When you buy through nexus on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
In addition to being the expectant and most hefty object in thesolar arrangement , the sun is also one of the most enigmatic entity in our cosmic neighborhood , which makes it hard for researchers to trap down exactly how it work . We are constantly learning new things about our home star , and 2023 has been no unlike . From learning more about the forthcoming solar maximum to bring out ancient superflares and mysterious heartbeat signal , here are the top 10 things we ’ve learned about the sun this year .
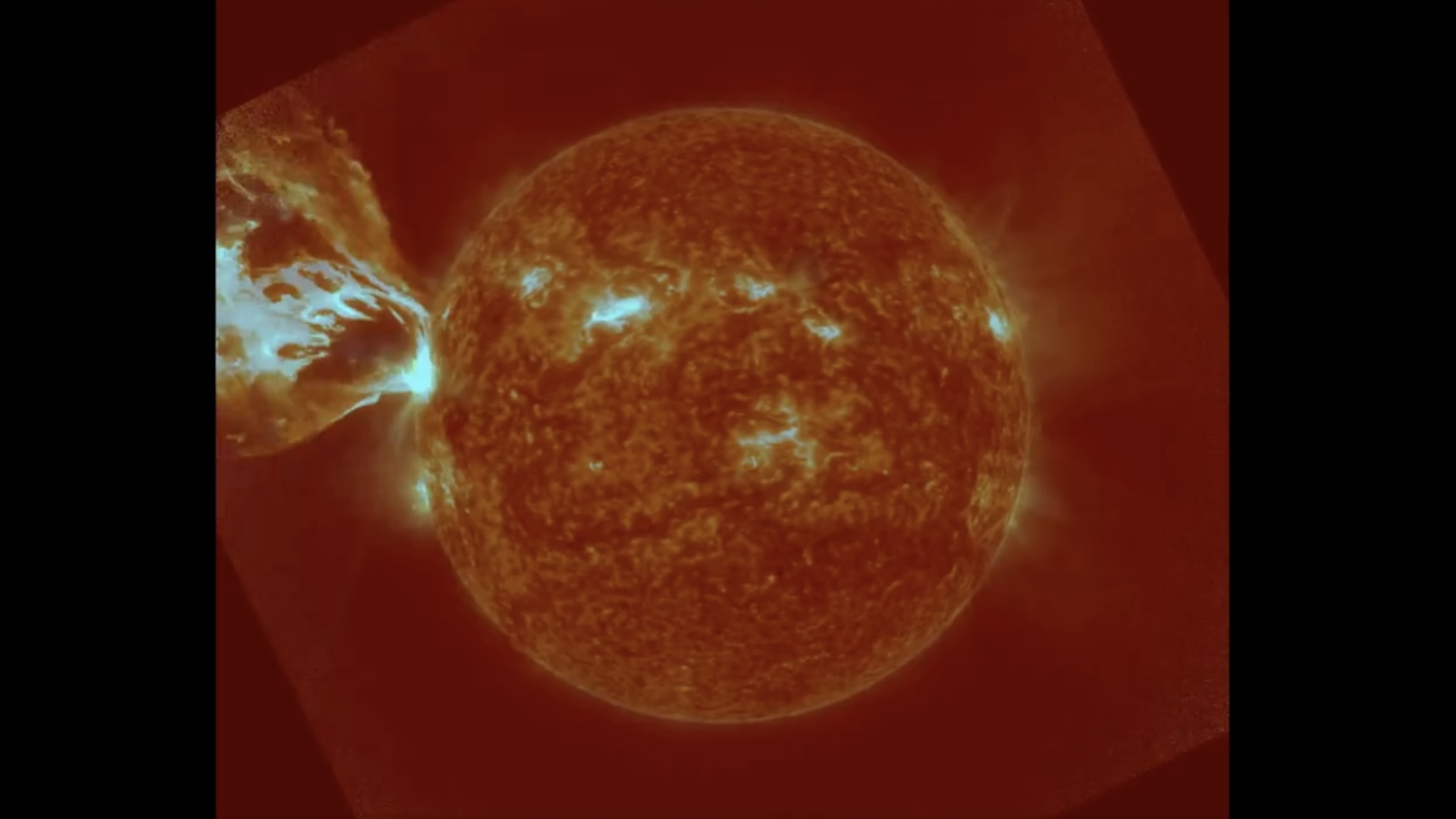
Solar maximum is right around the corner
The major news about the sun from this year is that we arefast approaching the solar maximumand that it ’s get going to be more explosive than we ab initio believe .
Back when the current solar cycle began in 2019 , prognosis from space atmospheric condition scientists suggested that the solar upper limit would get sometime from 2025 onward and be comparatively weak compare to retiring solar cycles . However , numerous warning signsearly in the class , includingrising sunspot numbers , powerfulX - course solar flaresandchanges in Earth ’s upper atmosphere , hinted that the solar cycles/second was not get on as expected .
In June , Live Science publish an exclusive , in - depth feature film on the upcoming solar maximum , which unveil that the explosive peak would likely arrive by 2024 and be more dynamic than the initial forecast suggest . And in October , space weather condition scientistsreleased an update forecastfor the current solar bicycle , which is more in line with what expert told Live Science .
