When you buy through connection on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
autochthonous the great unwashed enter North America at least four times between 12,000 and 24,000 years ago , work their languages with them , a raw linguistic model show . The model correlates with archaeological , climatological and genetic data , plunk for the idea that population in other North America were dynamic and diverse .
Nearlyhalf of the globe ’s language family are find oneself in the Americas . Although many of them are now intend out , diachronic philology psychoanalysis can surveil and compare living languages and trace them back in time to better realize the groups that first populated the continent .

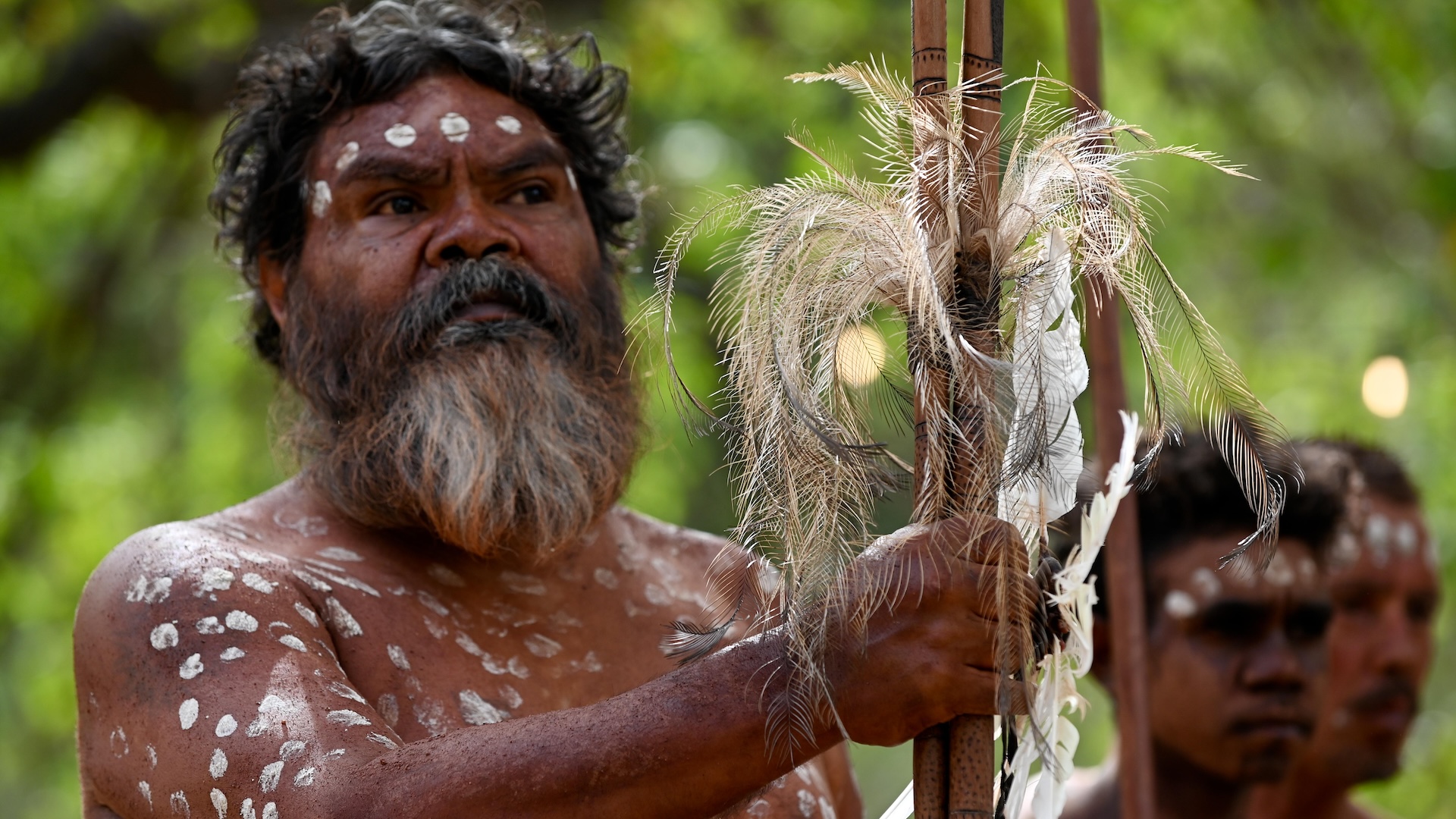
Indigenous Americans, illustrated here during a mammoth hunt, developed their diverse languages from 4 different population waves that came over from Siberia, a new study suggests.
In a study published March 30 in theAmerican Journal of Biological Anthropology , Johanna Nichols , a historical linguistic scientist at the University of California Berkeley , analyze structural features of 60 speech communication from across the U.S. and Canada , which revealed they come from two main language groups that entered North America in at least four distinct waves .
pertain : The first Americans are n’t who we thought they were
