When you purchase through link on our site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Perhaps the most mysterious electronic organ in the body , the braincontinues to astonish scientist despite the innumerous hours they ’ve spent set about to decipher its interior workings . Each young find about the brainpower brings a thousand new question in its wake .
Here are 18 thing we learned about the mastermind in 2023 that blew our mind .
2023 brought us dozens of new discoveries about the brain.
Related : Do we really practice only 10 % of our learning ability ?
1. Newly discovered part of the brain
In January , scientists described their discovery ofa kind of buckler in the brainthat helps clear away waste matter and act as a look - out stake for immune cells . The flimsy shield seems to help operate the flow of proteins and molecules between different compartment containing cerebrospinal fluid , a colorless liquid that run around the mind and within pipe through the harmonium .
2. Squid and human brains tied by evolution
Despite the 500 million years ofevolutionthat separate squids and human being , ourbrains develop in a very similar wayto the brains of these cephalopod mollusk . Scientists unwrap this by monitoring stem cadre called neural progenitor cubicle in developing squid conceptus . To establish a squid retina , where most of the animal ’s neural tissue is found , the cells must first organize a farseeing , densely packed structure that can also be spotted during the neural development of vertebrates like us .
3. ‘Junk DNA’ and big brains
The factor that enabled humans to grow notably bad brain may haveoriginally come from " junk DNA,“which does n’t code for any proteins , researchers uncover early this yr . At some point in time in human evolution , after we split from other primate , some of this junk DNA picked up the power to encode proteins . In animal and laboratory - dish experiments , several of these genes appeared key for boost brain maturation .
4. Injuries plugged with minibrains
Scientists usedcerebral organoids — miniature 3D exemplar of the brain — to repair brain injuries in blackleg . The organoids were grow from human stalk cells and transfer into rats ' visual cortex , the region of the mentality where info from the eyes is ab initio processed . The researchers go for to finally apply the technique in humans , but that ’s many years away .
5. Native language wires the brain
A person ’s native spoken communication may work how their brain unite up info - processing hubs within its social system , accord to astudy of people whose aboriginal languages were German and Arabicpublished in February . Differences in the study participant ' brains were chalk up to linguistic divergence between the language . However , more work is needed to uncover how cultural features of conversation might regulate brain structure .
6. Psychedelics invade brain cells
Psychedelics have shown promise as therapy for hard - to - dainty Great Depression , and now scientists recall it may bebecause they invade brain cells . Psychedelics , such as LSD , DMT and psilocin , can bond to receptors for the chemical substance messenger serotonin — but significantly , they can latch onto these receptors on the outside and interior of cells . Theoretically , this have in mind psychedelics might flip switches that traditional antidepressant , which generally increase the concentration of serotonin outside the cells , ca n’t reach . That may be why trippy drugs drive encephalon cells toward building new connexion .
7. Never-before-seen brain wave
Octopuses sire a type of brain wavenot seen in any other creature , even humanity . These long - persistent , outstandingly dull brain wave were memorialize using electrodes implanted in freely moving octopuses ' brains . Scientists are n’t yet certain what function these unique waves wait on , or if they ’re tied to a specific behavior .
8. Short-circuiting chronic pain
The psyche of hoi polloi with chronic painshow fluctuating convention of activitythat can be tied to the immanent experience of their pain , researchers have discovered . decipher these patterns could someday enable doctors to disrupt them with targeted therapy , thus shortsighted - circuit patients ' pain .
9. Brain surgery in the womb
In a first - of - its - kind surgical operation , doctorsrepaired a malformed line of descent vessel in a fetus ' brainprior to birth . The malformation occurs in an guess 1 in 60,000 nascency and is usually process after birthing , when it can sometimes be too recent to prevent damage or death . In March , doctors successfully treated the malformation sooner , in the uterus .