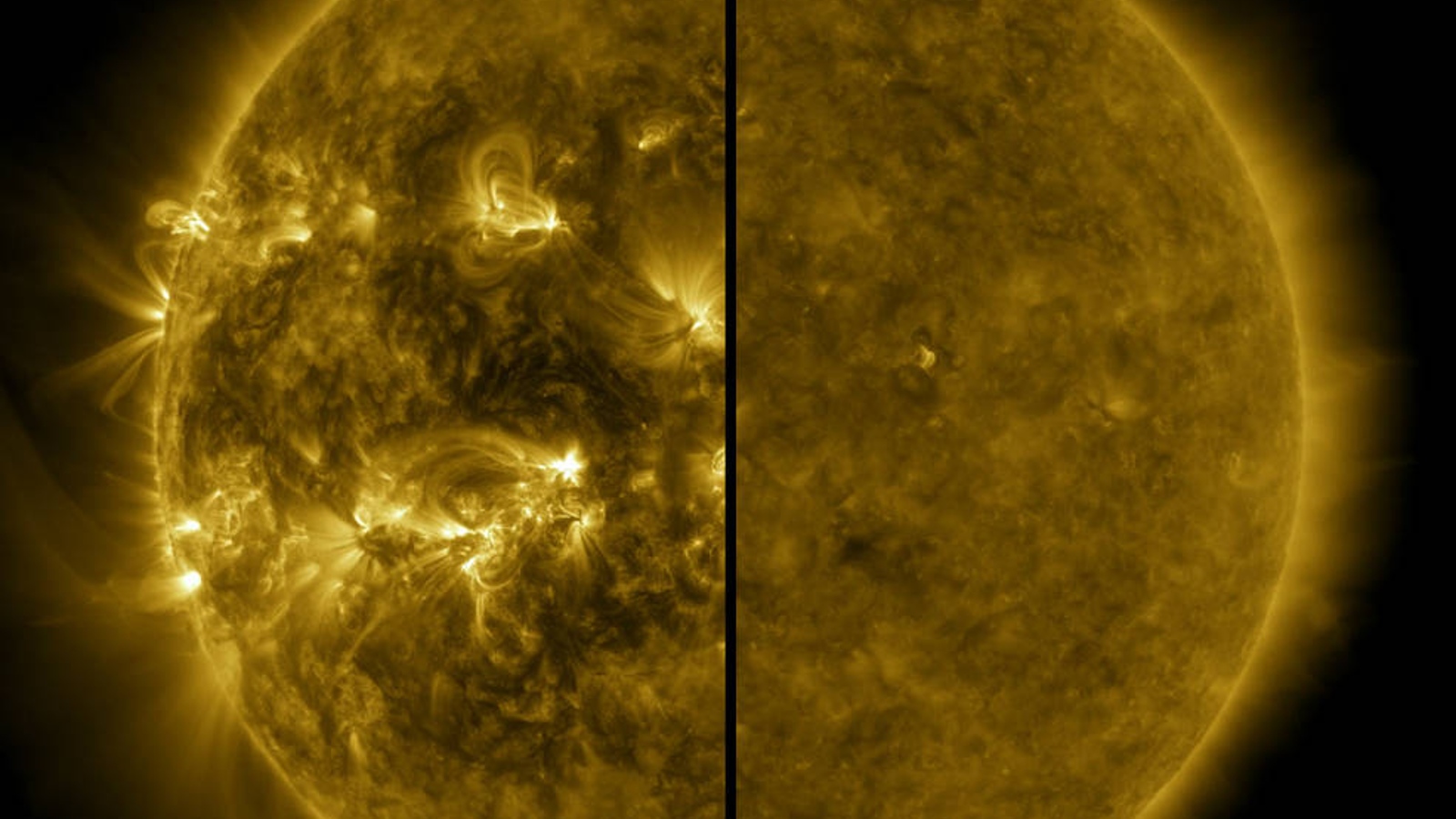
During the solar maximum (left), the sun is much more chaotic than during the solar minimum (right).
When solar utmost does arrive , we can expect to be bombarded with more solar storms , which will result infrequent auroral displays , radio blackouts , likely satellite problems anddisruptions to the migration patterns of some animals .
The sun is smaller than we realized
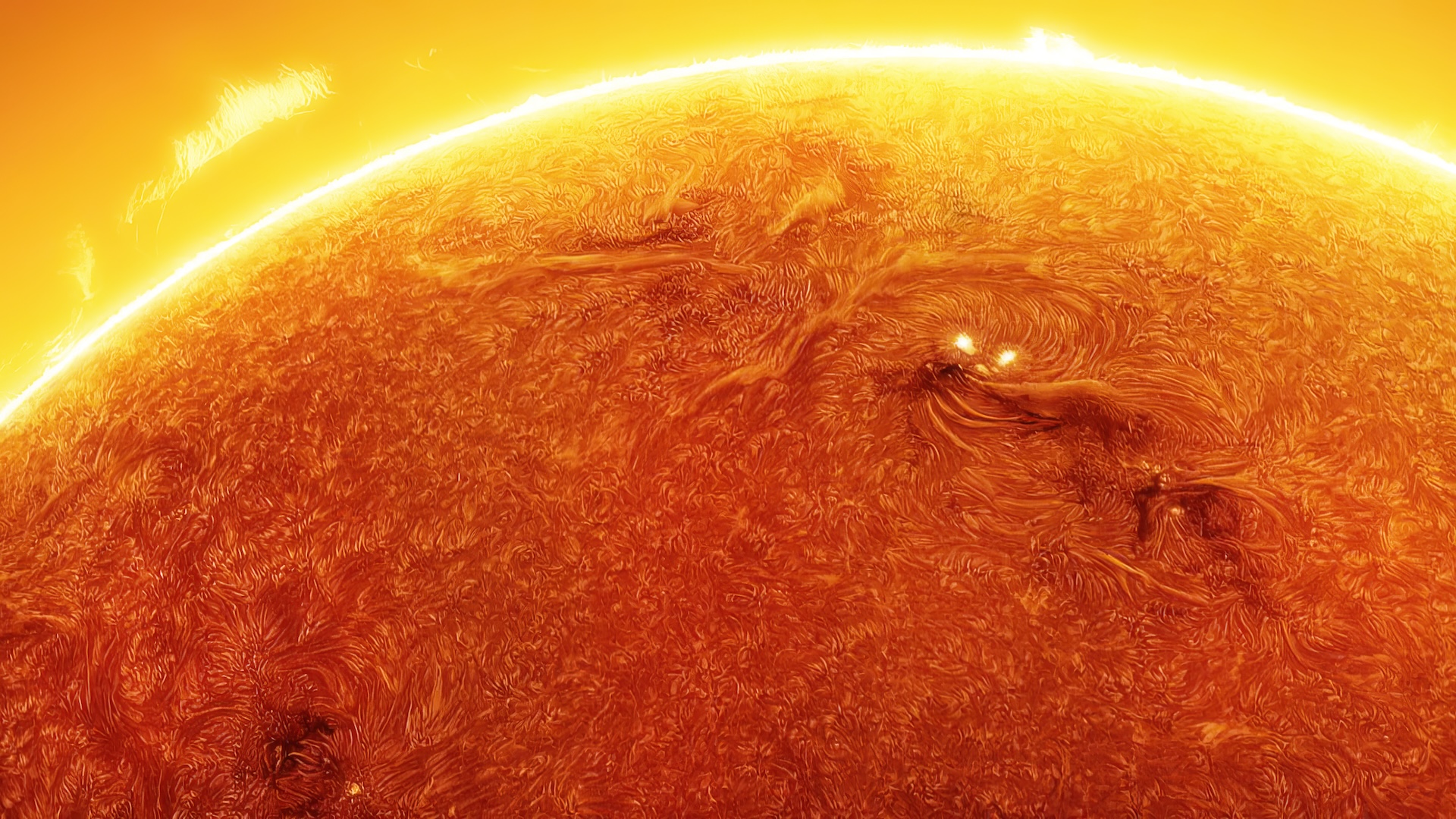
The outer edge of the Dominicus ’s ambience , or aureole , does not extend out quite as far as we previously suppose , a study published in November revealed .
