When you buy through links on our web site , we may earn an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
Astronomers peer into the heart of theMilky Wayhave chance on two gargantuan , never - before - seen structures . These vast " streams " of stars each contain the mass of 10 million suns and are up to 13 billion yr honest-to-god . They cross broad wrapping of the coltsfoot and may be some of the earliest building cube of ourMilky Way , scientists with the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy ( MPIA ) say .
The two social system — discover in a young study bring out March 21 inThe Astrophysical Journal — have been named Shiva and Shakti , after the godly Hindu twosome whose trades union is tell to have brought harmony to the universe . The newfound stellar streams appear to have merged with the early Milky Way between 12 billion and 13 billion years ago , fueling our galaxy ’s emergence .
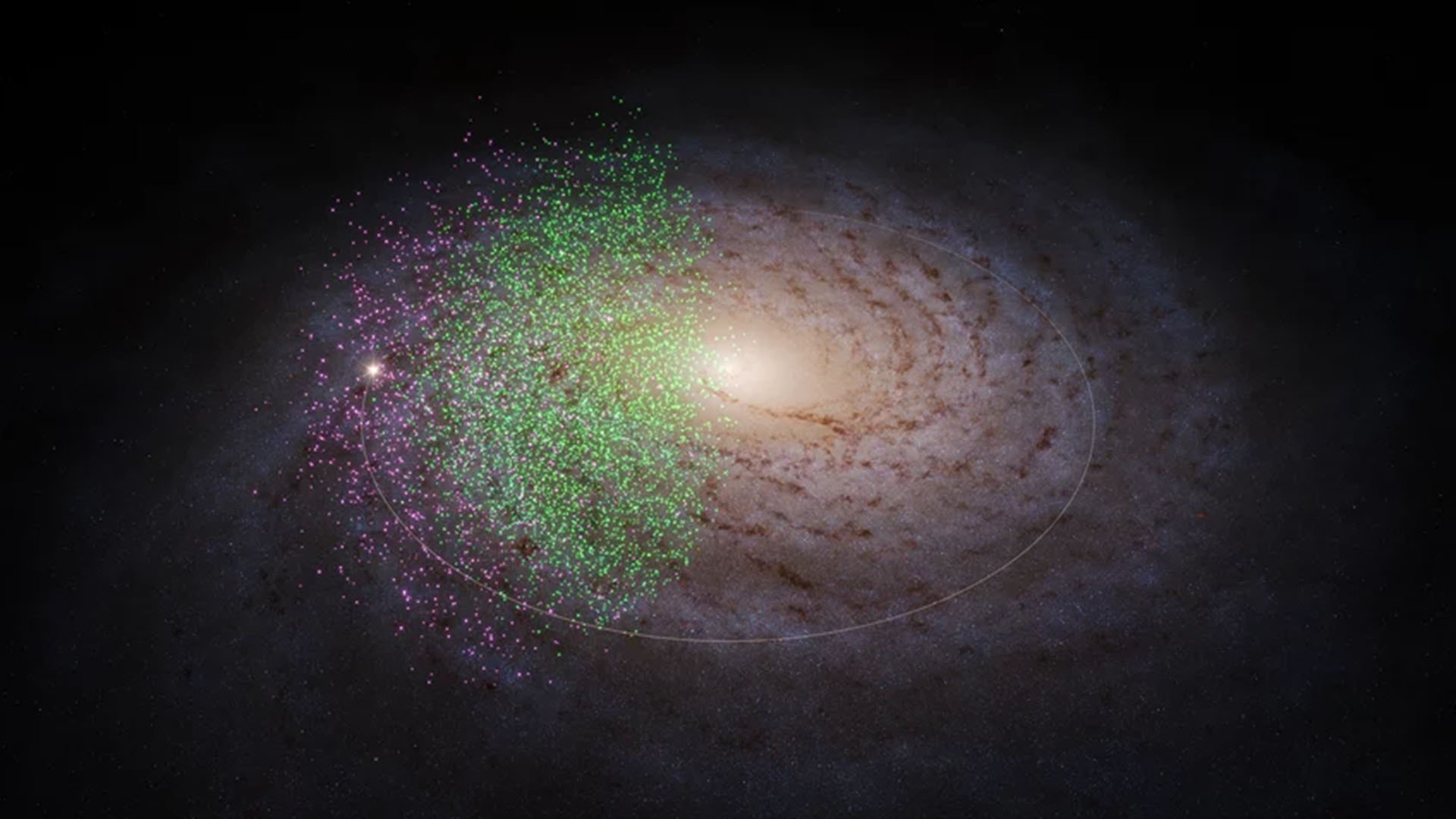

Two gargantuan streams of stars named Shiva (shown in green) and Shakti (purple) may be some of the oldest building blocks of the Milky Way galaxy.
