When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
By breaking up cluster of cancer cells , an previous affection drug called digoxin may help stop tumors from spreading to other organs , a small test display .
The inquiry is in its early day , though , so it will be some sentence before we know whether it ’s useful for treat Crab , including breast cancer , scientists say .

Breast canceris among the leading causes of cancer deaths in U.S. women , for the most part due to its power to overspread , or metastasize , from the bosom to other part of the body . These migrating genus Cancer cell can invade vital Hammond organ , like the brain or lungs , making treatment more challenging . Standard cancer treatment focus on killing neoplasm cells butaren’t specifically project to stop metastasis .
pass on tumour cells — the cancer cell that break away from tumors and come in the bloodstream — play a primal role in metastasis . These cell are more likely to form new tumors in other section of the dead body when they cluster together , as opposed to when they travel alone .
Related:‘I’ve never seen anything like this ' : scientist pirate cancer genes to turn tumors against themselves
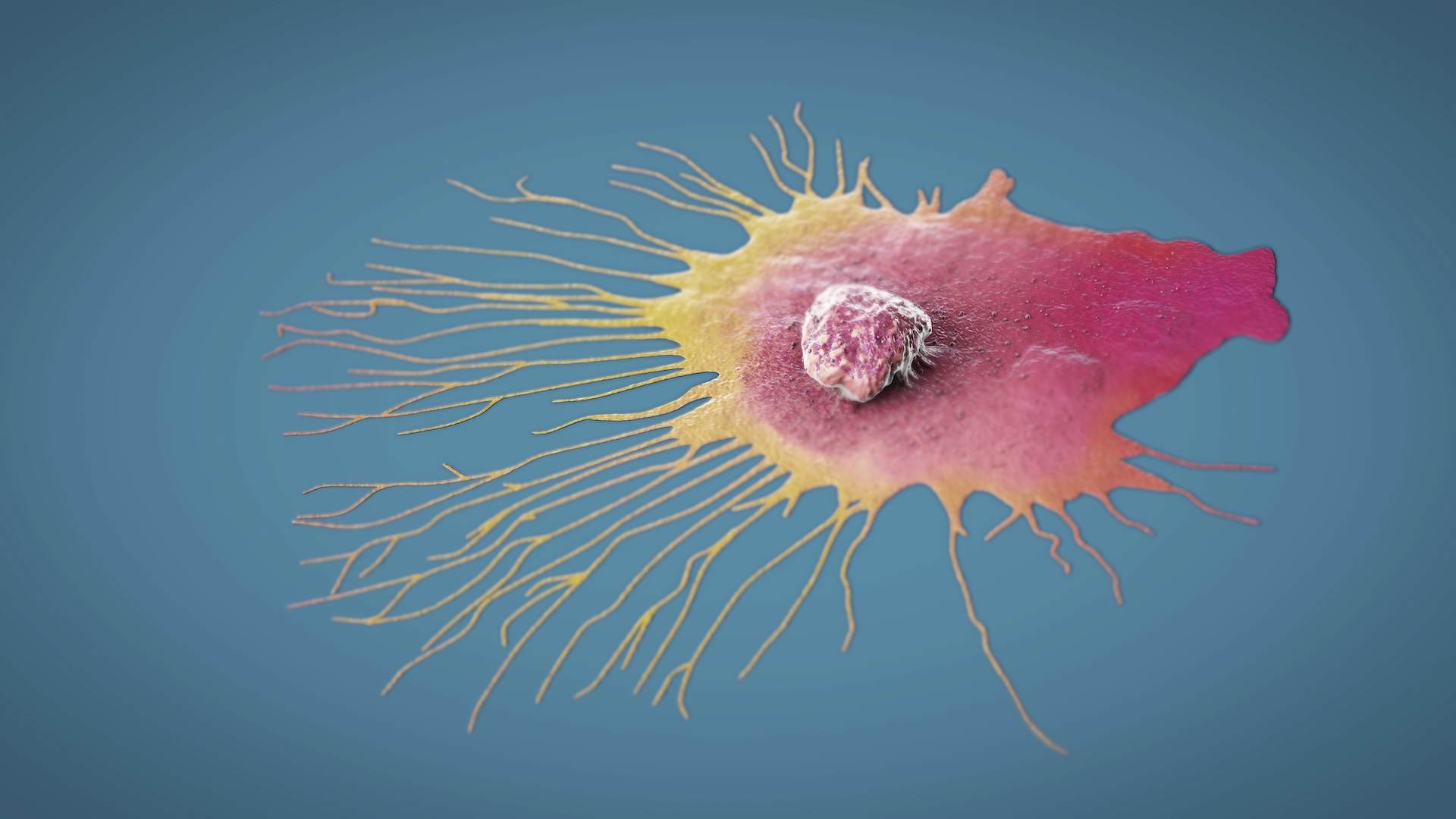
late researchin Switzerland identified exist drug that could help break up these clusters . experimentation in mice showed that the drug reduced the spread of breast genus Cancer , suggesting a potential unexampled feeler to limiting metastasis . These drug — lie with as Na+/K+ ATPase inhibitor — include digoxin and employment by altering the catamenia of charged particle in and out of cells .
Building on their former research , the scientists have now conducted a clinical trial to test whether digoxin could flinch cluster of circulating tumor mobile phone in women with metastatic breast Crab . Based on their early results , publish Jan. 24 in the journalNature Medicine , the research worker think digoxin could someday complement other treatment aimed at fight down primary tumors , mean cancers that have not yet spread .
First human study of digoxin in cancer
Digoxin is an old medication that was first derived from thefoxglove plant(Digitalis lanata)in 1930 . It ’s used to treatheart failureandatrial fibrillationand works by block structures in heart electric cell shout out sodium - potassium pumps , which keep the levels of Na and K inside cellular phone in check . hinder the pumps with Lanoxin leads to stronger muscular contraction and a dim fondness rate .
Now , scientists think this effect of Lanoxin could be leverage for cancer discussion .
By curb the sodium - potassium pump in tumor cell , Lanoxin causes the cells to assimilate more calcium . Previous researchhas shown that elevated Ca in prison cell can disrupt the constitution of sloshed junctions and desmosomes — anatomical structure that help cells get together . So digoxin likely weakens these connections between cancer cells that are clustering and causes them to give out aside .