Until recently , the beneficial way to measure the sun ’s Saint Ulmo’s fire was toobserve it during a solar eclipsewhen it becomes clearly visible around the lunar month . But new technologies have take into account scientist to measure the oscillations , or wave , that travel through the corona . These waves do not travel quite as far as expected .
The departure between the new findings and previous estimate is comparatively small : The sun is likely somewhere between 0.03 % and 0.07 % smaller than we thought . However , scientists say this could make a braggy difference in how we take our headliner .
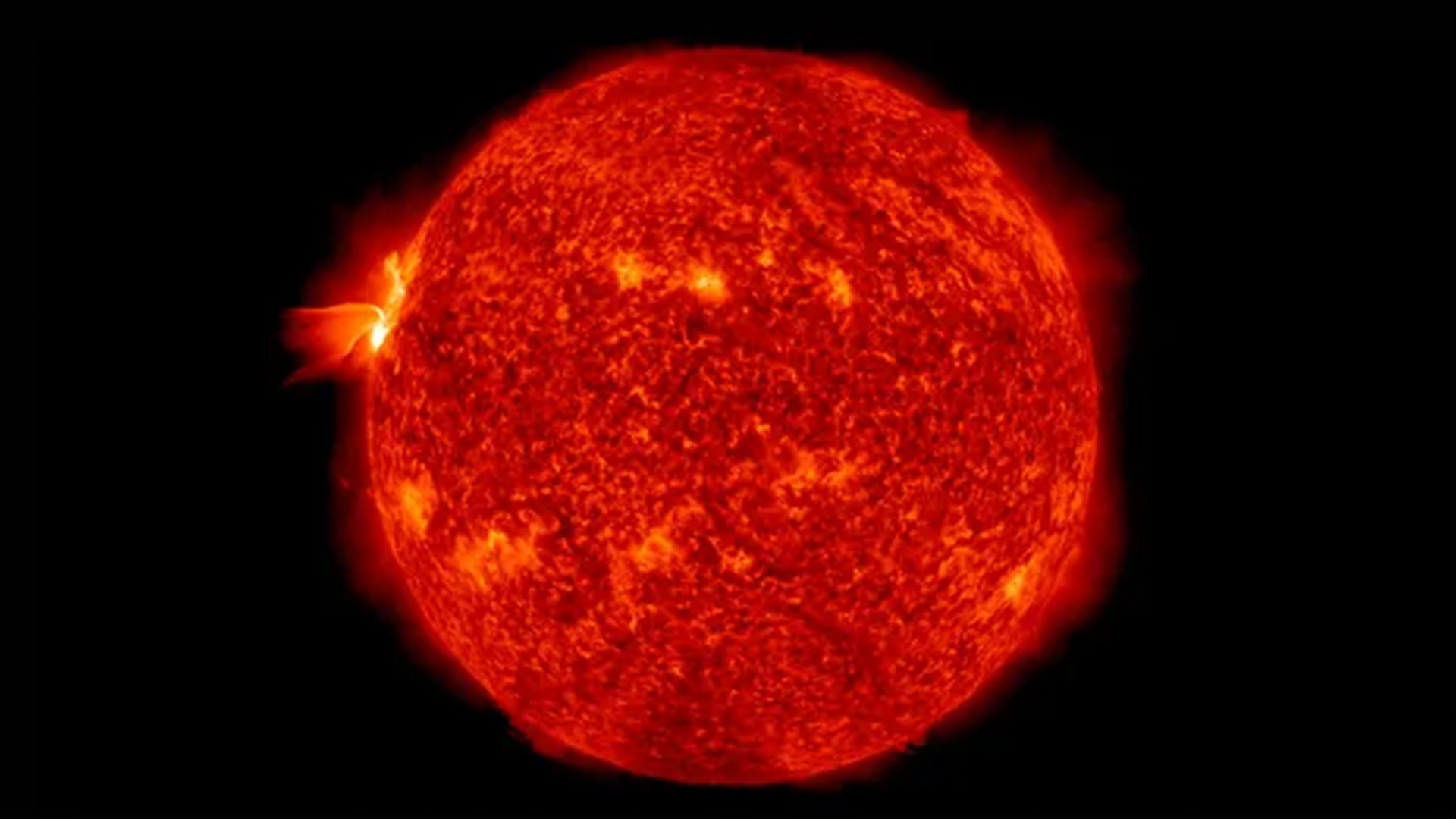

The sun may not be quite as big as we thought.
