When you purchase through linkup on our site , we may pull in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Few engineering have enamour the human imagination in quite the same way as robot . The musical theme of machines that can walk and talk like us has been a staple of skill fiction for decades . The world has been more prosaic — most substantial - world robots are disembodied arms break to thudding and insistent mill piece of work . But late breakthroughs in both artificial intelligence ( AI ) and robotlike ironware signify that the smart , humanoids of our resourcefulness are getting ever tight to reality .
Here are 12 of the most important milestones that nonplus us here .

1921 — Invention of the term “robot”
Since antiquity , people had imagined the theory of hokey humans — from the cadaver Golems of Judaic folklore to the mechanical servants of the Grecian god Hephaestus . chronicle is also litter with exemplar of complex automata design to wow audiences with their life - like apparent motion . But the give-and-take " robot " was first introduced by the Czech author Karel Čapek in his 1921 playR.U.R. , which stands for Rossumovi Univerzální Roboti ( Rossum ’s Universal Robots ) . The term is derived from the Czech word " robota , " which stand for forced labor , and the play feature unreal workers made of synthetic constitutional matter that rise up against their human masters — a narrative that would be echoed in many later employment .
1942 — Isaac Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics
robot became a pop scientific discipline fiction figure of speech , with legendary generator Isaac Asimov feature them prominently in many of his story . A major theme of his work was how these artificial human beings would interact with human company . In his 1942 short story " Runaround " he usher in the Three Laws of Robotics , which were presuppose to regularise how all robots in his fictional universe of discourse operated . The first law prohibited the robots from harming man , the second mandated robots to obey man unless it violated the first law , and the third ordered the machines to protect themselves as long as that did n’t infringe with the two other laws . While wholly fictional , Asimov ’s three natural law were influential on the development of honorable framework for AI and robotics .