The squad observed these effects in mice . To see whether digoxin could also interrupt tumor - jail cell clusters in human patients , they recruit nine charwoman with metastatic breast malignant neoplastic disease . The participant each had at least one mobilize tumor cell cluster at the prison term they were riddle .
During the discipline , the women take aim Lanoxin every day for seven day . To track the circulating tumor cells , the researchers pick up blood samples from the participant before discourse , two hr after their first State Department , and then again three and seven days into the study .
The size of the participants ' malignant neoplastic disease - cell clump shrank by an average of 2.2 cells per clump after treatment , the researchers found . The average clustercontained four cellsbefore treatment . No serious intervention side effects were reported .

Questions to answer
Although promise , the trial termination have some limitations .
The shrinking of tumor - cell cluster was statistically significant , but overall , the drug ’s effect was quite small , Dr. Daniel SmitandDr . Klaus Pantel , of the University Medical Center Hamburg - Eppendorf in Germany , wrote in acommentaryabout the raw written report .
In possibility , make fewer circulating clump might reduce the chance of the cancer spreading even further , they state . But it likely would not stop existing secondary tumour from growing , they added . In other words , the drug would in all likelihood be useful only at a certain stage of cancer onward motion .

Smit and Pantel also pointed out that digoxin did not forestall circulate tumor cells from cluster with healthy blood prison cell — a process that also drive cancer spread . what is more , found on clinical studies by other groups , they argue that , while breaking up cluster may slow metastasis , tumor cell that are migrating on their own are also tied to negative effects .
— Healthy breast cells can await like encroaching cancer , elaborate early diagnosis
— The 10 deadliest cancers , and why there ’s no remedy

— Severe COVID-19 may shrink cancer tumors , early data suggest
Smit and Pantel also note that patients with metastatic chest cancer have a range of clinical outcomes . " Therefore , an notice based on nine people with cancer is hypothesis - generating rather than fully conclusive , " they wrote .
Nonetheless , the trial hints that digoxin and standardised drugs could have a property in cancer tending . Now , the researchers plan to create newfangled molecules based on Lanoxin that could more effectively break up distribute clusters . They are also conducting experiments to see whether digoxin could be employ to other types of cancer .

This clause is for informational purposes only and is not meant to offer medical advice .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your show name .