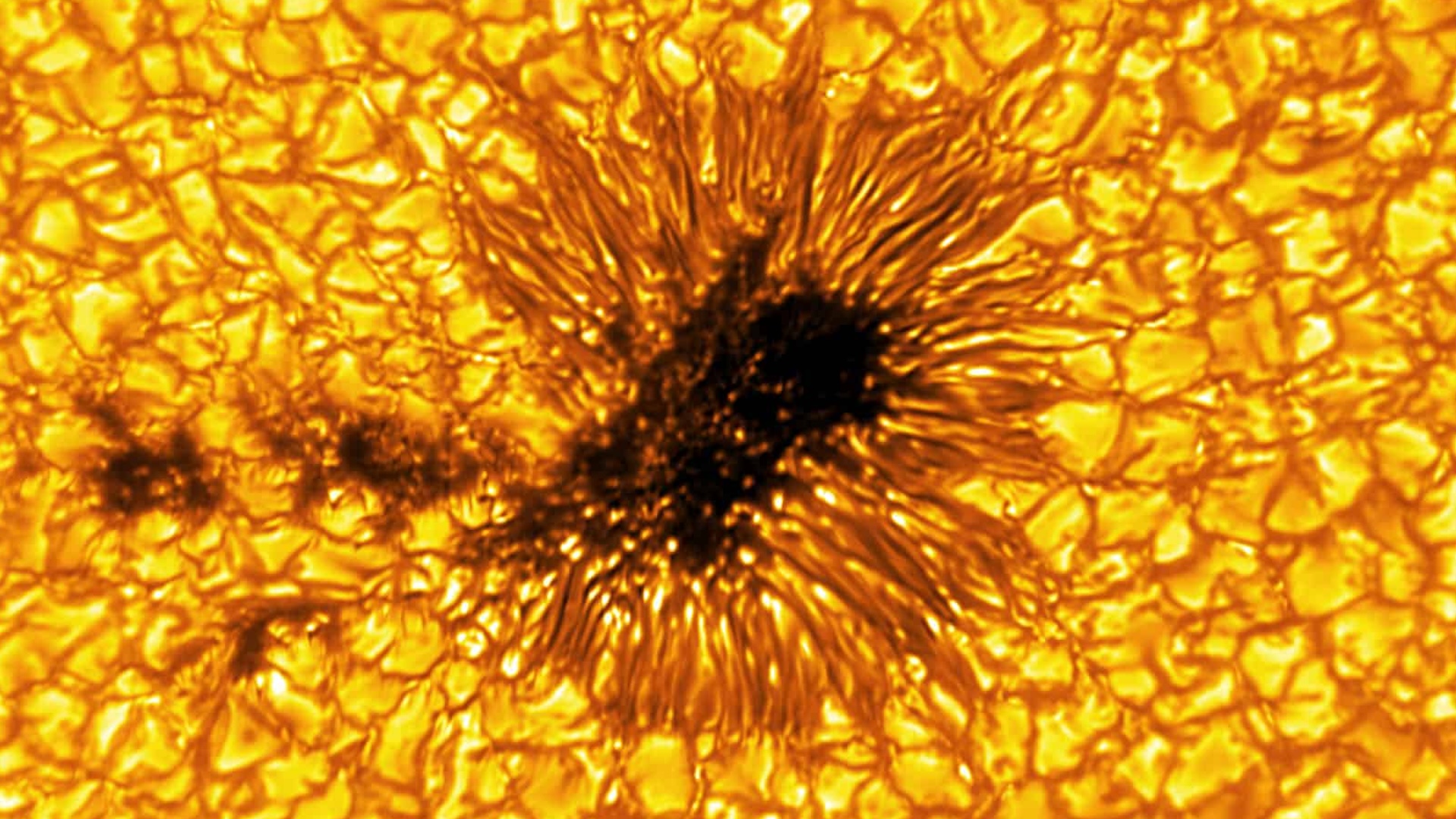
The sun has auroras too
Within thesolar organization , daybreak were antecedently thought to only occur on some planets and moons . But a sketch from November discover thatthe sun also has auroras(although they are a small dissimilar from the ones we see on Earth ) .
Astronomers detected radio bursts crunch above a sunspot after pointing a radio telescope at the dingy patch . The frequencies of the radio waves were very similar to the wavelengths given off byauroras on Earth , which powerfully evoke a standardised process is fall out on the Lord’s Day .
On Earth , auroras are born when solar storms and solar wind do into our major planet and temporarily countermine our magnetic buckler , which allows radiation therapy from the sunshine to shake up gas pedal corpuscle in the upper atm . However , researchers remember that solar break of day are created by negatron that are accelerated to incredibly high speeds along the sunshine ’s magnetised field of operation line alternatively .