1961 — The first industrial robot
It did n’t take long for ideas from science fiction to percolate through to the existent world . In the early 1950s , serial discoverer George Devol began workplace on a robotlike arm that could do repetitious tasks in factories . He teamed up with enterpriser Joseph Engelberger to imprint Unimation , the world ’s first robotics company , and in 1961 their Unimate robotwent to workon the assembly business line at a General Motors plant in New Jersey . The hydraulicly - powered arm had five arcdegree of exemption ( DoF ) — a measuring rod of dexterity that means its arm could move or rotate in five different directions . Programming the equipment necessitate the drug user to physically move the arm to different positions to teach it the call for sequence of actions , which was then memorialize in a magnetic warehousing equipment known as a drum memory .
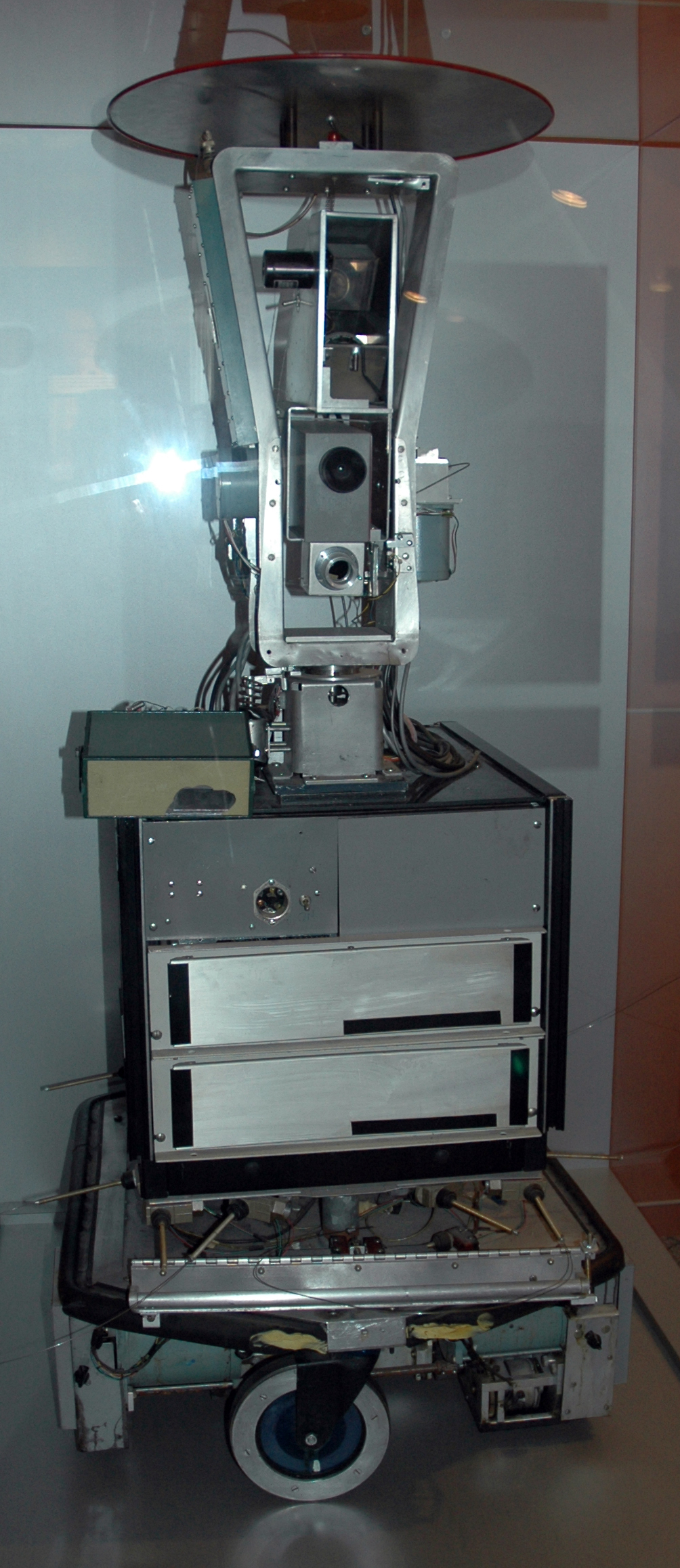
1966 — World’s first intelligent mobile robot
While pregnant progress had been made on the mechanically skillful capabilities of golem by the mid-1960s , they were still fundamentally dumb machines that needed to be program by hand . In 1966 , researchers at the Stanford Research Institute started work on a wheeled robot with cameras and tactual sensation detector that could reason about its action , make plan and navigate the real public . It could move between multiple rooms autonomously , avoiding obstacles , opening door , flicking light switch and pushing boxes around . The robot , which the squad named " Shakey , " received significant media attention — in 1970 — Life magazine even referred to it as thefirst electronic mortal . “Akey advancebehind the robot was its layered software architecture , which enabled it to rationality through project , something repeat in many subsequent automaton .