10. Life flashing before your eyes?
People ’s brains generate a fuss of activity in their last minutes of life , scientists revealed in May , andthis electric surge may reflect witting experiences — however , that ’s just a theory . It could be that this body process erupt as people " move toward the light " or see their " lives flashing before their centre , " as portray in many motion-picture show . Or , it could also just be " aberrant electrophysiological activity , " some experts say .
11. Mystery brain spiral signals
Spiral signal uncovered in the human brainmay help organise the organ ’s complex activeness . The spirals are mental capacity wave that go past over the surface of the brain and rotate around key points . These spirals may act as bridges of communication between dissimilar regions of the brain , scientists theorized in June .
12. Sex switch in mouse brains
Scientists discovered an " on switch " for libidoin the male mouse brain — and they think a similar control pith may exist in humans , although they have n’t found such circuitry yet . Flipping the switch drove manful mice to match with females and with inanimate object , and also trim the interruption time take between round of sex . As of now , no tantamount circuit has been found in distaff mice .
13. Pink Floyd in brain waves
In August , scientists revealed they were able-bodied to " read " people ’s brain waves andrecreate Pink Floyd ’s famous " Another Brick in the Wall,“which the volunteers had listened to during their brain recording . Some song snippets generated by the researchers really did audio like the 1979 protestation song — other snipping , however , sound much muddier .
14. A ‘tell’ for false memories
Your brain ’s natural action shift in a clear-cut way whenyou’re about to recall a false memory , or one in which the upshot never really pass . This " distinguish " specifically crops up in the hippocampus , a central brain region for store , scientist recently identify .
15. Brain changes across menstrual cycle