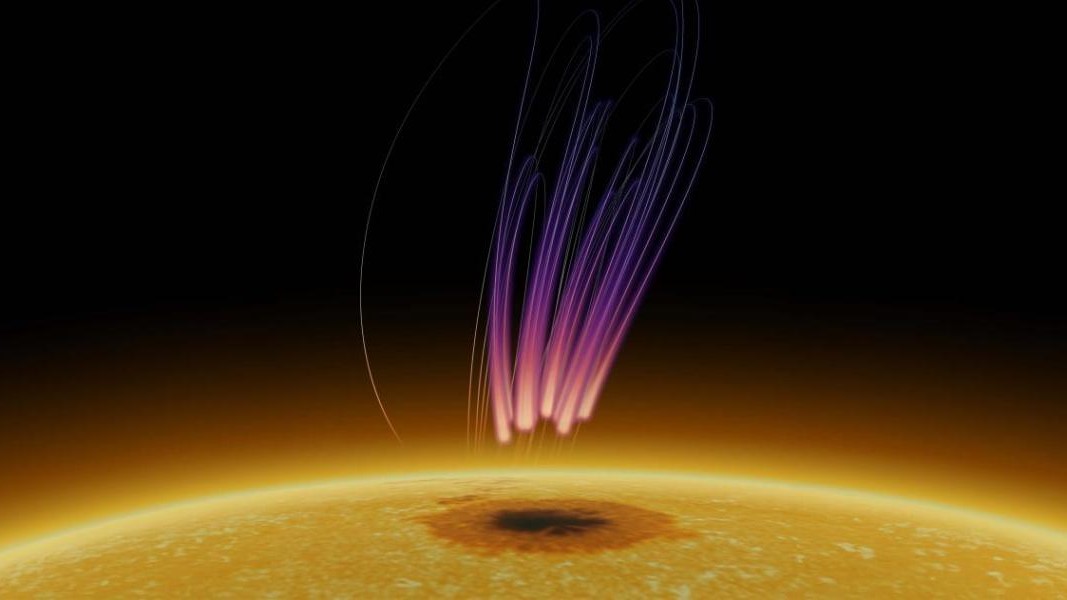

Researchers have found that the sun can produce aurora-like phenomenon above sunspots.
Biggest-ever solar storm unearthed
In October , researchers revealed that a superpowered solar storm , known as a Miyake Event , mosh into Earth around 14,000 years ago . And itcould have been the most herculean solar outburst to ever impinge on Earth , expert say .
researcher recover evidence of the cataclysmic event lurking within fossilized tree rings that were recently unearthed in the French Alps . The preserved plants all had off - the - chart levels of radiation in the same ring , which showed they all soaked up the radioactivity at the same time — and only a powerful Miyake Event could explain the levels of radiation the team found .
" A similar solar storm today would be catastrophic for our innovative technological company , " the investigator write .
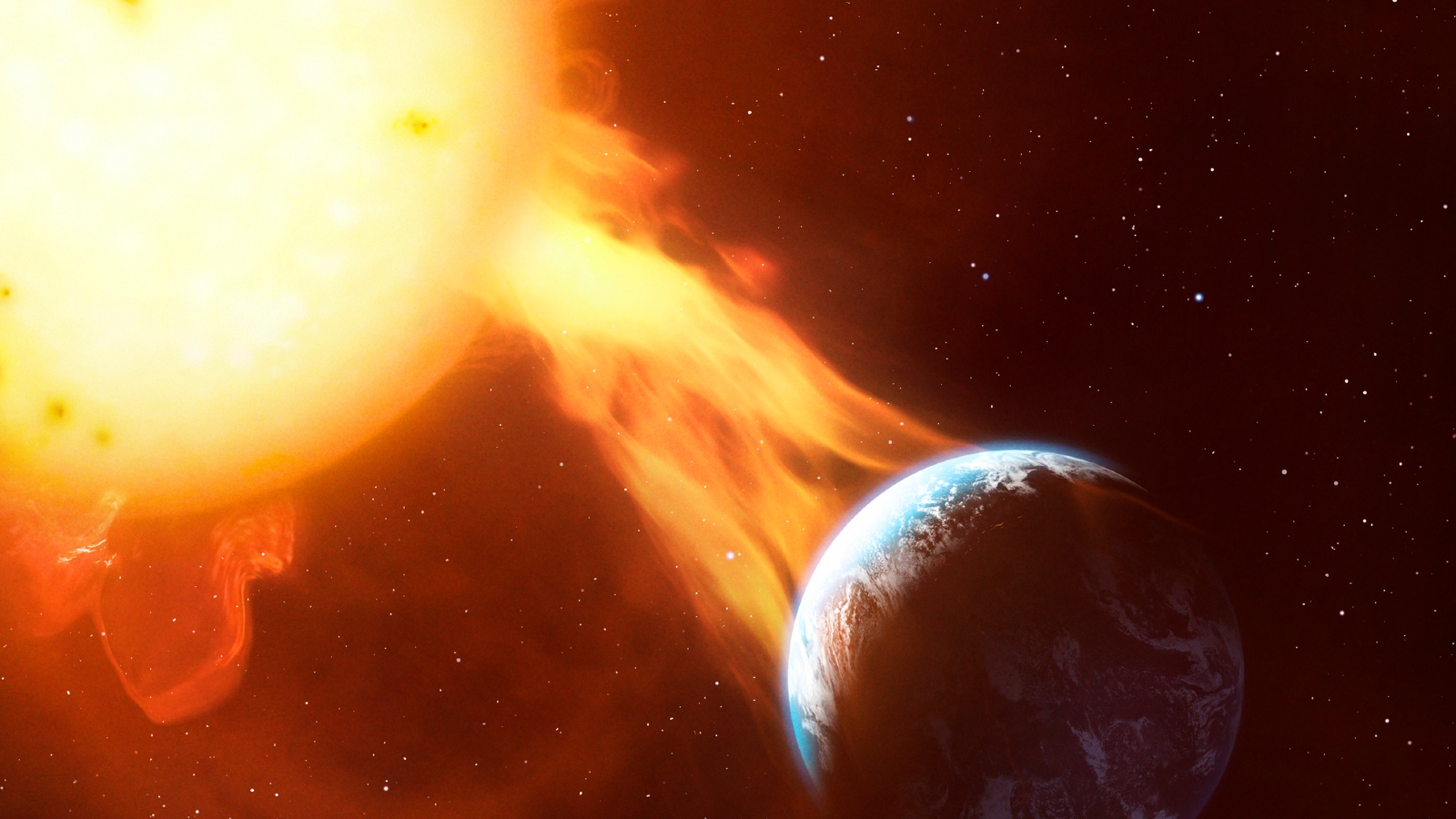

A superpowered solar flare slammed into our planet 14,000 years ago, ancient tree rings show.