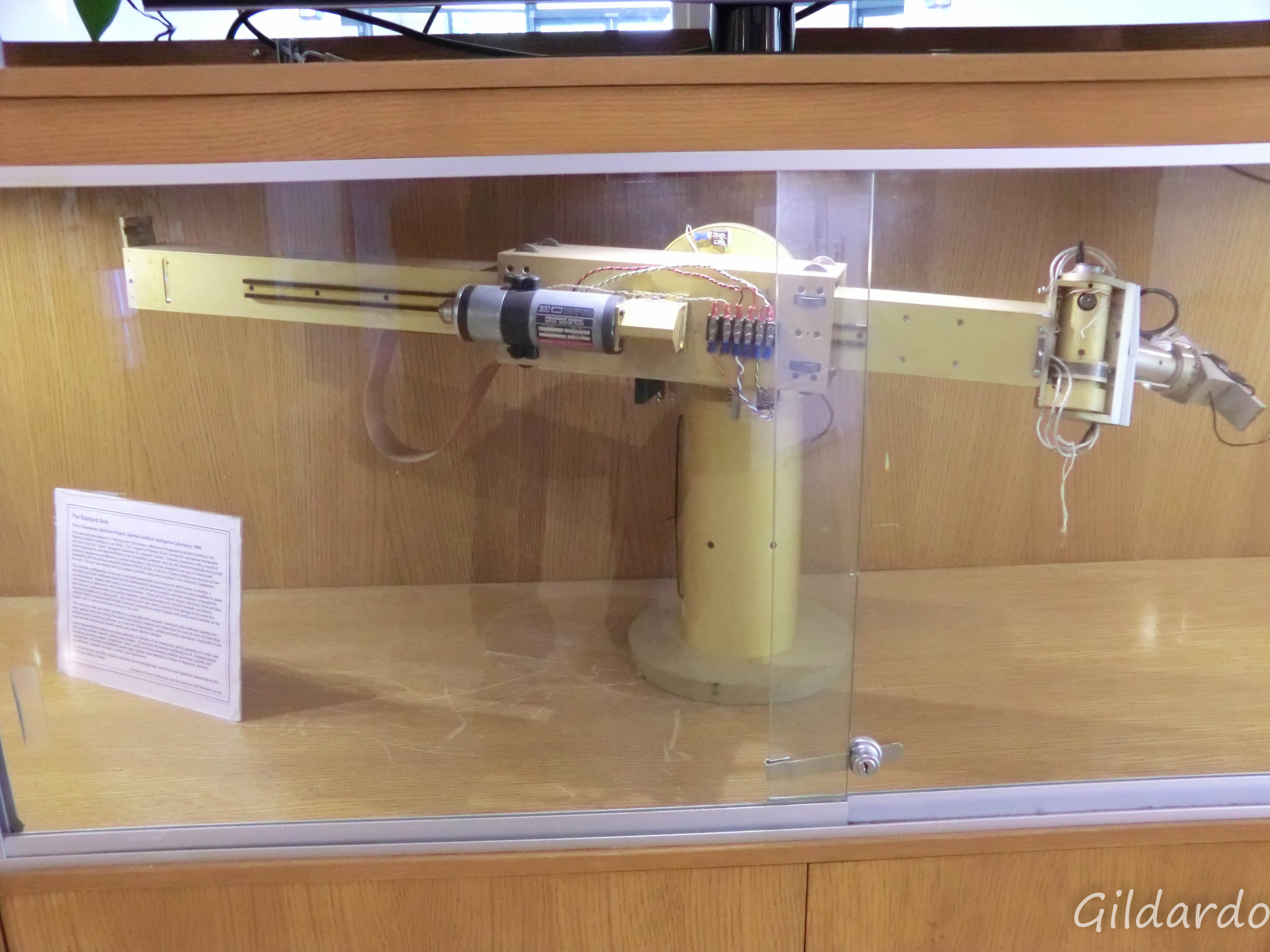
1969 — The Stanford Arm spawns a new industry
While the Unimate was the first robotic arm to go into production , the Stanford Arm became the pattern for the come forth industrial robotics industry . design in 1969by Victor Scheinman , who was then a student in the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Lab , the six - DoF arm was electrically powered and controlled by a computer . Over the following years Scheinman built increasingly sophisticated versions of the arm at both Stanford and MIT , before eventually starting a party call in Vicarm Inc. in 1974 to commercialise his work . He ended up selling his design to Unimation in 1977 , which relinquish the Programmable Universal Machine for Assembly ( PUMA ) golem in 1978 . The initial customer was General Motors , which used it toassemble automotive subcomponents .
