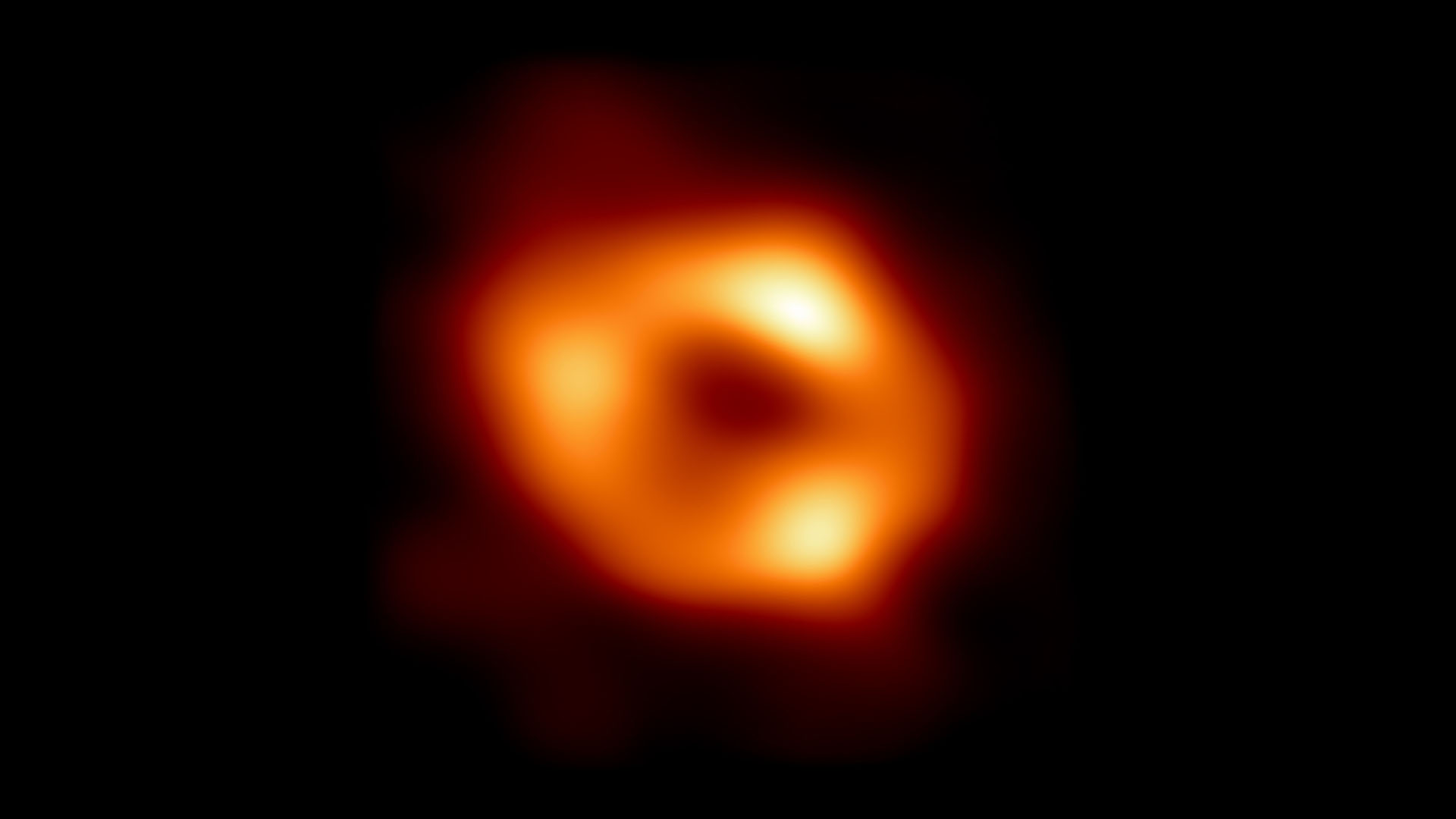

The image of Sagittarius A, the black hole at the heart of the Milky Way, captured by the Event Horizon Telescope.*
But the orange , doughnut - shaped doughnut of gas surrounding the galaxy could be distorted due to the way the data was sew together together . allot to raw research , release in the November issue ofMonthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , the pack is actually more stretch than it appear in the notable range of a function .
" Our [ revised ] prototype is slenderly elongated in the east - west direction , and the easterly half is bright than the western one-half , " discipline lead authorMiyoshi Makoto , an uranologist at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan ( NAOJ),said in a financial statement . " We conjecture that the ring epitome resulted from errors during EHT ’s imaging analytic thinking and that part of it was an artifact , rather than the factual astronomical structure . "
relate : inadvertent discovery of 1st - ever ' black hole triplex ' system challenges what we recognise about how singularities form
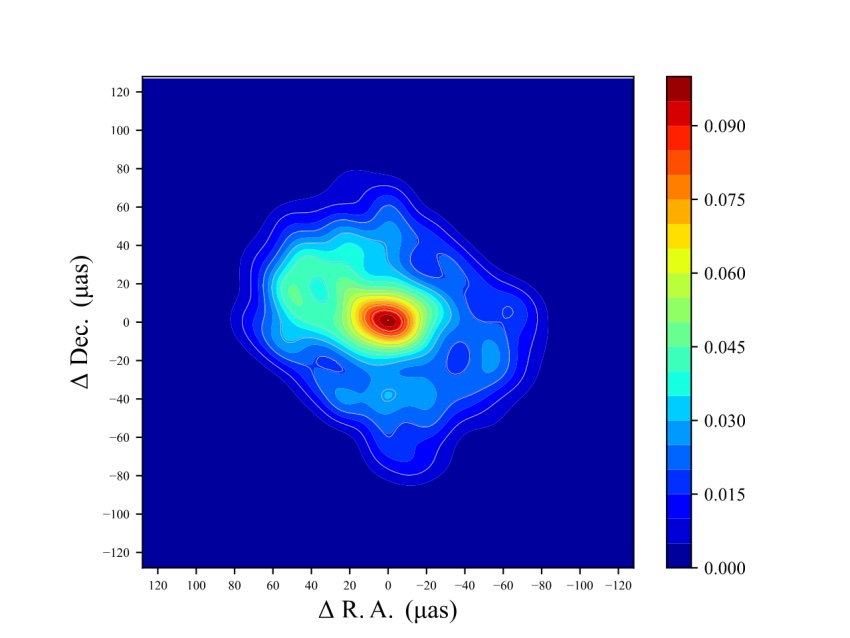
The team’s re-analysis of the Event Horizon Telescope data suggests the accretion disk around the Milky Way’s black hole should be more elongated from east to west
The EHT captured the image , as well as an prototype of the supermassive black hole at the center of the M87 galaxy , in 2017 . Theimage of the M87 black holewas discharge in 2019 , but it took two more years of data psychoanalysis before the Milky Way one was ready .
The imaging appendage was time - eat for a number of reasons . Firstly , plasm whiplash around the smutty hole ’s accretion disc at a singular speeding , learn bare minutes to make a complete ambit . Earth ’s location at the edge of the Milky Way also think of the researchers had to use a supercomputer to separate out out interference from the immense number of stars , gas and detritus clouds strew between our planet and Sagittarius A * .
— Some black kettle of fish have a ' heartbeat ' — and astronomers may finally know why

— A ' primordial ' black hole may zoom through our solar system every decade
— scientist may have finally solved the problem of the cosmos ’s ' missing ' black hole
To appropriate the figure of speech , the EHT bring readings from its radio telescope dot around the globe , then stitched the information together to construct the final image . But this puzzler piece approach could have leave noticeable gaps in the data .

To see to it the look-alike , the NAOJ astronomer give what they called " widely - used traditional " analytic thinking methods , make event that show the disk was more squished along its central axis than it appear in the original image .
The EHT squad has yet to notice on the novel findings , and it remains unclear which view of the disc is the most exact . The researchers behind the new study hope their finding will call forth a hefty discussion from which a more authentic picture of our galaxy ’s gargantuan black hole will come forth .