Ancient ‘superflares’ may have sparked life on Earth
keep on the ancient solar storm trend , a May study revealed that"superflares " from the early hyperactive Lord’s Day could have provided the free energy call for to spark sprightliness on Earthbillions of year ago .
Researchers recreated Earth ’s early atmosphere in the science lab and fired charged particles , like those found in solar wind , at the primitive gasses and establish that this make both amino acids and carboxyl battery-acid — building block for proteins and all constitutional life .
Similar experimentation revivify lightning have also created these compounds in the science laboratory . But the squad indicate that lightning strikes would not have provide anywhere nearly as much business leader as superflares , which makes them a less suited campaigner for kickstarting lifetime on Earth .
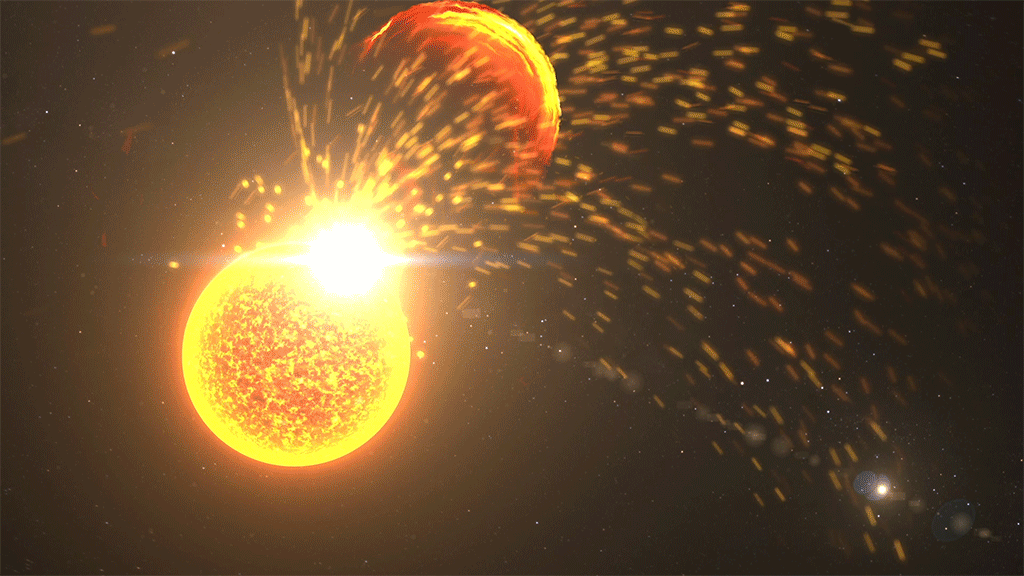

Ancient “superflares” could have sparked life on Earth, researchers claim.
However , much more work is require before any concrete conclusions can be made .
‘Ghost particles’ could reveal hidden dark matter
The Dominicus may be harboring hidden particles ofdark matterin its fiery guts andneutrinos , or " ghost particles " that are spat out by the sun , could be the headstone to incur them , a pre - print paper publish in August suggested .
Dark topic is an elusive type of issue whose indistinguishability is still a whodunit to scientists . grim matter seldom interacts with regular issue or sparkle but when it does it is theorized to utter neutrinos , which have almost no mass and no electric charge .
investigator hypothesized that the sun ’s core may have a eminent compactness of drear matter and , if this is the case , they omen that it will occasionally give off slimly more neutrinos than normal . However , these surplus neutrinos have not been observe so far .

Neutrinos spat out by the sun could lead us to a hidden treasure trove of dark matter.
Ancient anomaly in sun’s solar cycle
It currently have around 11 years for the Lord’s Day to dispatch one solar cycle , during which it transitions from solar lower limit to solar maximum and back again . But a pre - print paper publish in June suggests that past round may have been much shorter .
Researchers canvas ancient texts unearthed in Korea , which contain detailed accounts of auroral displays during the Maunder Minimum — a period of reduced solar action between 1645 and 1715 . They observe thatsolar cycles during this time in all likelihood lasted only eight years .
However , scientists have not been able to the right way explain why the solar cycle shortened during this menstruation .