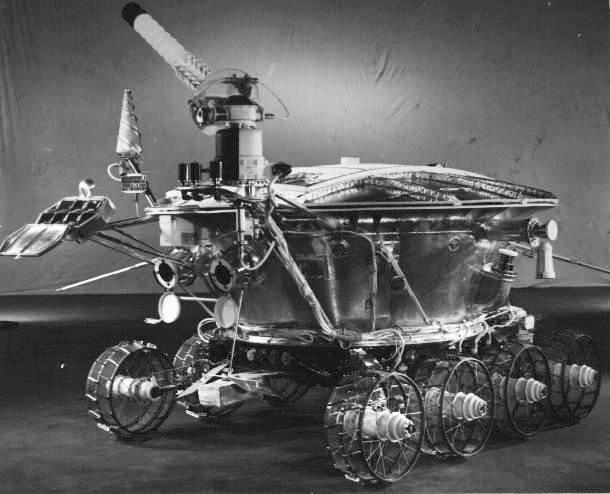
1970 — First robotic rover sent to the Moon
The giving birth of robotics overlapped with another major technical jump — the advent of the Space Age . scientist recognized that machines that could be assure remotely or even operate autonomously could be a hefty instrument for explore thesolar scheme . In 1970 , the Soviet Union landedLunokhod 1 , the human beings ’s first machinelike rover , on the moon . Shaped like a bathtub and with eight independently powered wheel , the rover could be see remotely from Earth via feeler and a feed from four camera . The solar - powered fomite operated for almost a class , roughly three and half times long than it was designed to last , and travelled 6.5 nautical mile ( 10.5 kilometers ) . It also used extendable probe to carry out more than 500 trial on the mechanical properties of lunar soil .
1990 — Rodney Brooks rewrites AI for robotics
By the 1980s , industrial robots that could carry out repetitive tasks in controlled environments had become commonplace , but endeavour to create more flexible and self-directed machines were foundering . Australianroboticist Rodney Brookshad the hunch that this plateau was due to the top - down approach researchers were call for . This involved a focus on imbue machines with abstract reasoning attainment and develop complex systems of numerical symbols to represent the universe around them . alternatively , he took inspiration from nature and focused on the feedback loop between sensing and action that enable advanced behavior in animals . He demonstrated that by take this bottom - up plan of attack , outlined in the 1990 paperElephants Do n’t represent chess game , it was possible to commingle multiple dim-witted behavioral modules to solve challenge beyond the golem that existed at the clock time .
1996 — Honda unveils first humanoid walking robot
Despite considerable progress in robotics , most machines were a far battle cry from the mechanically skillful people depicted in sci - fi . That exchange in 1996 when Honda unveiled itsP2 robot , which was the first mechanical man golem capable of walk independently on two leg . The companionship had start working on the trouble of two-footed motivity in the former 1980s by studying , and trying to duplicate , how humans walked . inquiry on P2 and its successors P3 and P4 eventually culminate in the growth of the company ’s iconic ASIMO mechanical man robot , which was unveiled for the first time in 2000 and set the standard for humanoid robotics going onward .
2000 — The da Vinci surgical robot cleared by the FDA
While most commercial robotics companies center on machines designed to replace brute confinement in factories , Intuitive Surgical decided to focus on the touchy procedure of minimally invasive surgery . They build up a four - armed robotic surgical system calledda Vincithat could be controlled remotely by a surgeon . The arms were able of hold operative instrument like scalpels , graspers and scissor grip and enabled the sawbones to carry out extremist - accurate cause . The equipment was cleared for use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2000 and has been used in more than14 million procedures .
2010 — Google unveils self driving car project
There had been scatter experiments in autonomous fomite over the years , but the first company to give serious resources to the estimation was Google . The firm commence developing self - driving cars in 2009 and drive more than 140,000 miles on public roads beforeannouncing the projectin October 2010 . early experiment were carry out in a limited Toyota Prius with a base hit gadget driver behind the wheel . But in 2015 the company carry out thefirst to the full autonomous rideon a public road in a custom - ramp up vehicle with steering wheel or pedals . After rebranding as Waymo , the fellowship started its first public trials of a driverless taxi divine service in Phoenix , Arizona in 2017 .