" What ’s truly amazing is that we can detect these ancient structures at all , " Pb bailiwick authorKhyati Malhan , an astrophysicist at MPIA pronounce in astatement . " The whitish Way has changed so importantly since these stars were assume that we would n’t expect to recognise them so clear as a mathematical group . "
relate : James Webb telescope corroborate there is something seriously wrong with our understanding of the universe
The researchers fleck the cosmic structures using theEuropean Space Agency ’s Gaia space scope — a floating lookout station that ’s been mapping the shape and structure of the Milky Way since 2014 . By charting the speed , military position and motion of more than 1.5 billion stars in our galaxy , Gaia ’s observations enable uranologist to draw connections between groups of stars that share like origins , help to piece together our galaxy ’s account .
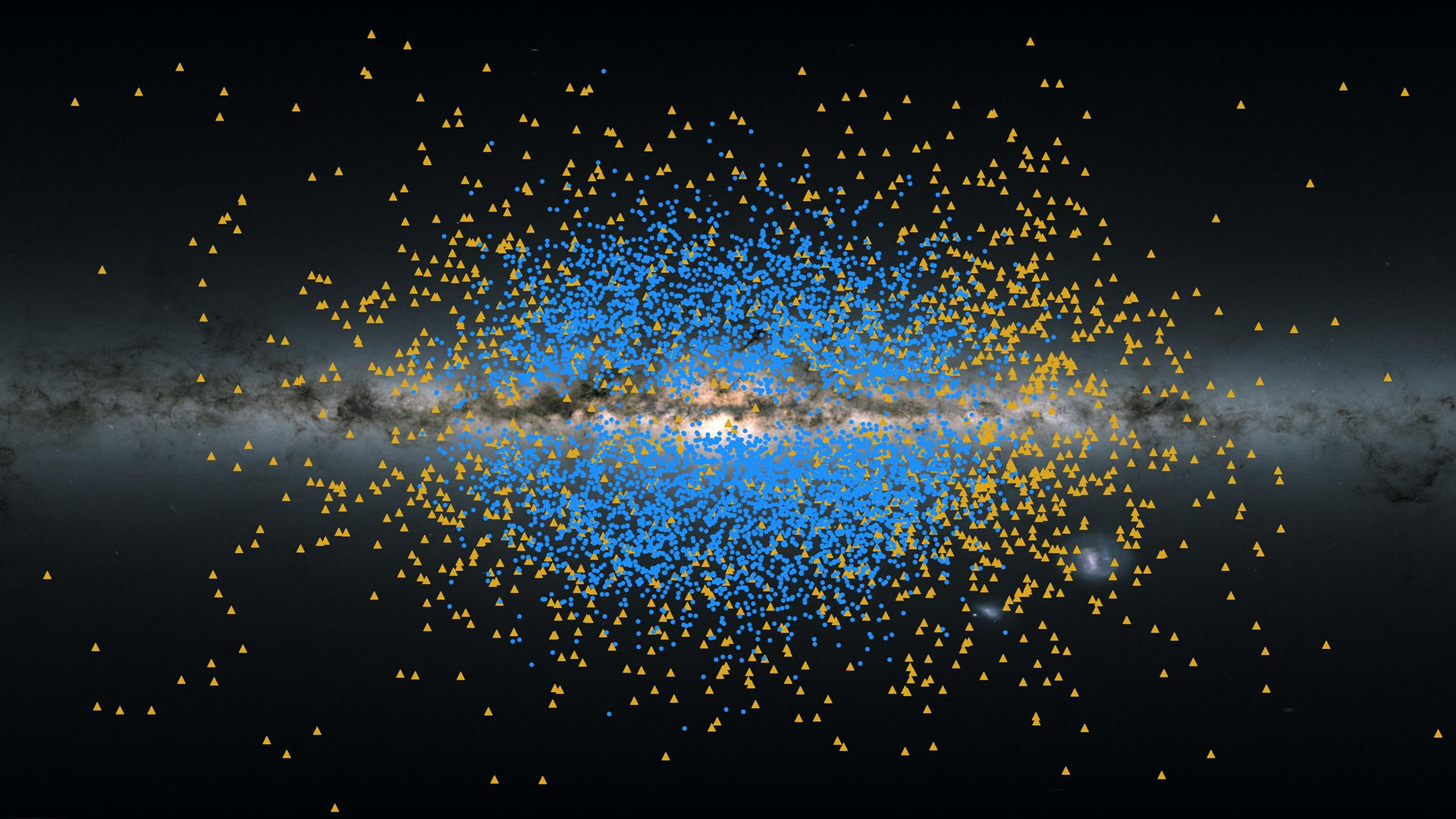
Another illustration showing the two stellar streams relative to a real view of the Milky Way band across the sky. Yellow dots show the location of the stars from the Shakti stream, while blue dots show the location of the stars from the Shiva stream.
It ’s opine that the whitish Way has collided with neighboring galaxiesat least a XII prison term over the last 12 billion years , with each merger funneling fresh stars into our germinate galaxy . The Gaia telescope has help reveal several of these collisions — including a previously obscure merger with theso - call Gaia sausagedwarf galaxy , which our insatiate Milky Way swallowed 10 billion yr ago , giving our coltsfoot its bulging center .
The millions of stars that make up Shiva and Shakti also seem to have contribute to our Galax urceolata ’s overall structure but are located a bit further from the astronomic center than previously identified fragment like the Gaia sausage balloon .