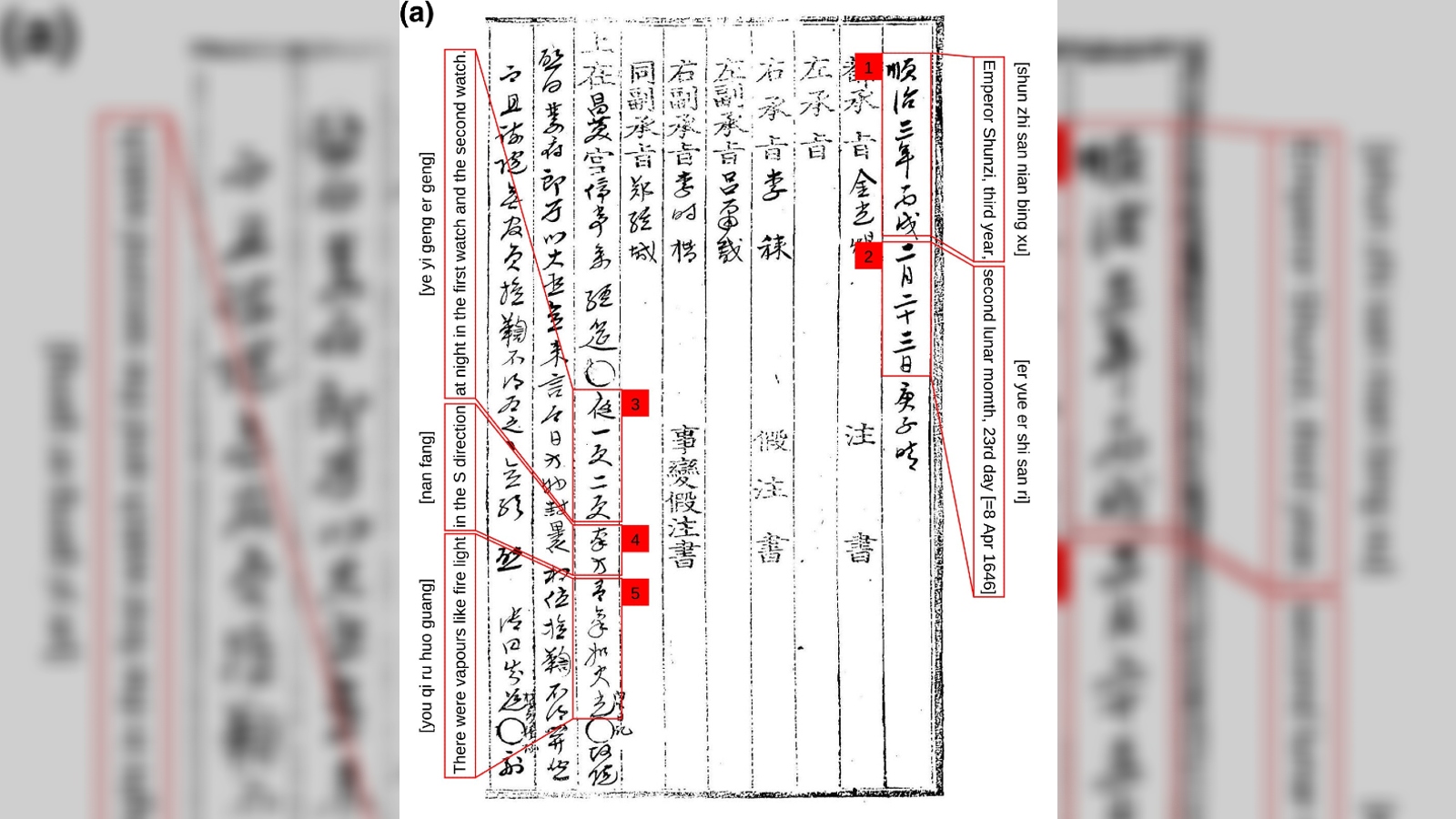
Ancient texts from Korea suggest the sun’s solar cycle used to be much shorter.
Mysterious ‘heartbeat’ puzzle solved
For more than a decade , scientist have chew over the origins of mysterious heartbeat - same patterns within streams of electromagnetic actinotherapy that shoot out of the Sunday during solar flares .
The streams of radiation therapy , known as solar radio flare-up , normally flow non - stop out of the sun . But sometimes , there are fluctuations or gaps in the flow , know as quasi - occasional pulsations , which when consider on a graph flavour similar to an electrocardiogram ( ECG or EKG ) of a human gist .
in the beginning this year , scientist consider some of these mysterious rule produce during a 2017solar flare . They feel that thepatterns were created by fluctuation within invisible fields of electrical currentthat run across loops of blood plasma on the solar surface .

Scientists finally got to the bottom of what was causing mysterious heartbeat-like signals coming from solar flares.
The sun has shooting stars
In July , scientist announced thediscovery of a young feature in the sunlight ’s corona — shooting maven .
These " stars " are clumps of plasm that fall through the sunshine ’s upper air , like meteoroid lessen to Earth , because they are cool than the circumvent plasma and , therefore , denser .
These heavy plasma balls can reach out up to 435 mile ( 700 klick ) across and seem to fall along magnetic field line created on the sun ’s open . Scientists dubbed this phenomenon coronal rainwater .
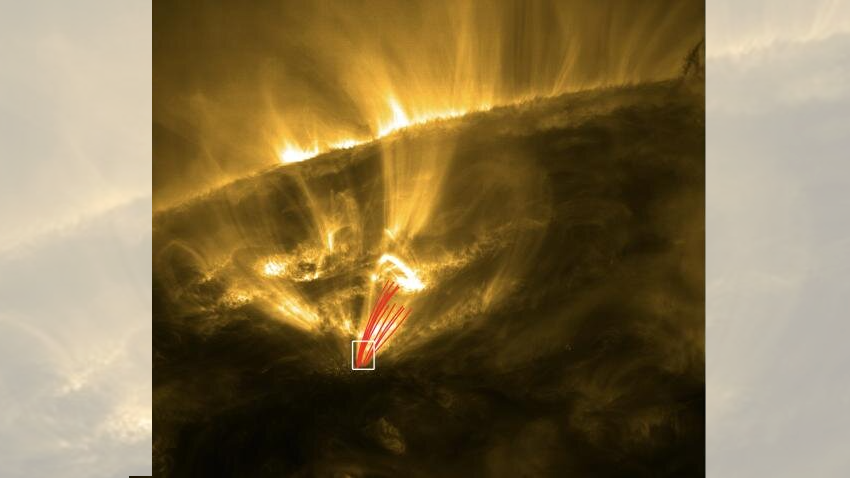

Previously unknown blobs of plasma are raining down through the sun’s corona.