The brain ’s structuregoes through elusive changes throughout a individual ’s catamenial cycle . These change appear in the microstructure of the Einstein ’s white matter — the insulated wires that carry between brain cells — as well as the thickness of its gray subject , the trunk of head cell . For now , it ’s obscure whether these learning ability changes affect knowledge or the risk of mastermind diseases . But the research could launch the door to such find in the future .
16. Complete insect brain map
Thefirst - ever complete mathematical function of an worm ’s braincontains 3,016 neurons . The fruit fly psyche atlas , fill in over 12 years and finally unwrap in June , show all the physical connections between the thousands of cellular telephone . It could facilitate pave the way for more - in advance contrived intelligence agency ( AI ) systems and help scientist decipher standardized structures in the human brain .
17. Most-complete human brain map ever
This year , scientist unveiled themost elaborated atlas of the human brain ever conceivedwhich details the arrangement of 3,300 types of brain cell , few of which were previously known to science . The atlas is half composed of neurons — the brain cellphone that pass on through chemical and electric messages — and one-half made up of non - neural cells .
18. Minibrain plugged into AI
— How many calories can the brain burn by suppose ?
— Consciousness ca n’t be explain by brain alchemy alone , one philosopher argue
— Can judgment prevail when they are ignore off from the world ?
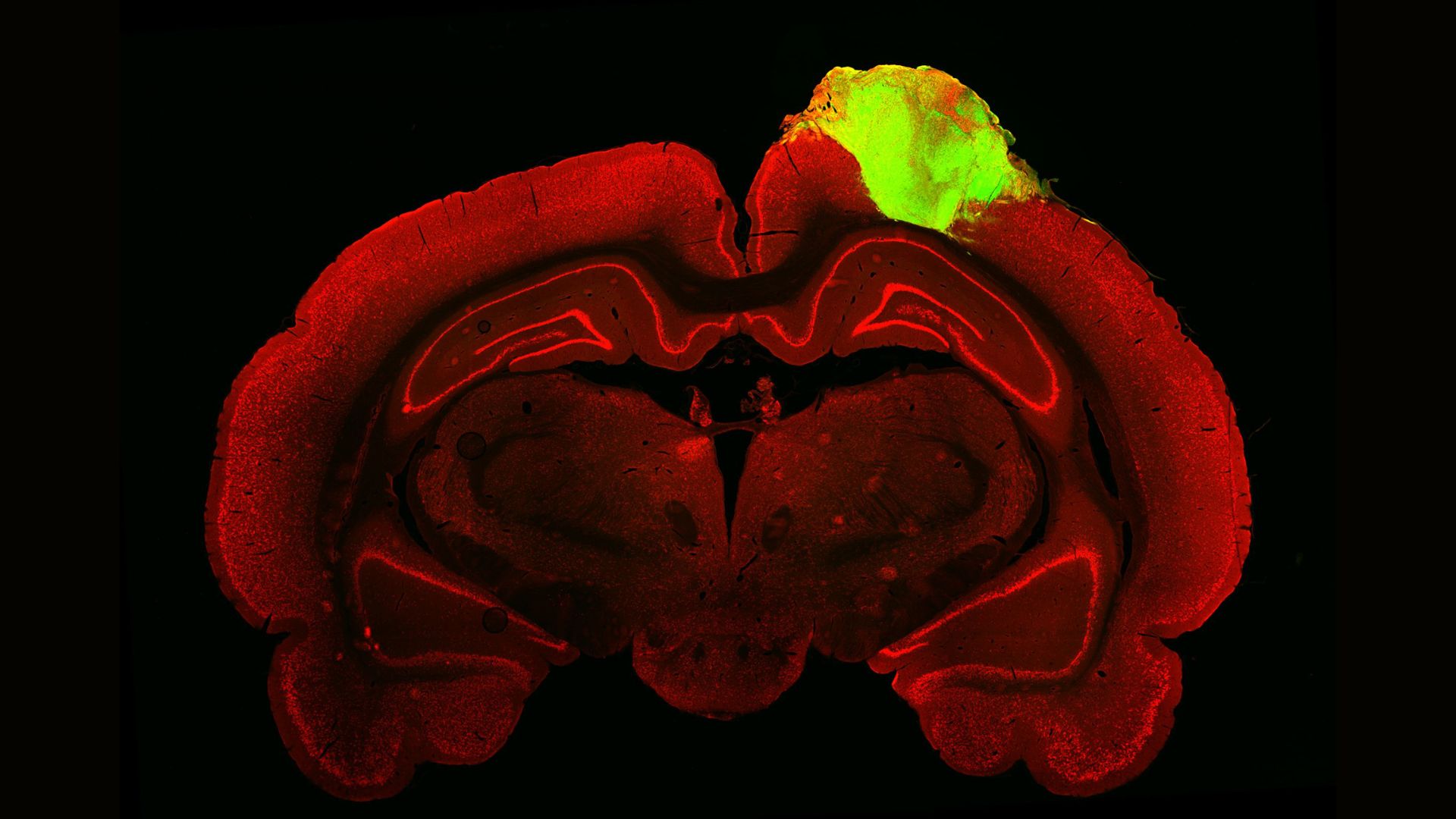
Scientists transplanted an organized clump of human brain cells, or organoid (green), onto this rat’s brain, shown here as a cross section.
For the first time , scientistsplugged a brain organoid into the middle of an AI systemand used the intercrossed computer to perform undertaking and reckoning . The experimentation could help pave the way for biocomputers that borrow joke from biology to become more energy efficient than standard information processing system .
Ever wonder whysome people build brawniness more easy than othersorwhy freckle do out in the sun ? Send us your questions about how the human dead body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your dubiousness answered on the website !