Nichols survey 16 features of these languages , including syllable structure , the grammatical gender of nouns and the direction consonants are produced when speaking . The languages split into two main groups : an other one where the first - person pronoun has an " n " sound while the second - soul pronoun has an " m " sound , and a previous group with languages that contain a sentence ’s Charles Frederick Worth of information in just one intelligence .
Further linguistic analysis indicated that mass arrived in the Americas in four trenchant waves . The first occurred around 24,000 years ago , when monumental glaciers cross much of North America . Nichols found no singular language feature article , suggesting a divers set of people and speech infix North America at that time . A second wave of people around 15,000 years ago play lyric with n - m pronoun , while a third wave 1,000 years later brought speech communication with simple consonants . A quaternary wave around 12,000 years ago then brought complex consonant .
Until relatively recently , researchers take for granted that Indigenous multitude first arrived in the Americas via a land bridgework from Siberia around 13,000 years ago . But Nichols’previous studyof the lingual data convinced her that this was not enough time for the well-nigh 200 autochthonous American languages to develop : alternatively , she proposed citizenry first go far nigher to 35,000 years ago .
A growing body ofarchaeological , geological and climatologicalandgeneticresearch has since pushed back the particular date of the earliest American arrival , with a new consensus that , sometime between30,000and 25,000 years ago , several undulation of citizenry made their means into the Americas .