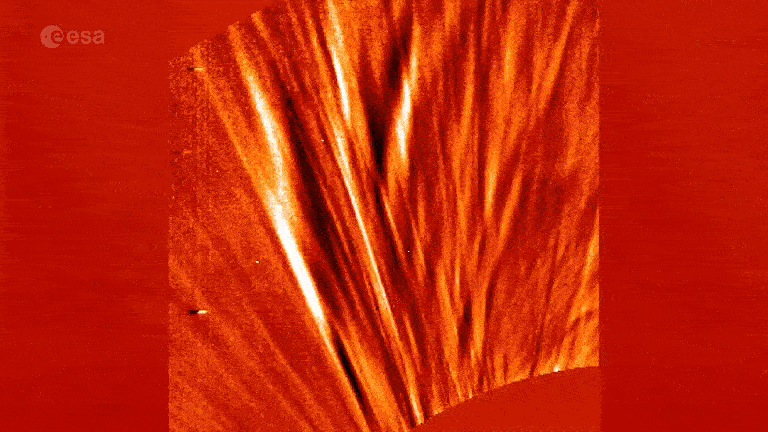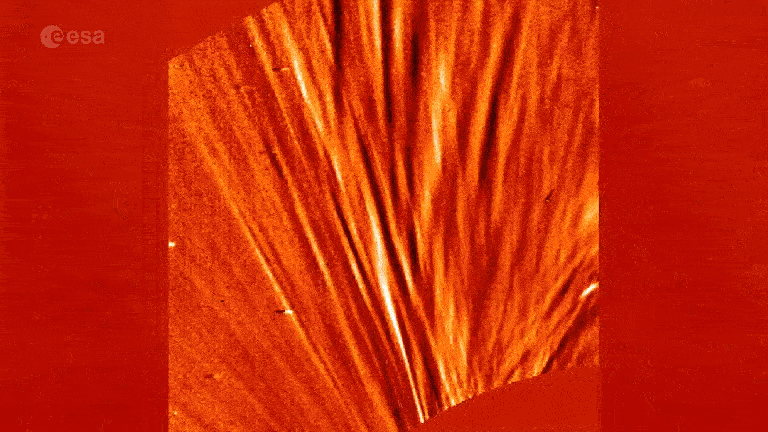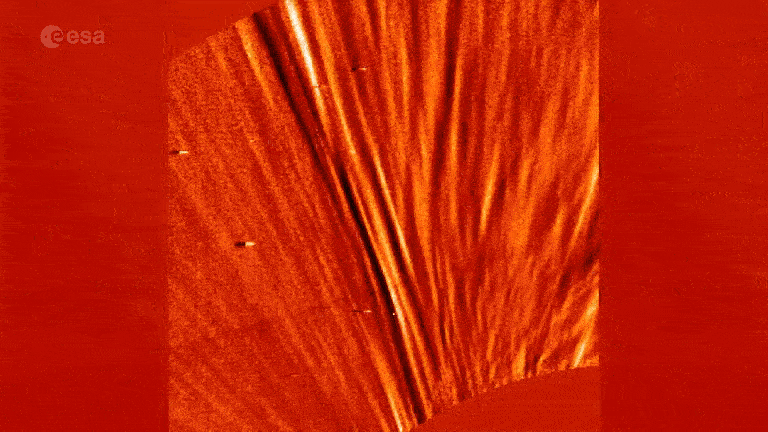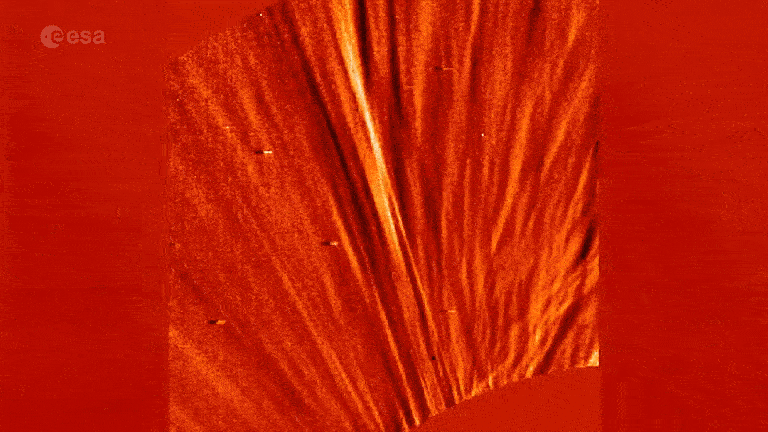
Mini solar wind ‘jets’ discovered
In August , scientists got a step closer to finally uncovering the origination of large outflows of solar speck , bonk as solar wind , that dash out of the sun ’s corona discharge .
TheEuropean Space Agency ’s Solar Orbiter espy flyspeck jet plane of plasma , known as picojets , shooting from bantam dark maculation on the sun , known as coronal maw . The mini jets are smaller than other solar jets but still pack a slug , andresearchers imagine that they provide the necessary energy to set off blow of solar wind .
Picojets could also explain why the verboten aureole ishotter than scientists await it to be .
Solar wind is constantly streaming out of the sun.