root to ' cocktail party job ' could assist people with listen personnel casualty
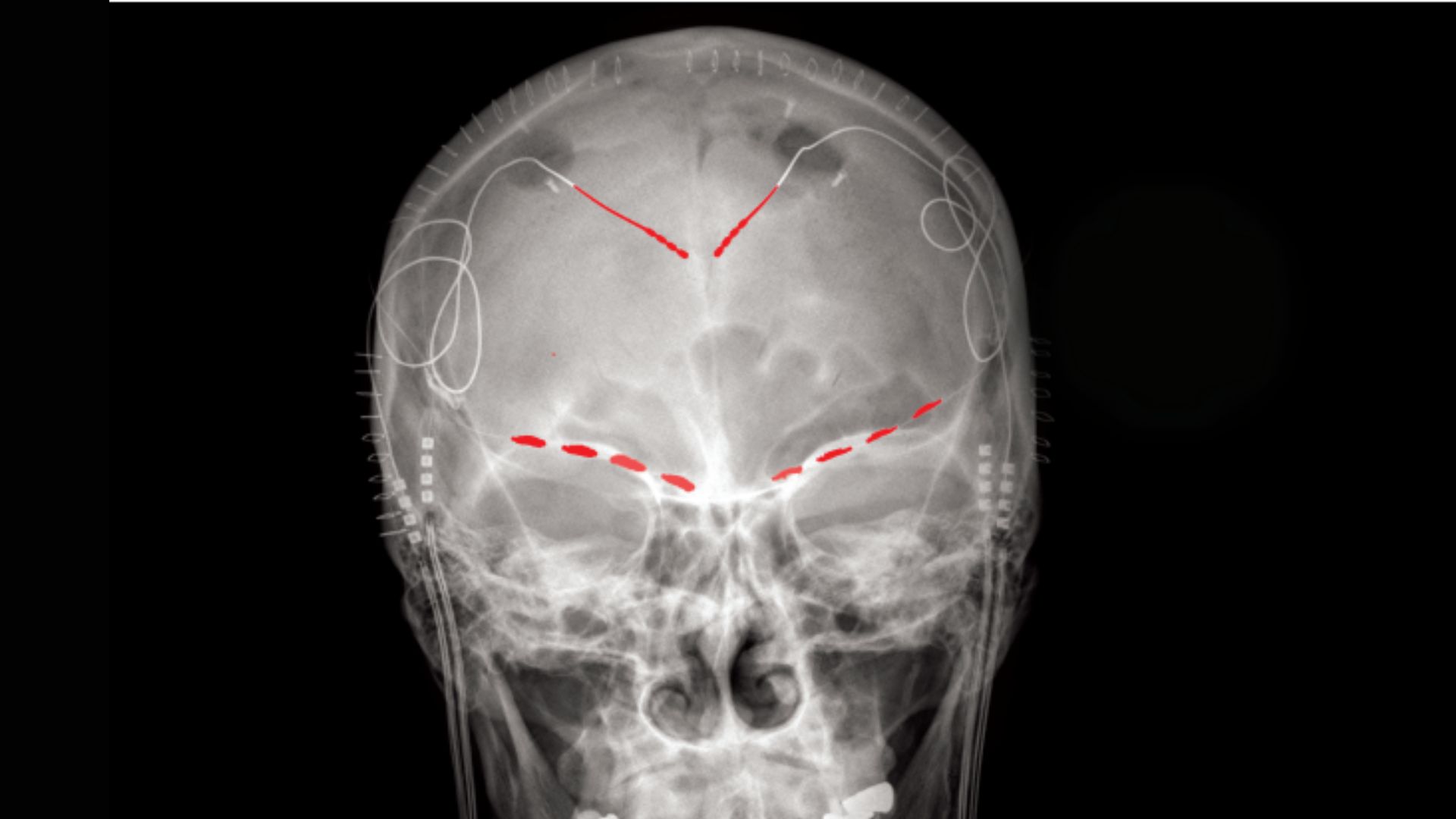
This X-ray image of one of the study participants shows where recording electrodes (red patches) were implanted into the brain. These implants were used to see how the participant’s brain activity changed as the severity of their chronic pain shifted through time.