Adding linguistic study to this work think of that " the four William Claude Dukenfield confirm each other , " Nichols articulate . " Now I think the interpretation is very solid . "
Andrew Cowell , a linguistic anthropologist at the University of Colorado Boulder who was not involved in the study , separate Live Science in an e-mail that Nichols ' study is interesting because " the language data reinforces growing recognition in other fields that North America was populated much earlier than was take over for many decades . "
Cowell noted , however , that the study ’s statistical psychoanalysis shows that two languages , " Yurok and Arapaho are classed quite otherwise , yet the two voice communication are known to be genetically associate as part of the Algic language super - family unit . " ( Yurok was spoken in far - Northern California , while Arapaho is spoken in Wyoming and Oklahoma . )

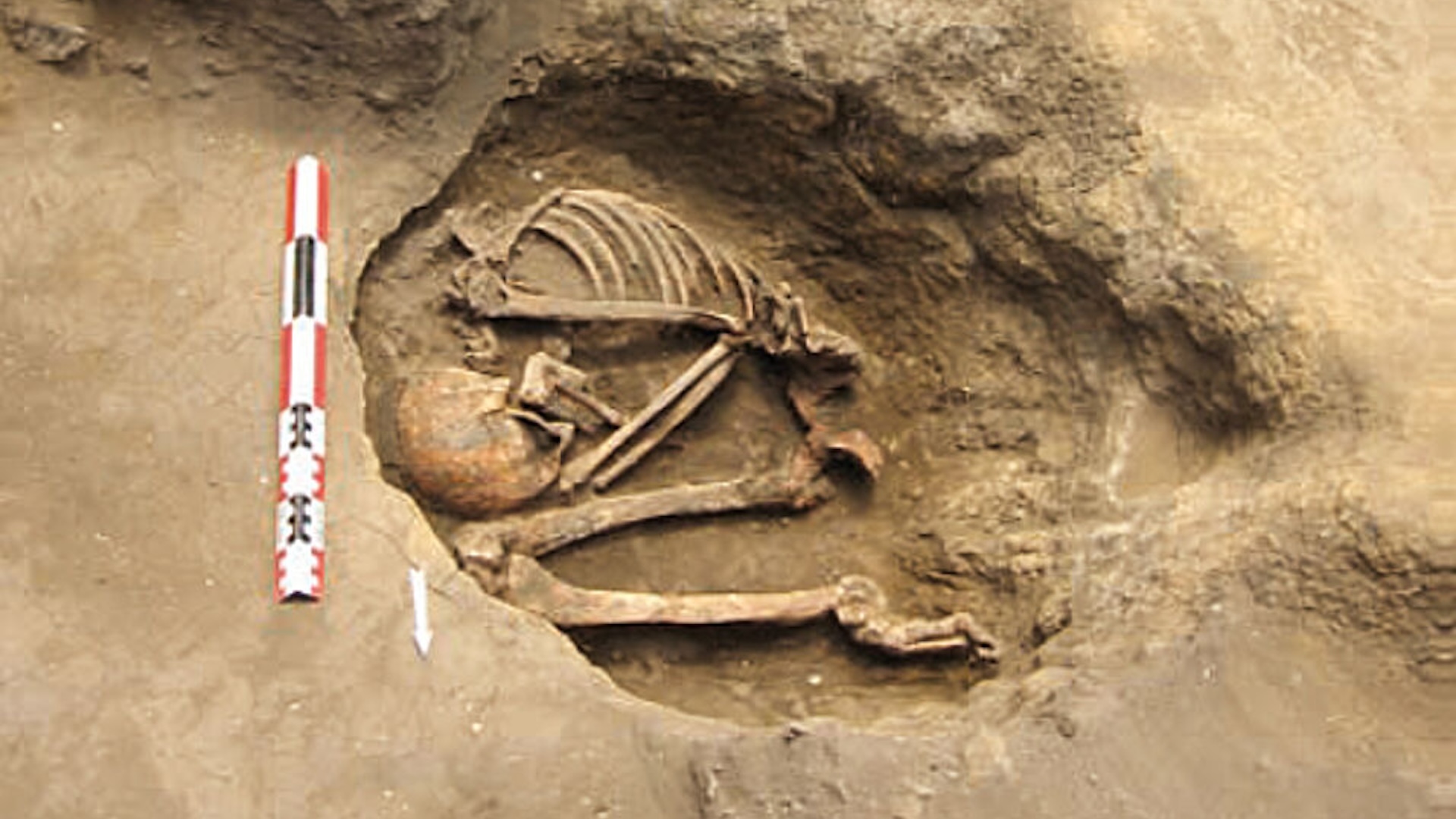
— Debate settled ? sometime human footprints in North America really are 23,000 twelvemonth previous , study discover
— The oldest archaeological website in the Americas
— The 1st Americans may have arrived by a ocean chalk ' highway '

— Ancient endemic linage of Blackfoot Confederacy conk back 18,000 years to last crank eld , DNA reveals
Additionally , oral communication can be heavy influenced by their neighbors , which can obscure how they were to begin with related , Cowell say .
While this unexampled survey presents a model for how languages enter andevolvedwithin North America , it does not speak to their origins , which are still nameless .

" It ’s likely that the people who prompt into North America left relation in Asia , " Nichols said , " and possible that some of those languages survive and have remained in Siberia . "
But the limits of the linguistic comparative method acting have in mind that we may never know for sure , Nichols said .