" Until now , we had only recognise these very early fragments that came together to form the Milky Way ’s ancient center , " study atomic number 27 - authorHans - Walter Rix , director of the department of galaxies and cosmology at MPIA , said in the command . " With Shakti and Shiva , we now see the first piece that seem comparably sure-enough but locate further out . These signify the first steps of our galaxy ’s increase towards its present sizing . "

The team ’s analysis showed that Shakti ’s stars scope further from the astronomic center and in a more circular range than Shiva ’s — but both social structure contain stars that are highly metallic element poor , meaning they lack the heavier elementsforged through stellar fusionlater in the universe ’s history . This means Shiva and Shakti likely contain some of the old stars in the Milky Way , making the newfound swarm some of the first construction blocks upon which the beetleweed germinate .
— ' This is a journey , not a destination ' : arresting single-valued function of the Milky Way ’s center exhibit Modern mysteries about our wandflower
— Astronomers feel heavy black hole span in the universe of discourse , and they ’ve been trap in an endless duel for 3 billion year

— ' nous - bollix ' James Webb telescope images reveal 19 spiral galaxies in the great detail ever seen
To better understand how Shiva and Shakti ’s spousal relationship with the Milky Way contributed to the current state of our galaxy , the team will continue studying them through several ongoing sky study . Sadly , there is a rigorous deadline for this research : Inabout 4.5 billion years , the Milky Way ’s next gravid collision will unfold as the nearby Andromeda galaxy merges with ours . Whatever lifetime live on our planet then will have a completely different view of the nighttime sky than we do today .