scientist hijacked the human oculus to get it to see a brand - novel color . It ’s call ' olo . '
The constant surveillance of modernistic life could worsen our mental capacity occasion in ways we do n’t fully sympathise , disturbing studies suggest
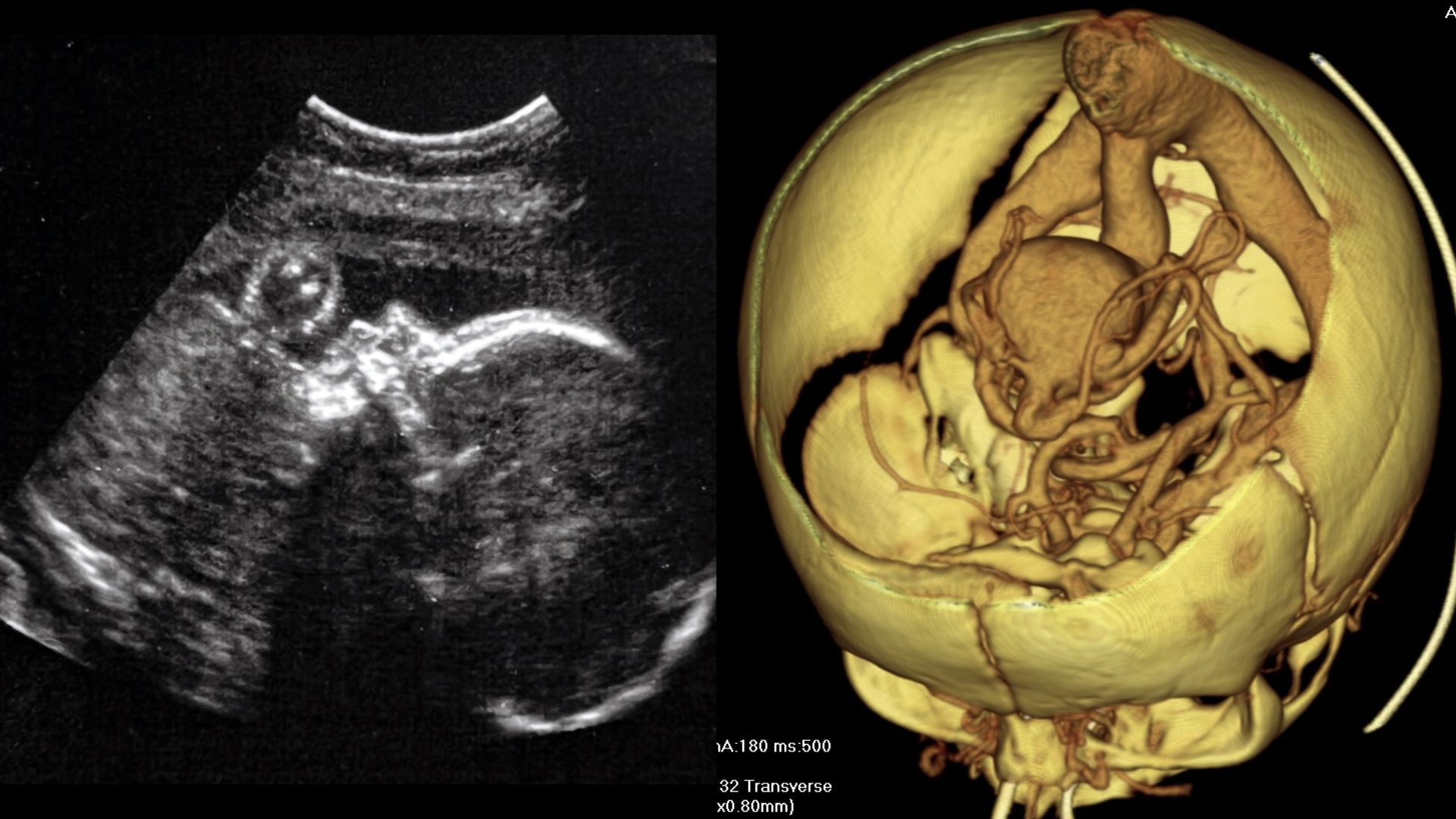
In fetuses with a rare malformation called “VOGM,” certain arteries in the brain connect directly to a major vein, rather than properly connecting to capillaries. VOGM looks like the image shown on the right.
