When you purchase through linkup on our web site , we may realize an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it turn .
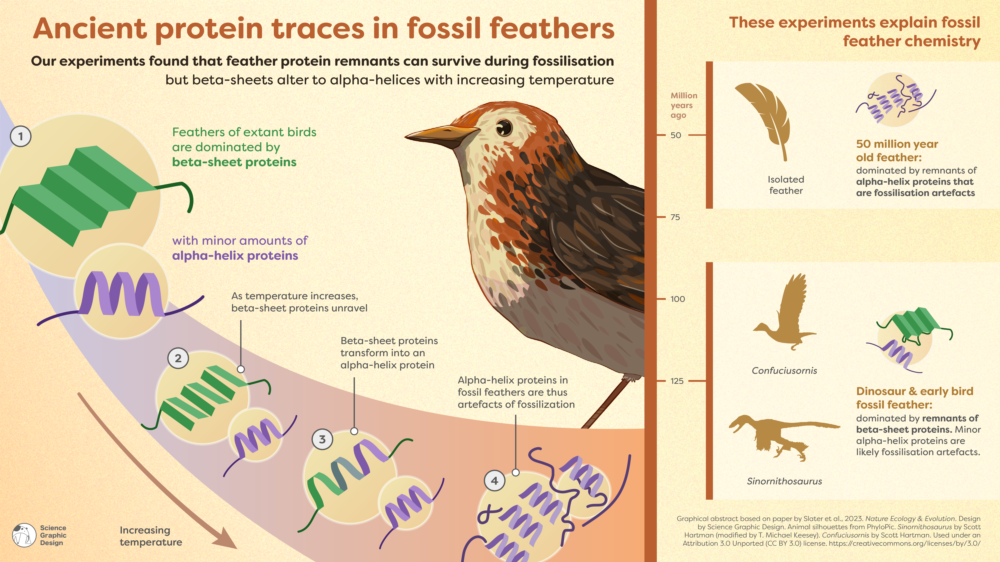
Feathers from modern - day birds have more in rough-cut with dinosaur feathers than expert previously thought and have a like protein composition , a unexampled X - beam analytic thinking reveals . The find offers new perceptiveness into the evolution of feather over hundreds of millions of years .
paleontologist examine feathers from three ancient animals , including a 125 million - year - quondam nonavian dinosaur calledSinornithosaurusfound inChina ; a 125 million - year - old early bird , also from China , sleep with asConfuciusornis ; and an unspecified species that lived in what is now the Green River Formation in Wyoming 50 million years ago , harmonise to a study print Sept. 21 in the journalNature Ecology and Evolution .

An isolated 50-million-year-old fossil feather from the Green River Formation in Wyoming.
After deport go - ray and infrared clear analysis on the ancient feathers , the investigator discover traces of corneous genus Beta - proteins ( CBPs ) , formerly known as beta - keratins , which are proteins necessary for strengthening plume for flight . The international team of researchers then study feather from today ’s birds , such as zebra finches ( Taeniopygia)and noticed that they check a interchangeable chemical substance structure .
Related : scientist changed scales on wimp feet to feathering by tweaking a exclusive factor
" These same beta protein are also present in modern bird feathers , " lead study authorTiffany woodlouse , a postdoctoral researcher of paleobiology at University College Cork in Ireland , told Live Science .
A chart showing the ancient protein traces found in fossil feathers.
Prior to this study , scientists think ancient animate being plume had a altogether different protein composition and were principally composed of alpha proteins , which are n’t as substantial as CBPs . However , this new written report showed that not only were the old feather mainly made up of CBPs but that those protein transformed into alpha proteins during fossilization , according to astatement .
" The dinosaur feathering we break down show that they mostly dwell of beta proteins , " woodlouse said . " So , the original report that ancient feathers were predominately compose of alpha protein was likely an artifact of fossilisation . "
— ' super rare ' fossilized dinosaur voice box advise they sounded birdlike
— Ancient birdie with T. rex - like skull discover in China
— Oddly modern skull raises new questions about the early evolution of birds
This new mentation not only shows that proteins can remain preserved in the fossil book for upward of 125 million years but also provides young mentation into the organic evolution of ancient feathering by " pushing the metre scales a good deal further than what we cerebrate , " Slater said .

" The chemistry of advanced - day feathers is actually a mountain more ancient than we previously thought , " Slater said . " Our inquiry aid rewrite the narrative and shows that the very basic building blocks that are required for powered flight were present at least 125 million eld ago . "