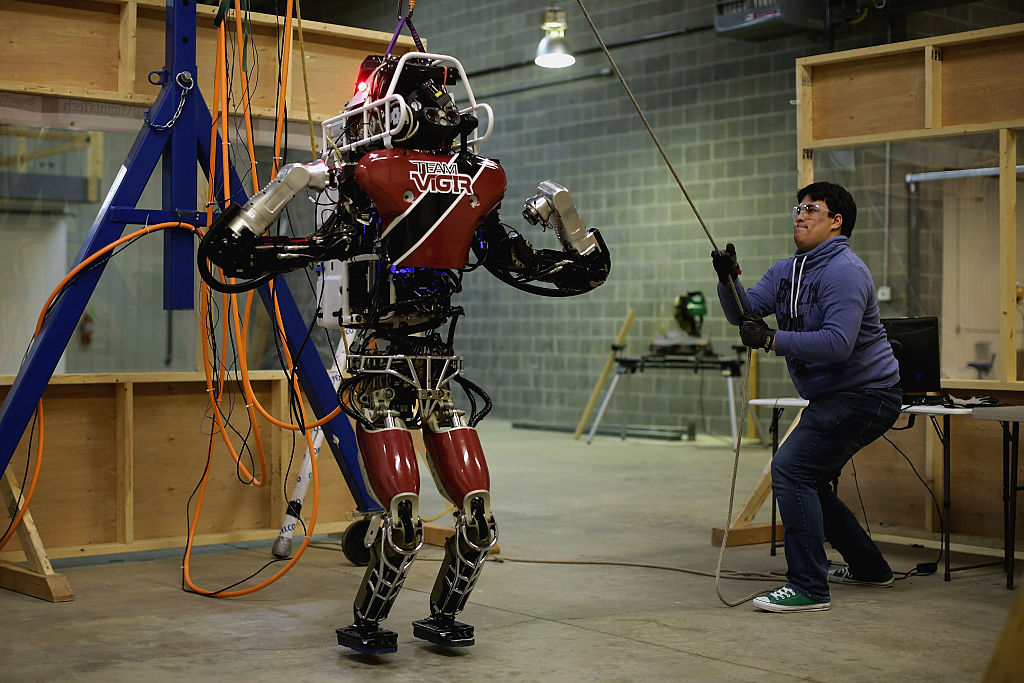
2012 — The DARPA robotics challenge is launched
One of the major catalyst for late breakthroughs in sassy , humanoid robot was theDARPA Robotics Challenge . Launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency in 2012 , the competition challenged teams to evolve semi - independent golem that could take out complex tasks in simulated catastrophe zones . The bots were task with walking across rubble , climbing ladder , closing blabbermouthed valves and even driving a usefulness vehicle . The final exam were hold in 2015 . While some teams competed with their own automaton , six were provided with humanoid Atlas robots built by Boston Dynamics . The company continued to break the automaton after the competitor was over , establish off increasingly advanced capableness over the years such asrunning out of doors , jumping andtackling parkourcourses .