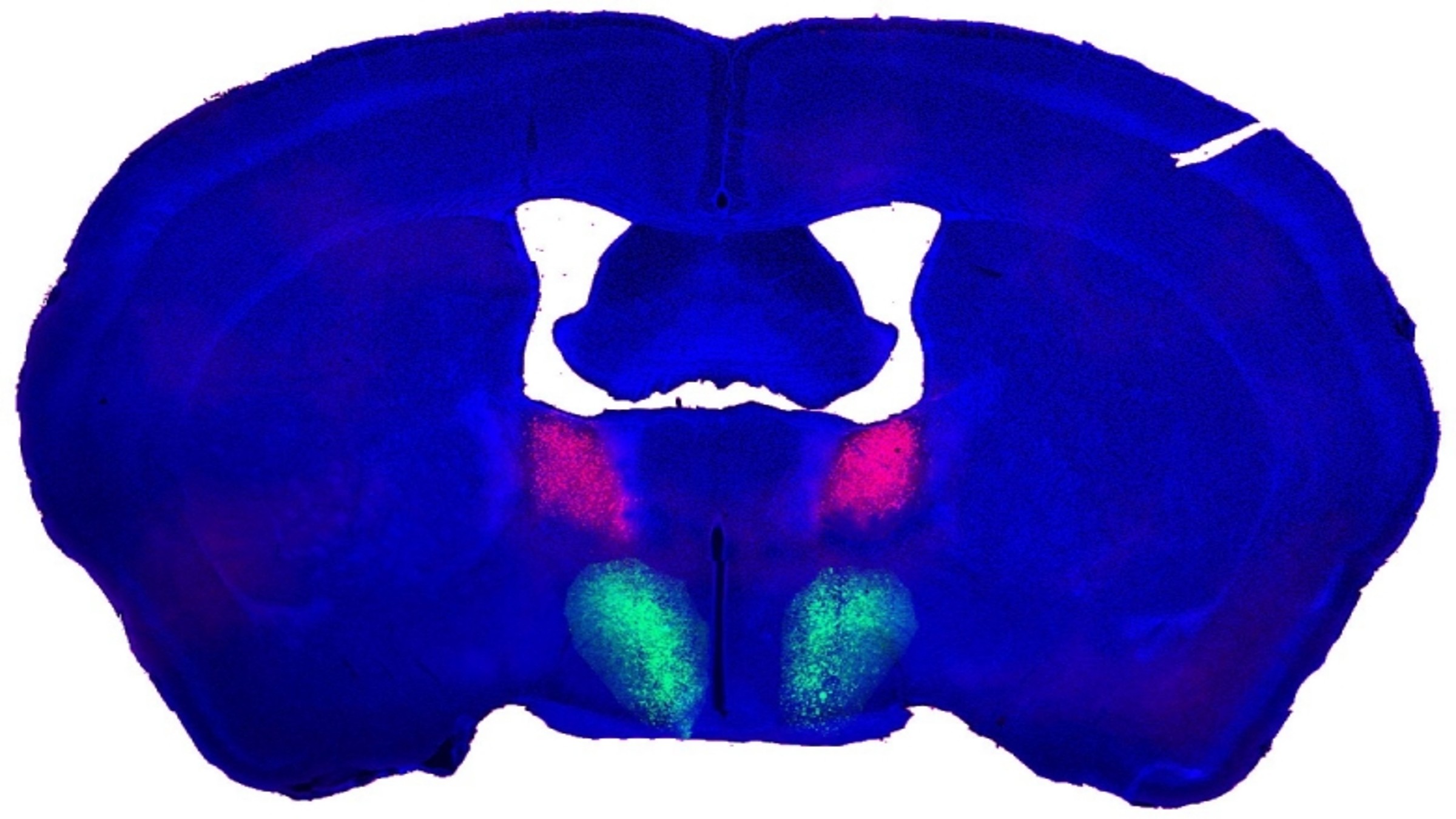
The neurons highlighted in this composite image of the male mouse brain — the preoptic hypothalamus (POA), in green, and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), in pink — are connected and regulate sexual behavior, a study found.
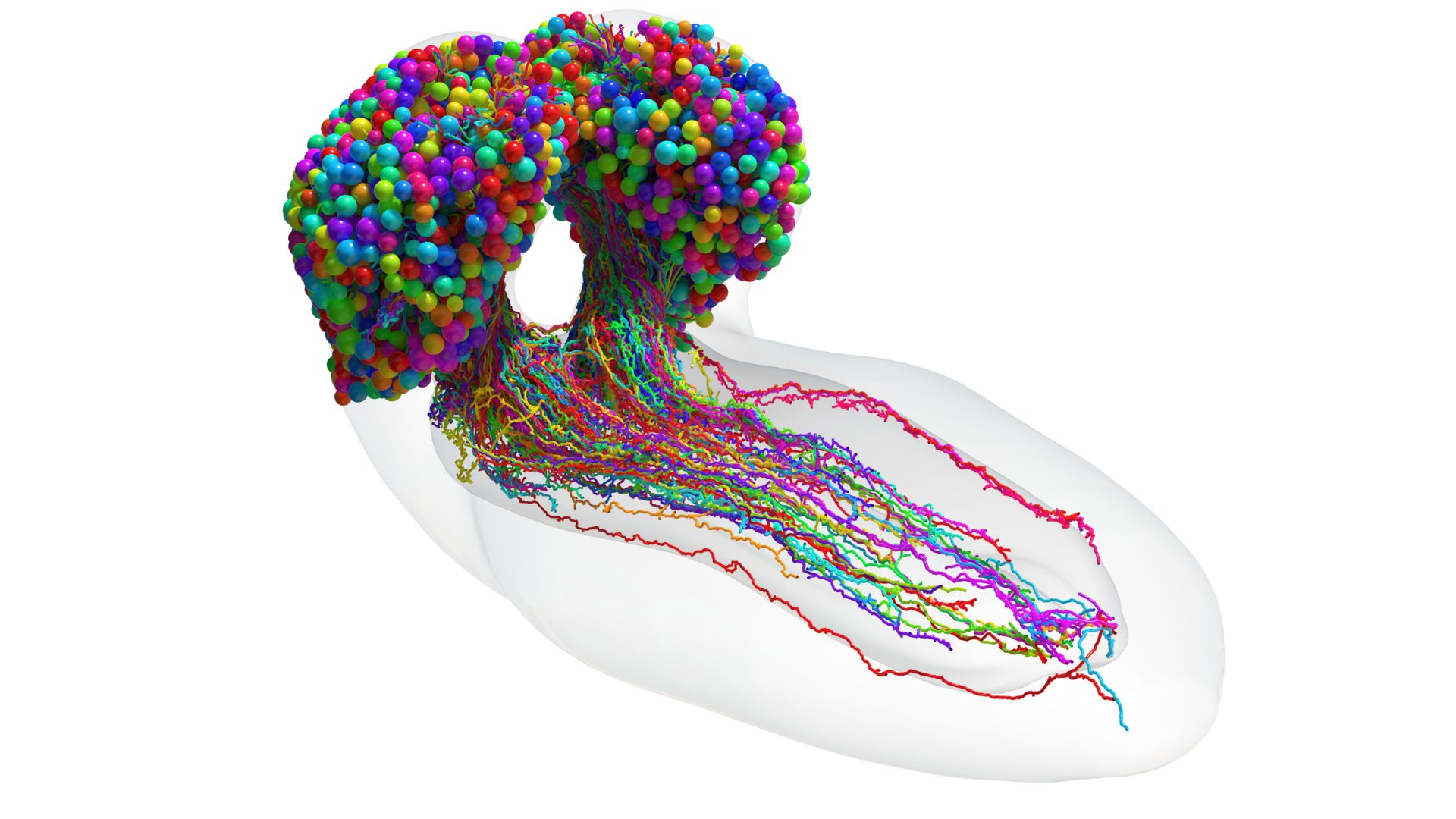
This image shows the complete set of neurons in a larval fruit fly brain, which were reconstructed using electron microscopy.