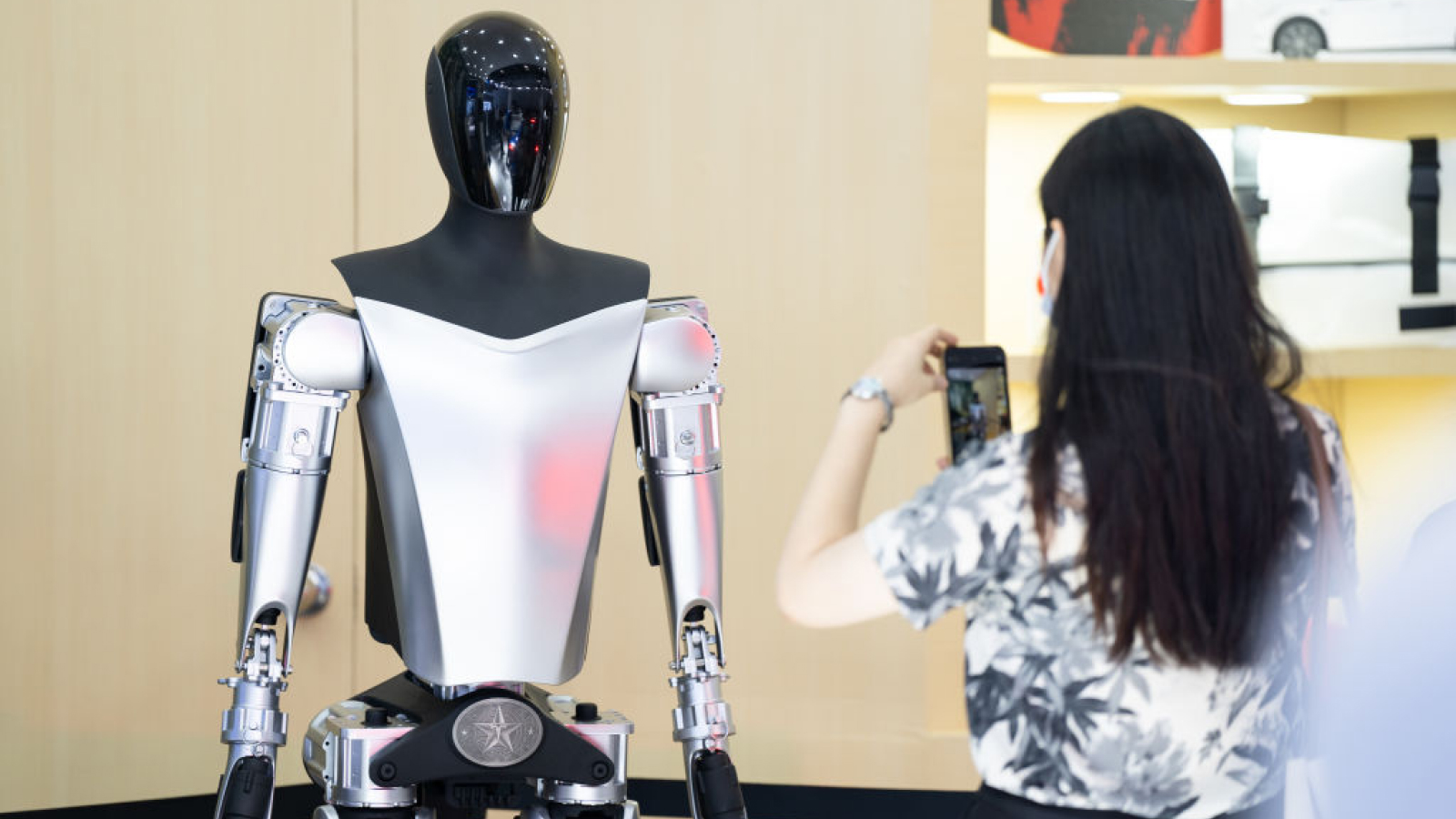
2020 — The first bipedal robot goes on sale
The startup Agility Robotics became the first troupe to free a commercial bipedal automaton afterselling two unitsof its Digit model to Ford . While not strictly a android , thanks to its " backward " legs that workmore like a bird’sthan a somebody ’s , the robot is roughly the sizing and shape of a modest human and designed to help out in warehouses and other industrial preferences . The release marked the beginning of a bonanza in commercial humanoid robotics , with company like Tesla , Figure and 1X unveiling their own offer shortly afterwards . And costs are falling rapidly — before this year Chinese society Unitree released itsG1 android golem , which costs just $ 16,000 .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your showing name .
cloud of 30 robots can ' hang like water supply ' and harden up to support the weight of a individual
golem : fact about machines that can take the air , talk or do tasks that mankind ca n’t ( or wo n’t )

The constant surveillance of modern biography could aggravate our Einstein function in way of life we do n’t fully understand , commove study suggest